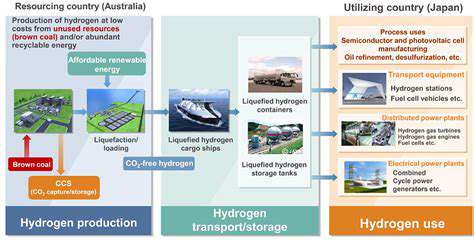
Emerging Markets: High Growth Opportunities in Renewable Energy

Harnessing the Power of the Sun
Solar power, a clean and renewable energy source, harnesses the abundant energy from the sun. This technology converts sunlight directly into electricity, offering a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. Harnessing this natural resource is crucial in mitigating climate change and reducing our dependence on finite energy sources. It's a technology that's continuously evolving, with advancements in efficiency and affordability making it more accessible to individuals and communities worldwide.
Economic Benefits of Solar Power
The solar industry creates numerous job opportunities, from manufacturing and installation to maintenance and research. This economic stimulus extends beyond the direct employment figures, boosting related industries and supporting local economies. The cost of solar panels has significantly decreased over the past few decades, making solar power increasingly competitive with traditional energy sources. This affordability is a major driver of widespread adoption and further economic growth.
Environmental Impact of Solar Power
One of the most significant advantages of solar power is its minimal environmental impact. Unlike fossil fuels, solar energy production doesn't release harmful greenhouse gases or pollutants into the atmosphere, significantly reducing air and water pollution. This clean energy source plays a vital role in combating climate change and protecting our planet's delicate ecosystems. Solar power offers a sustainable and environmentally responsible energy solution for the future.
Technological Advancements in Solar Cells
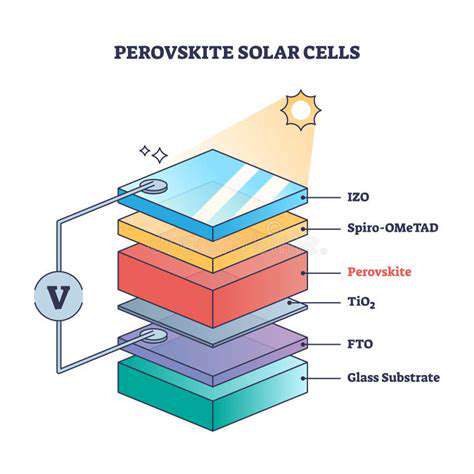
Continuous research and development are driving advancements in solar cell technology. Scientists are constantly exploring new materials and designs to improve efficiency and reduce costs. These advancements lead to more affordable and reliable solar panels, making solar power even more attractive for widespread adoption. New technologies, like perovskite solar cells, are showing promising results, pushing the boundaries of solar energy potential.
Residential Solar Installations
Installing solar panels on residential rooftops is becoming increasingly popular. Homeowners can significantly reduce their energy bills and contribute to a cleaner energy future by generating their own electricity. The financial incentives, such as tax credits and rebates, further encourage homeowners to invest in solar energy solutions. This promotes energy independence and reduces reliance on the grid.
Commercial Solar Applications
Solar power is not limited to residential use; it's also a viable option for commercial applications. Businesses can leverage solar energy to power their operations, reduce their carbon footprint, and enhance their brand image as environmentally conscious entities. Businesses can also generate considerable cost savings by reducing electricity bills. Large-scale solar farms and rooftop installations are common examples of commercial solar applications.
The Future of Solar Power
The future of solar power looks bright, with continued advancements in technology and decreasing costs. Solar energy is poised to become a dominant force in the global energy sector. As the technology matures and becomes even more accessible, solar power will likely play an increasingly crucial role in meeting the world's energy demands in a sustainable and environmentally responsible manner. Government policies and public awareness campaigns will play a significant role in promoting its widespread adoption.
Wind Energy: Harnessing the Power of the Breeze
Harnessing the Power of Wind: A Global Perspective
Wind energy, a clean and renewable energy source, is experiencing rapid growth in emerging markets, driven by increasing energy demands and government incentives. This global expansion presents substantial investment opportunities for companies seeking to capitalize on the burgeoning market for renewable energy solutions. The potential for significant returns is attracting both private sector investors and government entities eager to diversify their energy portfolios and reduce their reliance on fossil fuels. This trend is particularly pronounced in regions with strong and consistent wind resources.
