Decentralization of Energy Generation and Local Economic Development: Job Creation
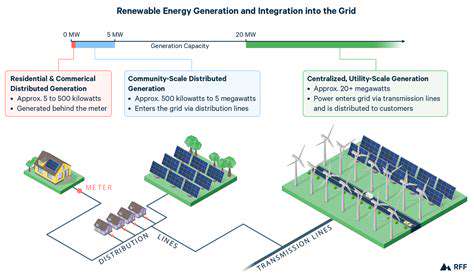
The energy sector is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by the increasing adoption of distributed energy resources (DERs). These resources, such as rooftop solar panels, wind turbines, and battery storage systems, are located closer to the point of consumption, offering a range of benefits for both consumers and the grid. This decentralization of energy generation and storage is fundamentally changing the way electricity is produced and delivered. This shift is not just about technological advancements; it also reflects a growing awareness of the need for more resilient and sustainable energy systems.
DERs are becoming increasingly important components of modern energy infrastructure. Their flexibility and responsiveness to real-time energy demands are significant advantages. This localized generation capability can enhance grid stability and reduce reliance on large, centralized power plants. The potential for DERs to contribute to a more sustainable energy future is substantial.
Technological Advancements and Economic Incentives
Several technological advancements have fueled the rise of distributed energy resources. Improved battery storage technology allows for more efficient and reliable energy storage, enabling DERs to operate more effectively. The declining costs of renewable energy technologies, such as solar photovoltaic panels, have made DERs more economically viable for residential and commercial customers. This has created a virtuous cycle, where lower costs encourage wider adoption, leading to further reductions in costs.
Government policies and incentives play a crucial role in promoting the adoption of DERs. Financial incentives, such as tax credits and rebates, can significantly reduce the upfront costs for consumers, making DER installations more attractive. Furthermore, policies that encourage the integration of DERs into the grid are essential for fostering the widespread adoption of these technologies.
Grid Modernization and Enhanced Reliability
The increasing integration of DERs necessitates the modernization of the electricity grid. Smart grid technologies are becoming essential for managing the complexities of a decentralized energy system, enabling real-time monitoring and control of energy flows. This allows for better integration of intermittent renewable energy sources, ensuring grid stability and reliability. This is a critical step towards a more resilient and responsive energy infrastructure.
The distributed nature of DERs can enhance grid resilience by providing backup power during outages and reducing the impact of large-scale disruptions. This localized energy generation can reduce the strain on the central grid, making it more robust and less susceptible to widespread failures. Such improvements are crucial in maintaining essential services during emergencies.
Job Creation Across the Energy Spectrum
Solar Power Innovations Driving Job Creation
The burgeoning solar energy sector is experiencing rapid growth, fueled by declining costs and increasing government support. This innovative approach to energy generation is creating a significant number of jobs, from manufacturing and installation of solar panels to the design and maintenance of solar farms. The development of advanced solar technologies, such as perovskite solar cells, is further expanding opportunities in research and development, promising even greater job creation in the future. This trend is particularly impactful in rural communities where solar power can provide both clean energy and economic development.
Furthermore, the rise of community solar projects is fostering local job creation. These projects allow individuals and businesses to invest in solar installations, even if they do not have the space for their own systems. This decentralized approach to solar energy not only reduces reliance on centralized grids but also supports local economies through the generation of jobs in installation, maintenance, and project management.
Wind Energy's Impact on Employment Opportunities
The wind energy sector, with its focus on harnessing the power of wind turbines, also plays a significant role in job creation across the energy spectrum. From the manufacturing of turbine components to the construction and maintenance of wind farms, this industry provides numerous employment opportunities. The development of larger and more efficient wind turbines, as well as the increasing use of offshore wind farms, are driving further growth in this sector and expanding the pool of jobs available.
The skilled labor needed for wind energy projects, including engineers, technicians, and construction workers, is in high demand. This demand is further amplified by the growing global focus on renewable energy sources, leading to a surge in investments and projects, which in turn creates even more employment opportunities.
Hydropower's Sustainable Role in Job Creation
While often overlooked in the discussion of decentralized energy, hydropower continues to be a crucial source of clean energy. The operation and maintenance of existing hydropower plants, as well as the development of new, smaller-scale hydropower projects, offer significant opportunities for job creation. This sector requires a skilled workforce to manage and maintain these complex systems, creating employment in engineering, operation, and maintenance.
Geothermal Energy and the Potential for Job Growth
Geothermal energy, harnessing the Earth's internal heat, presents a potentially substantial source of job creation. While currently less prevalent than other renewable energy sources, geothermal energy has a significant role to play in decentralized energy production. The development of geothermal power plants, especially in regions with suitable geological conditions, requires skilled labor in design, construction, and operation. The ongoing research and development in geothermal technologies further expand these employment prospects.
