Grid Modernization for Offshore Wind
HVDC Technology: A Deep Dive
High Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) transmission technology plays a crucial role in modern power grids, enabling the efficient transmission of large amounts of electricity over long distances and across geographical barriers. HVDC systems offer significant advantages over conventional alternating current (AC) transmission, particularly for long-distance power lines. This superiority stems from their ability to minimize transmission losses and enhance system stability, making them a vital component in expanding the capacity and reliability of the global energy infrastructure.
The core principle behind HVDC lies in the conversion of alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) at the sending end, transmission of the DC power over long distances with minimal loss, and then reconverting it back to AC at the receiving end. This process, while complex, allows for the effective transportation of power across vast distances, often traversing challenging terrains or crossing bodies of water, where AC transmission would be less practical or efficient.
Subsea Cable Infrastructure: Connecting the Continents
Subsea cables represent a critical component of global energy transmission, providing a vital link between continents and islands. These cables, often composed of advanced materials and sophisticated designs, are engineered to withstand the immense pressure and corrosive environments of the underwater depths. Their deployment requires extensive planning and execution, including meticulous route surveys, careful cable laying procedures, and robust maintenance strategies to ensure the longevity and reliability of the connection.
The development of advanced materials and innovative cable designs has greatly improved the operational efficiency and lifespan of subsea cables. The use of high-strength materials, like high-quality copper and advanced polymers, enhances the cable's ability to withstand the demanding underwater conditions. This, in turn, improves the reliability of long-distance power transmission between geographically dispersed locations.
Enhanced Grid Reliability and Efficiency
The integration of HVDC and subsea cable technologies significantly enhances the overall reliability and efficiency of power grids. HVDC systems, with their reduced transmission losses, allow for the transportation of larger amounts of power with less energy waste. This translates to greater grid stability and a more resilient power supply, crucial in meeting the growing demands of modern society.
Moreover, subsea cables, by providing direct connections across vast bodies of water, enable the interconnection of geographically disparate grids, fostering greater energy security and resilience. This interconnectedness allows for the sharing of power resources, mitigating potential supply disruptions and ensuring a more robust and reliable energy infrastructure.
Technological Advancements and Innovations
Ongoing research and development efforts are constantly pushing the boundaries of HVDC and subsea cable technology. Innovations in converter technology, insulation materials, and cable construction techniques are leading to more efficient, reliable, and cost-effective solutions. These advancements are crucial in meeting the growing energy demands and addressing the challenges of integrating renewable energy sources into the power grid.
Environmental Considerations and Sustainability
The environmental impact of transmission infrastructure is a crucial consideration in the development and deployment of HVDC and subsea cables. Careful planning, selection of environmentally friendly materials, and responsible construction practices are essential to minimize the environmental footprint of these systems. Assessing potential impacts on marine ecosystems, minimizing electromagnetic interference, and utilizing sustainable materials in cable construction all contribute to responsible energy infrastructure development.
Minimizing the visual impact on the landscape, both above and below water, and adopting environmentally friendly construction methods are also crucial aspects of sustainable infrastructure development. Implementing robust monitoring and maintenance strategies to ensure the long-term environmental safety of these critical energy transmission systems is essential.
Smart Grid Technologies and Advanced Control Systems

Smart Grid Technologies: A Revolution in Power Delivery
Smart grids are transforming the way electricity is generated, transmitted, and distributed. They leverage advanced technologies to create a more efficient, reliable, and sustainable energy system. This transformation is driven by the need to address growing energy demands, integrate renewable energy sources, and improve grid resilience. Smart grids offer the potential to significantly reduce energy waste and enhance grid stability. The integration of advanced metering infrastructure, communication networks, and control systems allows for real-time monitoring and control of energy flow.
These technologies are designed to optimize the operation of the entire electricity network, from power generation to consumer delivery. This includes improving grid efficiency and reliability, while also enhancing the integration of renewable energy sources and supporting the growth of distributed energy resources.
Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI)
AMI is a critical component of smart grids, enabling two-way communication between utilities and consumers. This allows for real-time monitoring of energy consumption, which provides consumers with detailed usage patterns. AMI plays a vital role in empowering customers to manage their energy consumption more effectively. It also provides utilities with valuable data for optimizing grid operations and identifying potential issues.
Distribution Automation (DA)
DA systems utilize advanced sensors, communication networks, and control systems to automate the operation of distribution networks. This automation allows for faster response times to outages and disturbances, improving grid reliability and reducing downtime. By automating various aspects of the distribution network, DA systems significantly enhance grid resilience. Automated switching and control of distribution equipment can quickly isolate faults and restore power to affected areas.
DA systems also enhance the efficiency of the distribution network by optimizing the flow of electricity. This, in turn, leads to a reduction in energy losses and improved grid stability.
Demand Response Programs
Demand response programs incentivize consumers to adjust their energy consumption based on real-time grid conditions. This helps to balance supply and demand, reducing the strain on the grid during peak periods. These programs offer significant benefits for both consumers and utilities. Incentivized participation can result in lower electricity bills for consumers, while utilities benefit from reduced peak demand, leading to lower operating costs. Consumers also gain a better understanding of their energy usage and can take steps to reduce consumption.
