Decentralization of Energy Generation for Remote Communities
Beyond Technology: Addressing Community Needs and Capacity Building
Bridging the Digital Divide
Closing the digital gap remains fundamental to successful decentralization efforts. Numerous communities face limitations in internet access and digital skills, creating barriers to participation in decentralized networks. These obstacles restrict economic prospects and civic involvement. Initiatives that establish community internet hubs and digital education programs prove essential for ensuring equitable access to decentralization benefits across all socioeconomic groups and locations.
Empowering Local Organizations
True decentralization extends beyond technological implementation to the strengthening of community institutions. By bolstering existing local groups and nurturing grassroots initiatives, we can develop more impactful and enduring solutions. This approach requires providing necessary tools, educational resources, and guidance to help communities effectively harness decentralized technologies while adapting them to local contexts, thereby fostering genuine ownership and self-determination.
Building Local Capacity
Developing local expertise forms the foundation of sustainable decentralization. Educational initiatives that equip community members with technical knowledge for operating decentralized systems prove indispensable. Comprehensive training should encompass not only technical skills but also competencies in project coordination, community mobilization, and creative problem-solving. Empowering individuals with the abilities to create and sustain their own decentralized projects ensures lasting community development and self-sufficiency.
Promoting Financial Inclusion
Decentralized technologies hold significant promise for expanding financial access. By providing alternative financial services with lower barriers to entry, these systems can empower underserved populations. Potential applications include decentralized payment networks that circumvent conventional banking structures, simplifying money transfers for users, or peer-to-peer lending platforms that extend credit to those traditionally excluded from formal financial systems. Such innovations play crucial roles in stimulating local economic growth and fostering financial independence.
Fostering Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing
Successful decentralization thrives on cooperative networks and information exchange between communities. Establishing channels for communities to connect, exchange successful strategies, and learn from collective experiences proves paramount. This might involve creating digital discussion platforms, hosting educational events, or supporting regional alliance formation. Through collaboration, diverse communities can pool their knowledge and assets, yielding more inventive and effective solutions tailored to their specific circumstances. Genuine community empowerment through decentralization demands a spirit of cooperation.
The Future of Energy Access in Remote Communities
Decentralized Microgrids for Remote Areas
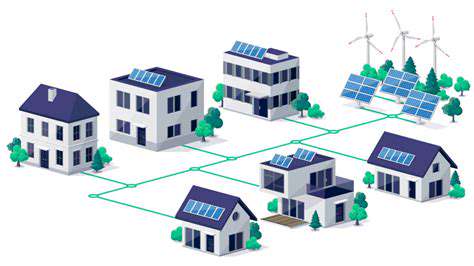
The shift toward decentralized energy production offers revolutionary potential for isolated communities seeking independence from unstable central grids. Microgrid systems, consisting of localized power generation units, provide particularly effective solutions. These adaptable networks can incorporate multiple renewable sources—including solar, wind, and hydro—while being engineered for reliability during disruptions, guaranteeing more dependable energy access for remote populations.
This localized energy approach enhances community self-governance over power resources. It enables customized system designs that maximize efficiency and minimize ecological harm based on specific local conditions. Additionally, microgrid implementation stimulates local economies by creating employment opportunities in system installation, maintenance, and operation.
Renewable Energy Integration: A Key Component
Renewable sources form the backbone of successful decentralized energy systems in remote locations. Many isolated regions possess abundant solar, wind, or hydro resources, and their incorporation into microgrids substantially decreases fossil fuel dependence. This transition toward renewables not only reduces carbon footprints but also promotes environmental stewardship, safeguarding community health and ecological balance.
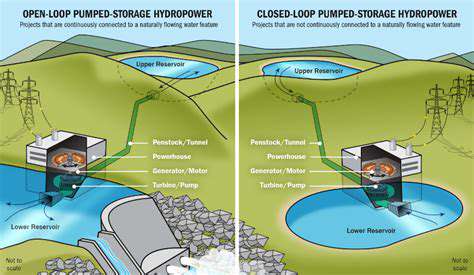
The intermittent nature of solar and wind power requires innovative storage solutions for consistent energy supply. Emerging technologies like advanced battery systems, pumped hydro storage, and other cutting-edge solutions are addressing these challenges, enabling more reliable renewable energy utilization in microgrid applications.
Technological Advancements Driving Decentralization
Breakthroughs in energy storage, intelligent grid technologies, and digital management systems are accelerating decentralized energy adoption in remote areas. These innovations improve microgrid performance and reliability, making them increasingly practical for communities pursuing sustainable power solutions.
Smart grid technologies exemplify this progress, enabling real-time energy monitoring and distribution optimization within microgrids. This dynamic control mechanism enhances system stability and minimizes outage risks through intelligent load management.
Economic Opportunities and Community Empowerment
Decentralized energy generation creates substantial economic benefits for remote communities. Local job creation in microgrid installation, upkeep, and management fosters economic independence and community development. This economic stimulation often extends beyond the energy sector, catalyzing broader regional growth.
Local energy ownership also empowers communities to steer their power future. This autonomy builds community resilience and sustainability by engaging residents directly in energy planning and decision-making processes.
Addressing Challenges and Ensuring Sustainability
Despite clear advantages, decentralized energy implementation in remote areas faces obstacles including funding limitations, technical knowledge gaps, and regulatory complexities. Overcoming these barriers requires innovative financing approaches, skill development programs, and supportive policy frameworks to ensure project longevity.
Active community involvement remains critical for project success. Engaging local populations in system design, development, and operation cultivates ownership while ensuring solutions align with community priorities. This participatory model forms the foundation for enduring decentralized energy success.