Biomass Energy and Rural Economic Development
Biomass energy, utilizing organic matter for fuel, offers a unique opportunity to address both energy needs and rural economic development. The utilization of agricultural residues and other biomass sources for energy production leads to job creation in areas involved in harvesting, processing, and utilizing biomass. This sector provides employment opportunities across various levels of the supply chain, from farmers to processing plant workers to energy production technicians.
Energy Efficiency Improvements and Job Creation
The focus on energy efficiency measures, including improvements in building insulation, appliance efficiency, and industrial processes, is a crucial component of the decentralized energy movement. These improvements, while not directly involving the generation of energy, create jobs in installation, design, and consulting. Energy efficiency specialists, contractors, and engineers are in high demand as energy-efficient technologies and practices become more widespread.
Smart Grid Integration and Emerging Technologies
The integration of smart grids and emerging energy storage technologies plays a vital role in the transition to a decentralized energy system. The development and deployment of these technologies require specialized skills and expertise in engineering, software development, and system integration. This sector is crucial for managing the fluctuating nature of renewable energy sources and ensuring a reliable and efficient energy supply, leading to job creation in these emerging fields.
Stimulating Local Economies Through DERs
Harnessing the Power of Distributed Energy Resources
Distributed Energy Resources (DERs) are crucial in stimulating local economies. By decentralizing energy generation, DERs empower communities to take control of their energy production and consumption. This localized approach fosters innovation, creates new job opportunities in installation, maintenance, and operation, and reduces reliance on large, centralized power plants, which often have limited local economic impact. The development and integration of DERs, such as rooftop solar panels, small-scale wind turbines, and energy storage systems, can lead to significant economic benefits at the local level, boosting local businesses and supporting local employment.
The ripple effect of DER adoption extends beyond direct job creation. Local businesses, from construction companies to electrical supply stores, will experience increased demand for goods and services. This heightened demand can lead to the expansion of local businesses, attracting further investment and fostering a more robust and resilient local economy. Furthermore, the reduction in reliance on distant energy sources can lead to reduced transmission and distribution costs, freeing up capital that can be reinvested in the community.
Enhancing Community Resilience and Sustainability
Decentralizing energy generation through DERs strengthens community resilience in the face of disruptions, whether from natural disasters or grid failures. Local energy production reduces reliance on a single, centralized source, enhancing the reliability and sustainability of energy supply. This localized approach can significantly reduce the vulnerability of communities to large-scale power outages and improve the speed of recovery during emergencies. Furthermore, investing in DERs often aligns with sustainability goals, promoting environmental responsibility and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
The integration of DERs can also lead to a more sustainable energy future. By promoting renewable energy sources, DERs contribute to reducing carbon emissions and mitigating climate change. This focus on sustainable practices attracts businesses and residents committed to environmental responsibility, further boosting the local economy and creating a more desirable place to live and work.
Creating a Vibrant Local Energy Sector
The deployment of DERs fosters the development of a robust local energy sector. This involves training programs for technicians, engineers, and installers, creating new skill sets and opportunities for local residents. The growth of this sector can attract further investment in research and development, leading to the innovation of new technologies and solutions tailored to local needs. This localized energy sector can become a hub for knowledge sharing and collaboration, attracting entrepreneurs and fostering a culture of innovation.
Beyond Job Creation: Community Benefits and Sustainability
Community Revitalization through Decentralized Energy
Decentralized energy systems, by their very nature, foster community engagement and revitalization. Local ownership and control of energy resources empowers communities to shape their own energy futures, leading to tangible improvements in local infrastructure and economic development. This shift from centralized, often distant, energy providers creates opportunities for local jobs in maintenance, installation, and community-based renewable energy initiatives. For example, a community-owned solar farm not only reduces carbon emissions but also provides residents with access to affordable energy and fosters a sense of shared responsibility for the environment.
The potential for local entrepreneurship is considerable. Decentralized energy systems create a fertile ground for innovative businesses focused on energy efficiency, renewable energy technologies, and energy storage solutions. This fosters a vibrant local economy, creating opportunities for skilled tradespeople, engineers, and entrepreneurs to establish themselves and contribute to the overall well-being of the community. The resulting local jobs and economic activity contribute to a more resilient and self-sufficient community.
Environmental Sustainability and Resilience
Decentralized energy systems are fundamentally tied to environmental sustainability. By reducing reliance on large-scale, centralized power plants, communities can drastically decrease their carbon footprint. This shift towards renewable energy sources, like solar, wind, and geothermal, contributes directly to mitigating climate change and fostering a healthier environment for future generations. These decentralized systems are often more resilient to natural disasters and grid failures, as local generation and storage can maintain power during outages, leading to a more stable and secure energy supply for the community.
The transition to decentralized energy systems also promotes a more sustainable approach to resource management. Local energy production often relies on locally available resources, minimizing the need for long-distance transportation and reducing the environmental impact associated with energy extraction and distribution. This sustainable approach is critical in ensuring a healthy and resilient environment for the community and the planet as a whole.