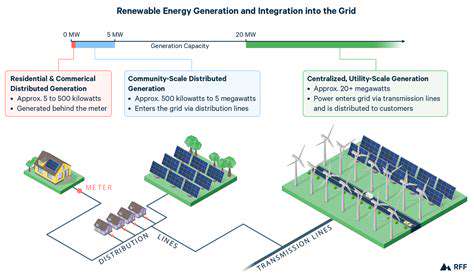
Renewable Energy Integration
Smart grids are essential for effectively integrating renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, into the electricity network. These intermittent energy sources require sophisticated management systems to maintain grid stability. Smart grids provide the necessary tools and technologies to manage the fluctuating nature of renewable energy production.
This integration can lead to significant benefits, such as reduced reliance on fossil fuels and a more sustainable energy future.
Cybersecurity Measures
As smart grids rely heavily on interconnected digital systems, cybersecurity is a critical concern. Robust security measures are essential to protect the grid from malicious attacks and unauthorized access. Implementing advanced security protocols and technologies is vital to safeguarding the integrity and reliability of the smart grid infrastructure. Protecting critical infrastructure from cyber threats is paramount to ensure the continued operation of the smart grid.
Grid Modernization and Future Trends
The ongoing modernization of electricity grids is driven by the need for enhanced reliability, efficiency, and sustainability. Smart grid technologies are at the forefront of these efforts, enabling utilities to optimize grid operations and integrate renewable energy sources more effectively. Future trends suggest a continued evolution of smart grid technologies, including the integration of advanced analytics and artificial intelligence. These advancements will further improve grid performance and resilience.
Continued research and development will lead to even more innovative solutions that optimize energy efficiency and facilitate a transition to a more sustainable energy future.
Designing effective products and experiences requires a deep understanding of the cultural contexts in which they will be used. This goes beyond simple translation; it involves grasping the underlying values, beliefs, and assumptions that shape user behavior. A product designed for one culture might be completely inappropriate or even offensive in another, highlighting the crucial role of cultural sensitivity in the design process. Consider the different communication styles, social norms, and expectations that vary across cultures. This awareness is paramount to building products that resonate with diverse user groups and avoid misunderstandings.
Regulatory Frameworks and Stakeholder Collaboration

Regulatory Landscape for Financial Institutions
The current regulatory framework for financial institutions is a complex web of interconnected laws, regulations, and guidelines designed to ensure stability, protect consumers, and maintain public confidence in the financial system. These regulations cover a wide range of activities, from lending and investment banking to insurance and payment processing. Understanding and complying with these regulations is crucial for the long-term success and sustainability of any financial institution.
Compliance with these regulations is not merely a matter of avoiding penalties. It also fosters a culture of ethical conduct, transparency, and accountability within the institution. This, in turn, enhances investor confidence and strengthens the institution's overall reputation in the market.
Impact on Consumer Protection
Regulatory frameworks significantly impact consumer protection by establishing clear standards for financial products and services. These standards often include requirements for disclosure, fair pricing, and dispute resolution mechanisms. Consumers benefit from these protections, as they are better informed and empowered to make sound financial decisions.
Beyond disclosure and pricing, regulations also aim to prevent predatory lending practices and other forms of abuse. This protection is essential for vulnerable populations and helps ensure that financial products and services are accessible and affordable for all.
Stakeholder Engagement and Collaboration
Effective regulatory frameworks necessitate active engagement and collaboration among various stakeholders. This includes government agencies, industry associations, financial institutions, and consumer advocacy groups. Open communication and collaboration are essential for developing regulations that address emerging challenges and promote a more stable and equitable financial system.
Stakeholder input is crucial for ensuring that regulations are practical and effective in achieving their objectives. This approach also ensures that the regulations accurately reflect the needs and perspectives of various groups.
Global Regulatory Harmonization
The increasing interconnectedness of global financial markets necessitates a degree of regulatory harmonization across countries. While complete harmonization may be challenging, efforts to align regulations and standards across borders can help mitigate risks and ensure a more stable global financial system. This is critical for international trade and investment, which are heavily reliant on a predictable and consistent regulatory environment.
Transparency and Accountability
Regulations often mandate specific reporting requirements and disclosure obligations for financial institutions. Transparency in financial activities is paramount for fostering trust and accountability. This allows investors, regulators, and the public to assess the risks and performance of financial institutions more effectively. Such regulations contribute directly to maintaining investor confidence and ensuring the stability of the financial system.
Strong regulatory frameworks are vital to promoting open communication and preventing the proliferation of misleading or incomplete information within the financial sector.
Emerging Trends and Future Challenges
The financial landscape is constantly evolving, with new technologies and innovative business models emerging. Regulations must adapt to these changes to ensure that they remain effective and relevant. The increasing use of fintech and digital currencies presents significant challenges for regulators, requiring them to adapt quickly and proactively to maintain the stability and integrity of the financial system.
Enforcement and Monitoring
Effective enforcement mechanisms are crucial for ensuring compliance with regulatory frameworks. These mechanisms often involve audits, inspections, and sanctions for non-compliance. Robust monitoring and enforcement mechanisms are essential for deterring misconduct and maintaining public confidence in the financial system. This aspect of the regulatory framework often includes provisions for investigating and prosecuting violations of financial regulations.