Decentralization of Energy Generation for Disaster Relief
The reliance on centralized power grids, while efficient in some aspects, presents vulnerabilities to disruptions, whether natural disasters, cyberattacks, or infrastructure failures. Localized power generation, by its very nature, enhances energy security by creating redundant and resilient energy sources within communities. This distributed approach ensures a more stable and reliable energy supply, minimizing the impact of unforeseen events on crucial services and daily life.
Economic Benefits of Decentralized Power
Localized power generation can stimulate local economies by creating jobs in construction, maintenance, and operation of the facilities. The reduced reliance on long-distance transmission lines also translates into lower energy transmission losses, leading to substantial cost savings for consumers over the long term. Furthermore, it can foster local entrepreneurship and innovation, leading to new business opportunities related to renewable energy technologies and energy storage solutions.
Environmental Impact of Localized Power
Decentralized energy systems, particularly those utilizing renewable sources like solar and wind, significantly reduce the carbon footprint associated with energy production. Localized generation minimizes the environmental impact of long-distance transmission lines, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and improving air quality in local communities. This shift towards localized power generation is crucial in mitigating climate change and promoting a more sustainable energy future.
Technological Advancements in Localized Generation
Rapid advancements in renewable energy technologies, coupled with innovations in energy storage, are making localized power generation more practical and affordable. Solar panels, wind turbines, and other renewable energy sources are becoming increasingly efficient and cost-effective, enabling communities to generate their own power with minimal environmental impact. Smart grid technologies further enhance the integration and management of distributed energy resources.
Community Engagement and Ownership
Localized power generation fosters a sense of community ownership and responsibility for energy production. By empowering communities to participate in the design, construction, and operation of local energy systems, it cultivates a stronger sense of collective responsibility for environmental stewardship and energy security. This participatory approach can lead to more sustainable and equitable energy solutions tailored to specific community needs.
Policy Support and Incentives
Governments can play a vital role in promoting localized power generation by implementing supportive policies and financial incentives. These incentives can range from tax breaks and subsidies for renewable energy installations to streamlined permitting processes for community-based energy projects. Clear and consistent policies that encourage the development of localized power generation can significantly accelerate the transition to a decentralized energy future.
Addressing Challenges in Localized Power Generation
While localized power generation offers numerous benefits, challenges remain, such as intermittency of renewable sources, the need for energy storage solutions, and the integration of distributed generation into existing grids. Overcoming these challenges requires ongoing research and development in areas like energy storage, grid modernization, and smart grid technologies. Addressing these challenges is crucial for the successful implementation of decentralized energy systems.
Beyond the Grid: Renewable Energy Solutions

Harnessing the Sun's Power
Solar energy, a clean and abundant resource, is rapidly gaining traction as a viable alternative to traditional fossil fuels. Solar panels convert sunlight directly into electricity, reducing our reliance on finite resources and minimizing harmful greenhouse gas emissions. The technology behind solar panels has significantly improved, resulting in more efficient energy production and lower costs. This allows for wider adoption, from residential rooftops to large-scale solar farms. Deploying solar energy also creates jobs in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance, boosting local economies.
Furthermore, advancements in energy storage technologies are crucial for making solar power more reliable. Battery storage solutions are becoming more affordable and efficient, allowing for the capture and release of solar energy throughout the day. This ensures a consistent power supply, even when the sun isn't shining. This consistent power supply is a game changer for integrating solar energy into existing power grids and ensuring it is a reliable source of power.
Tapping into the Wind's Kinetic Energy
Wind power, another critical renewable energy source, leverages the kinetic energy of moving air. Wind turbines convert this energy into electricity, offering a sustainable and environmentally friendly alternative to fossil fuels. Large-scale wind farms are becoming increasingly common, generating significant amounts of clean energy and reducing carbon footprints. The technology behind wind turbines has also improved, resulting in increased efficiency and reduced maintenance costs.
The geographical locations ideal for wind farms play a crucial role in their viability. Areas with consistent and strong winds are often selected for the construction of these facilities. This strategic placement maximizes energy production and minimizes the need for extensive infrastructure.
Careful consideration of environmental impacts, such as the potential effects on bird populations, is essential in the development of wind farms. Careful planning, mitigation strategies, and thorough environmental assessments are needed for responsible development.
The construction and maintenance of wind farms can also create employment opportunities in various sectors.
Exploring Geothermal and Hydropower Potential
Geothermal energy, harnessed from the Earth's internal heat, offers a constant and reliable source of energy. This renewable energy source uses the heat from deep within the Earth to generate electricity or heat buildings. Geothermal power plants can be strategically located near geothermal reservoirs, maximizing energy output and minimizing transmission losses. Geothermal energy is particularly useful in regions with high geothermal activity, where the technology can be effectively implemented.
