Corporate Renewable Procurement for Semiconductors
Beyond Procurement: Integrating Sustainability Throughout the Supply Chain
Environmental Impact Assessment and Mitigation
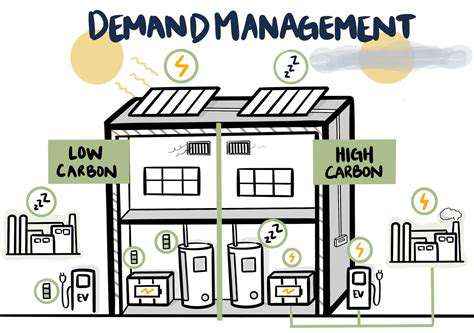
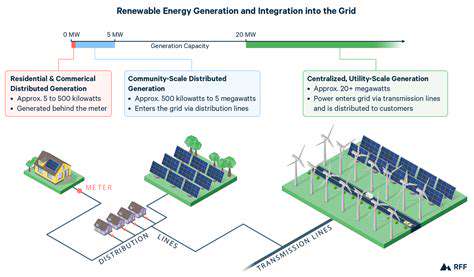
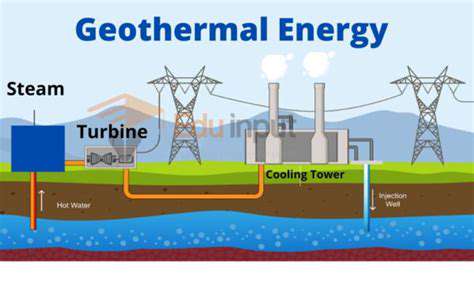
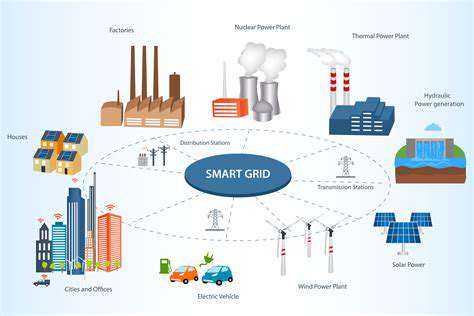
A crucial aspect of integrating sustainability into the supply chain lies in understanding and mitigating the environmental impact of each stage. This involves conducting thorough environmental impact assessments (EIAs) throughout the entire lifecycle of products, from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal. These assessments should identify potential environmental risks and vulnerabilities associated with specific suppliers, manufacturing processes, and transportation methods. Implementing sustainable practices, such as using renewable energy sources, reducing water consumption, and minimizing waste generation, are essential steps in minimizing environmental harm.
Furthermore, companies need to develop robust strategies for measuring and reporting on their environmental footprint. This requires transparent data collection and analysis, enabling companies to track progress towards sustainability goals and identify areas for improvement. Implementing environmental management systems (EMS) can provide a structured framework for managing environmental risks and opportunities across the supply chain. This includes establishing clear environmental targets, monitoring performance, and regularly reviewing and updating sustainability strategies.
Social Responsibility and Ethical Sourcing
Beyond environmental concerns, incorporating social responsibility into the supply chain is equally vital. This entails ensuring fair labor practices, fair wages, and safe working conditions for all employees throughout the supply chain. Ethical sourcing practices require companies to actively monitor supplier labor conditions, ensuring compliance with international labor standards and human rights agreements. Companies must engage with suppliers to foster a culture of respect and ethical treatment of workers, and to promote transparency and accountability throughout the supply chain.
Promoting diversity and inclusion within the supply chain is a critical component of social responsibility. This includes actively seeking out suppliers who embrace diversity in their workforce, promote equal opportunities, and create inclusive workplace environments. By supporting these principles, companies can contribute to a more equitable and just global economy. This also includes ensuring fair trade practices and supporting local communities in regions where raw materials are sourced.
Economic Viability and Innovation in Sustainable Practices
While environmental and social considerations are paramount, integrating sustainability into the supply chain must also be economically viable. Innovative solutions are critical to achieving this balance. For example, companies can explore alternative materials and technologies that are both environmentally friendly and cost-effective. This might involve exploring bio-based materials, using recycled content, or adopting lean manufacturing principles to reduce waste and improve efficiency. Implementing circular economy models can also enhance economic viability by promoting product reuse, recycling, and repurposing.
The development of innovative financing mechanisms that support sustainable supply chain initiatives is also important. This can include green bonds, carbon offsetting programs, and other financial instruments that incentivize sustainable practices. These strategies can help to offset the initial costs of transitioning to sustainable practices, making them more accessible and appealing to companies. By demonstrating the economic benefits of sustainability, companies can encourage wider adoption and build a more sustainable future.
Investing in research and development for new sustainable technologies and processes is another key component. By investing in innovation, companies can develop new solutions that reduce environmental impact, improve social conditions, and enhance economic viability. This approach creates a virtuous cycle where sustainability drives innovation, and innovation leads to further sustainable practices throughout the supply chain.
Promoting collaboration between businesses, NGOs, and governments is crucial. This collaboration can foster the sharing of best practices, resources, and knowledge, accelerating the transition to a more sustainable supply chain.
Companies must adopt a long-term perspective, recognizing that sustainable practices may require significant upfront investment and changes to existing processes. However, the long-term economic and social benefits can be substantial. This approach also reduces risk by mitigating environmental and social liabilities.
Incentivizing sustainable practices by rewarding suppliers who demonstrate high environmental and social performance is also essential. This can create a competitive advantage for companies that prioritize sustainability and encourage wider adoption within the supply chain.