Developing nations often lack the infrastructure necessary for large-scale energy production. Wind energy projects, however, can effectively address this infrastructure gap by creating new jobs and stimulating economic growth in rural communities. The construction and maintenance of wind farms require skilled labor, creating employment opportunities that can significantly benefit local economies and reduce poverty. Furthermore, the reduced reliance on imported fossil fuels can bolster national energy security and strengthen the financial stability of these emerging markets.
Technological Advancements Driving Growth
The evolution of wind turbine technology has been a key driver of the growth in wind energy. Modern turbines are significantly more efficient than their predecessors, capturing a greater percentage of the wind's kinetic energy and producing more power. These advancements not only enhance the profitability of wind farms but also make them more environmentally friendly by reducing the overall footprint required for energy generation. Innovation in materials and engineering continues to push the boundaries of wind energy's potential, making it a more viable and sustainable option for future energy needs.
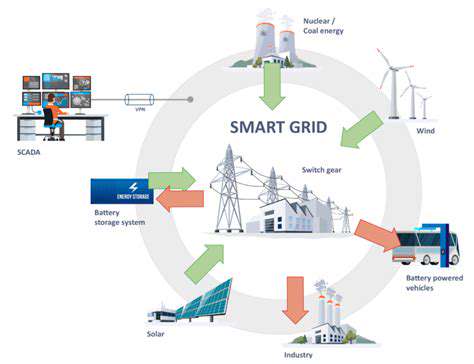
Furthermore, the development of smart grid technologies is enabling better integration of wind energy into existing power grids. This increased integration allows for the efficient management of fluctuating wind speeds, optimizing the output and reliability of wind power systems. These technological advancements contribute to the overall sustainability and economic viability of wind energy projects in emerging markets.
Investment Opportunities and Challenges
The burgeoning wind energy sector in emerging markets presents a wealth of investment opportunities, especially for those companies with experience in renewable energy projects. The potential for high returns and the social benefits associated with clean energy development attract significant private sector interest. However, substantial capital investment is often required for the initial setup and ongoing maintenance of wind farms. This capital requirement can act as a barrier to entry for some investors, particularly in less developed regions.
Regulatory hurdles and permitting processes can also pose challenges. Navigating the complexities of local regulations and securing necessary approvals can be a significant hurdle for project developers. Overcoming these challenges requires a strong understanding of local regulations, robust project planning, and effective communication with relevant government bodies. Despite these challenges, the long-term potential and sustainable nature of wind energy make it a compelling investment opportunity in emerging markets.
Hydropower and Geothermal: Complementary Renewable Solutions
Hydropower: Harnessing the Power of Water
Hydropower, a mature renewable energy technology, utilizes the natural flow of water to generate electricity. This involves damming rivers or utilizing existing water bodies to create a controlled head of water. The force of the falling water spins turbines connected to generators, converting the kinetic energy of the water into electrical energy. Hydropower plants can be large-scale installations, often requiring significant upfront investment in dam construction and infrastructure, or smaller-scale systems suitable for specific communities or remote areas. The environmental impact of hydropower projects is a complex issue, with concerns about habitat disruption, downstream flow alteration, and potential displacement of communities. Careful planning and environmental assessments are crucial for minimizing these negative impacts and maximizing the benefits of this powerful renewable resource.
The efficiency of hydropower plants varies depending on factors like the volume and consistency of water flow, the design of the dam and turbines, and the overall system infrastructure. Well-maintained and well-designed hydropower facilities can achieve high efficiency rates, making them a reliable source of renewable energy. However, fluctuating water levels and drought conditions can significantly impact the output of a hydropower plant, highlighting the need for careful water resource management and potential integration with other renewable energy sources.
Geothermal Energy: Tapping Earth's Internal Heat
Geothermal energy, harnessed from the Earth's internal heat, presents a compelling alternative for renewable energy generation. This method involves extracting heat from the Earth's crust, using this heat to produce steam, which then drives turbines connected to generators to produce electricity. Geothermal resources are geographically concentrated, meaning the technology is most effective in areas with high geothermal activity, such as volcanic regions. While geothermal power plants can operate reliably, their establishment requires sophisticated geological knowledge and careful assessment of the potential for environmental impacts, including the release of gases and the potential for ground subsidence.
The cost of developing geothermal energy infrastructure can be substantial, and the technology is not suitable for all geographical locations. However, the potential for reliable and continuous power generation from geothermal resources, coupled with the minimal reliance on external fuel sources, makes it a valuable asset in regions with suitable geological conditions. The long-term economic viability of geothermal projects often depends on the price of electricity and the availability of suitable geothermal reservoirs.