Economic Development and Job Creation Beyond the Grid
The decentralization of energy infrastructure goes beyond simply creating jobs in the energy sector. A thriving local energy sector fosters ancillary industries, creating opportunities for skilled trades, technicians, and maintenance personnel. This ripple effect extends to businesses involved in design, installation, and maintenance of decentralized systems, creating a self-sustaining economic ecosystem. Beyond direct employment, the decentralization of energy offers a unique opportunity to revitalize local economies and create new avenues for economic development.
The decentralized model fosters a more diversified and resilient economy, less vulnerable to fluctuations in global energy markets. This leads to more stable local economies, which in turn strengthens communities and improves the overall quality of life for residents. By leveraging local resources and expertise, the decentralized energy model creates a sustainable and economically viable pathway for community growth and prosperity.
Furthermore, the development and implementation of decentralized energy systems often require local expertise and skills development. This creates opportunities for training and upskilling programs, which can address local workforce needs and promote economic empowerment within the community. This sustainable and localized approach to energy generation empowers communities to develop a robust and resilient local economy.
The Crucial Role of Policy and Investment
Policy Frameworks for Decentralized Energy
Effective policies are crucial for fostering the growth of decentralized energy systems. These policies need to go beyond simply acknowledging the need for change; they must actively incentivize investment, streamline permitting processes, and establish clear regulatory frameworks that address the unique characteristics of distributed generation. This includes promoting the adoption of innovative technologies, encouraging public-private partnerships, and establishing clear property rights for energy assets in a decentralized setting. A well-designed policy framework can significantly reduce barriers to entry for new players in the sector, driving innovation and accelerating deployment.
Furthermore, policies should address potential challenges such as grid integration, interoperability, and the need for robust energy storage solutions. Clear guidelines and standards are vital to ensure the seamless integration of decentralized generation sources into existing grids, minimizing disruptions and maximizing efficiency. This also requires addressing the potential for energy fluctuations and grid instability that decentralized systems might introduce, and proactive measures should be in place to mitigate these risks.
Investment Strategies for Decentralized Energy
Attracting private investment is essential for the successful development and deployment of decentralized energy systems. This requires a comprehensive understanding of the market dynamics and a clear demonstration of the potential financial returns. Attractive returns can be achieved by presenting a clear pathway for investors, outlining the various investment opportunities available, including renewable energy projects, energy storage solutions, and smart grid infrastructure. Transparency and accountability in investment practices are critical to building investor confidence.
Government support, through tax incentives, grants, and subsidies, can play a crucial role in stimulating investment. These incentives can be tailored to specific technologies and projects, making them more attractive to investors. Public-private partnerships can also be instrumental in leveraging resources and expertise from both sectors, creating a synergistic approach to investment and development.
Technological Advancements in Decentralized Energy
Technological advancements are driving the evolution of decentralized energy systems. Innovation in areas such as energy storage, smart grids, and microgrids is constantly pushing the boundaries of what's possible. These advancements are making decentralized energy systems more efficient, reliable, and affordable, opening up new possibilities for energy access and sustainability.
The integration of renewable energy sources like solar and wind power into decentralized systems is becoming increasingly sophisticated. This is leading to more efficient energy generation and reduced reliance on centralized power plants. Continuous research and development in these areas are essential for further progress and cost reduction.
Community Engagement and Ownership Models
Decentralized energy systems offer unique opportunities for community engagement and ownership. Community-owned renewable energy projects can foster a sense of local responsibility and empower residents to actively participate in the transition to a sustainable energy future. This participatory approach can help build trust and acceptance of new technologies within communities.
Creating mechanisms for community ownership and participation can ensure that the benefits of decentralized energy are distributed equitably. This includes developing transparent and accessible models for community-based energy projects, ensuring that the benefits extend beyond the initial investors to the broader community.
Regulatory and Legal Frameworks for Decentralized Systems
Clear and consistent regulatory frameworks are essential for the smooth and sustainable growth of decentralized energy systems. These regulations must address issues such as permitting, grid integration, safety standards, and liability. Developing flexible and adaptable regulations to accommodate the dynamic nature of decentralized technologies is crucial for encouraging innovation and investment.
Regulations need to be in place to ensure the safety and reliability of decentralized energy systems. This involves defining clear standards for equipment, installation, and maintenance. Establishing a transparent and accessible permitting process is also vital for streamlining the deployment of these systems, encouraging participation, and facilitating growth.
Addressing Infrastructure Challenges in Decentralized Energy
Successfully implementing decentralized energy systems requires a robust and reliable infrastructure. This includes the development of smart grids, energy storage solutions, and transmission lines to facilitate the flow of energy from decentralized sources to consumers. The infrastructure must be designed to handle the variability and intermittency of renewable energy sources, ensuring a consistent and reliable energy supply.
Developing efficient and cost-effective microgrids is crucial for connecting decentralized energy generation sources to consumers in a localized manner. This requires careful planning and consideration of the specific needs of each community, as well as the integration of existing infrastructure. Addressing the challenges related to grid integration and interoperability is vital to ensure a smooth and efficient transition.