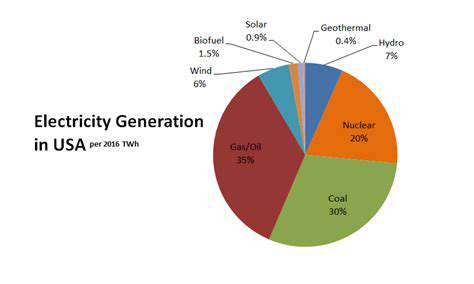
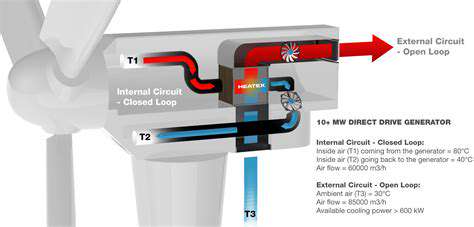
Decentralization of Energy Generation for Industrial Parks
Decentralized energy systems represent a significant departure from the traditional, centralized model. Instead of relying on large-scale power plants and transmission grids, decentralized systems distribute energy generation across various locations, empowering individuals and communities to participate in energy production and consumption. This shift towards localized control offers numerous benefits, including greater resilience and reduced reliance on centralized infrastructure.
This fundamental shift in energy infrastructure is driven by the need for greater sustainability and resilience. Centralized systems are often vulnerable to disruptions, such as natural disasters or grid failures, which can leave large populations without power for extended periods. Decentralized systems, by their very nature, are more resistant to such disturbances.
Key Components of Decentralized Energy
A decentralized energy system comprises various components, including renewable energy sources like solar panels, wind turbines, and small-scale hydroelectric plants. These sources are often integrated with energy storage solutions, such as batteries or pumped hydro, to manage intermittent energy production and ensure a consistent supply.
Smart grids and advanced metering infrastructure play a crucial role in optimizing energy distribution and consumption within the decentralized system. These technologies enable real-time monitoring and control of energy flow, allowing for efficient resource management and reduced waste.
Benefits of Decentralized Energy Systems
Decentralized energy systems offer substantial benefits in terms of sustainability, resilience, and economic development. The reduced reliance on fossil fuels translates to lower carbon emissions and a decreased environmental impact. This approach also fosters greater energy independence and reduces vulnerability to disruptions in the centralized energy supply.
Decentralization empowers communities and individuals by enabling them to participate in energy production and ownership. This can lead to economic opportunities in local communities, particularly in rural areas and developing nations, often underserved by traditional energy infrastructure.
Challenges in Implementing Decentralized Energy
Despite the numerous advantages, the implementation of decentralized energy systems faces certain challenges. One significant hurdle is the need for substantial investments in new technologies and infrastructure, such as renewable energy generation and energy storage solutions.
Interoperability and standardization of different technologies and systems are also crucial for efficient operation and integration. Establishing robust regulatory frameworks and policies to support the transition to decentralized energy systems is essential to ensure a smooth and successful implementation.
The Future of Decentralized Energy
The future of decentralized energy looks promising as technological advancements continue to drive down costs and improve efficiency. Advanced energy storage solutions, smart grid technologies, and innovative business models are paving the way for a more sustainable and resilient energy future.
The integration of decentralized energy systems with other technologies like the internet of things (IoT) and blockchain will further enhance their capabilities and create new opportunities for innovation and economic growth. This transition will undoubtedly reshape the global energy landscape, offering a path towards a more sustainable and equitable energy future.
Personalized support plans are crucial for effectively addressing individual needs and fostering positive outcomes. These plans are tailored to specific circumstances, taking into account unique learning styles, individual strengths, and potential challenges. A well-crafted plan ensures that the support provided is relevant and impactful, maximizing the potential for success. This individualized approach is often more effective than a one-size-fits-all strategy, leading to greater engagement and improved results.