Complementary Capabilities for a Sustainable Future
Hydropower and geothermal energy, while distinct technologies, offer complementary advantages that can contribute to a sustainable energy future. Hydropower often provides a baseload energy source, offering reliable and consistent power output, while geothermal energy can provide a more fluctuating but potentially significant supplementary energy source, particularly in regions with suitable geological conditions. Integrating these two renewable resources in a balanced energy portfolio can enhance the resilience and sustainability of energy systems, contributing to a more diversified and robust energy infrastructure.
The integration of hydropower and geothermal energy can also contribute to a more efficient energy grid by ensuring a reliable supply of electricity while reducing dependence on fossil fuels. Successful implementation of these complementary renewable resources necessitates careful planning, community engagement, and environmental considerations to maximize benefits and minimize negative impacts, creating a sustainable energy future that benefits both the environment and local communities.
By combining the strengths of both technologies, emerging markets can achieve significant progress towards renewable energy goals. Careful site selection, economic feasibility studies, and robust environmental impact assessments are crucial for successful projects. These combined efforts can lead to a more sustainable and resilient energy landscape.
Beyond the Technologies: The Role of Infrastructure and Policy
The Crucial Role of Physical Infrastructure
Modern infrastructure, encompassing roads, bridges, ports, and utilities, forms the bedrock upon which economic development in emerging markets can flourish. Reliable transportation networks facilitate the movement of goods and people, boosting trade and connecting communities. Effective communication systems, including robust internet access and reliable telecommunications, are essential for businesses to operate efficiently and for individuals to access crucial information and services. Strong electricity grids provide the power needed to support industrial growth, manufacturing processes, and essential services, ultimately driving economic activity and improving the standard of living for populations.
The quality and accessibility of infrastructure directly influence a country's ability to attract foreign investment and support local entrepreneurship. Poor infrastructure can create significant bottlenecks, hindering productivity and competitiveness. Thus, investing in modernizing and expanding infrastructure is not just a matter of physical improvements but a critical step toward sustainable economic growth and poverty reduction within these emerging economies.
The Importance of Supportive Policies
Encouraging a business-friendly environment is paramount for emerging markets to thrive. Policies that promote transparency, reduce bureaucratic hurdles, and protect property rights attract foreign direct investment. Stable macroeconomic policies, including sound fiscal and monetary management, create a predictable and attractive environment for businesses to invest and expand. Moreover, policies that address labor market issues, such as skills development and fair labor practices, are vital for ensuring a qualified and engaged workforce. These policies will create a positive impact on the development of a thriving and sustainable economy.
Strong regulatory frameworks that ensure fair competition and protect consumers are also crucial. These frameworks not only foster a healthy business environment but also promote innovation and efficiency, thereby driving economic growth. Investment in education and healthcare systems, while seemingly separate from infrastructure, are intrinsically linked to a nation's productivity and overall well-being, thereby fostering a sustainable economic future.
The Interplay Between Technology and Infrastructure
Emerging markets are poised to leverage technology to overcome infrastructure challenges and leapfrog traditional development stages. For instance, mobile money platforms can circumvent the need for extensive banking infrastructure, connecting underserved populations to financial services. Likewise, innovative technologies can improve energy efficiency, reducing reliance on outdated infrastructure and lowering costs. Digital platforms can also foster e-commerce, connecting businesses to broader markets, thereby promoting economic growth and job creation.
However, the effective integration of technology requires robust digital infrastructure. Reliable internet access and affordable data rates are essential for leveraging these technological advancements. Furthermore, a skilled workforce equipped to develop and implement technology solutions is crucial for maximizing the benefits of these innovations. Therefore, investing in both physical and digital infrastructure, along with training programs, is essential for achieving sustainable growth in emerging markets.
The Role of Governance and Institutional Capacity
Effective governance plays a critical role in fostering a conducive environment for economic growth in emerging markets. Strong and transparent institutions are essential to maintain the rule of law, protect property rights, and ensure equitable access to resources. Corruption undermines investment, distorts markets, and hinders economic progress. Thus, a robust legal framework and transparent governmental processes are indispensable for attracting investment and fostering sustainable economic growth.
Furthermore, an effective regulatory environment that facilitates competition and protects consumers is also vital. This includes the ability to enforce contracts, resolve disputes efficiently, and uphold the principles of fair market practices. Building strong institutions and promoting effective governance are therefore crucial for creating a stable and predictable investment climate that allows emerging markets to realize their full economic potential.