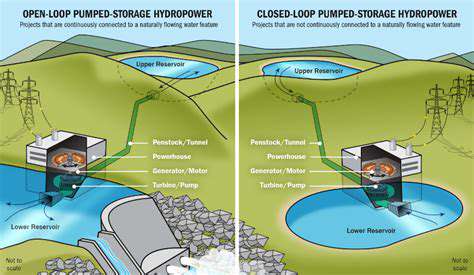
Hydropower, another renewable energy source, utilizes the energy of flowing water to generate electricity. Hydroelectric dams capture the potential energy of water, converting it into usable power. Hydropower projects can be particularly effective in regions with abundant water resources. Dams can also serve multiple purposes, including flood control and irrigation.
However, the environmental impact of large-scale hydropower projects must be carefully considered. Potential impacts on aquatic ecosystems and migratory patterns should be thoroughly evaluated and mitigated during the planning process. Careful environmental assessments and robust mitigation strategies are essential.
Bamboo fabric, derived from the rapidly renewable bamboo plant, offers a compelling alternative to traditional materials like cotton and polyester. Its unique properties, including exceptional softness and breathability, make it an attractive option for a wide range of applications. The sustainable nature of bamboo farming, requiring minimal water and pesticides, further enhances its appeal in an increasingly environmentally conscious world.
The Future of Disaster Preparedness: A Holistic Approach
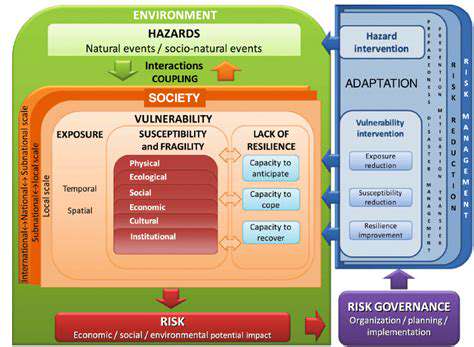
Predicting and Preventing Disasters
Advancements in technology, particularly in data analysis and predictive modeling, are revolutionizing our ability to forecast natural disasters like earthquakes, floods, and wildfires. By analyzing historical data, current weather patterns, and environmental factors, scientists can create more accurate and timely predictions, allowing communities to prepare and evacuate proactively. This data-driven approach is crucial for mitigating the devastating effects of these events.
Early warning systems are being enhanced with real-time monitoring and sophisticated algorithms to pinpoint the location and intensity of approaching disasters more precisely. This allows for more targeted and effective responses, saving lives and minimizing damage. The integration of satellite imagery and drone technology also plays a vital role in providing crucial information about the extent of damage and areas requiring immediate assistance.
Community Engagement and Preparedness
Effective disaster preparedness requires a strong emphasis on community engagement and education. Residents need to be informed about potential risks in their area, and provided with clear instructions on what to do before, during, and after a disaster. This includes workshops, drills, and community outreach programs that empower individuals to take an active role in their own safety and the safety of their neighbors.
Communicating disaster preparedness information in multiple languages and formats is essential to ensure that all members of the community, including those with diverse needs, can access and understand it. This will foster a sense of collective responsibility and ensure that everyone is equipped to handle a crisis effectively.
Infrastructure Resilience
Building resilient infrastructure is critical to minimizing the impact of disasters. This involves designing and constructing buildings, transportation systems, and utility networks that can withstand extreme weather events and natural hazards. Modern construction techniques, using materials that can withstand high winds, floods, and seismic activity, are critical to reducing casualties and property damage.
Investing in infrastructure that is adaptable and sustainable is a critical component of future disaster preparedness. This will help communities to recover more quickly from disasters and build back better, promoting long-term resilience.
Technological Advancements in Response
The deployment of robots, drones, and other advanced technologies is significantly enhancing disaster response efforts. These tools can access hazardous areas, assess damage, and provide crucial information to rescue teams, enabling them to reach affected individuals more quickly and efficiently.
Using cutting-edge technologies like 3D modeling and virtual reality can aid in the planning and execution of rescue operations, streamlining the response process and minimizing casualties. Furthermore, these technologies can be used to train first responders on how to best handle different types of disaster scenarios, improving their preparedness and effectiveness.
International Cooperation and Knowledge Sharing
Global collaboration in disaster preparedness is essential to share best practices and knowledge among different countries and communities. International organizations can play a vital role in coordinating efforts, providing technical assistance, and sharing resources to support disaster-stricken areas.
Exchanging information and experiences about disaster response strategies and recovery methods across national borders is crucial for enhancing preparedness and building resilience on a global scale. This will help nations learn from each other's successes and challenges, leading to more effective and coordinated responses to future disasters.