Hybrid Renewable Energy Systems with Integrated Wind Power
Technological Advancements and System Design Considerations
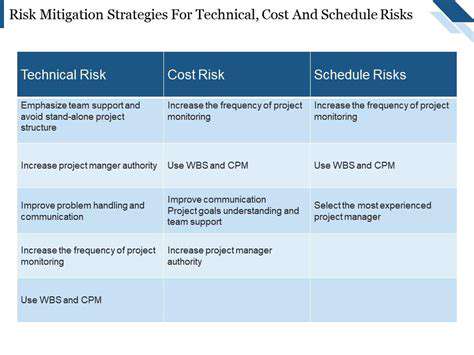
Technological Advancements in Hybrid Renewable Energy Systems
Significant advancements in renewable energy technologies are crucial for the successful implementation of hybrid systems. These advancements encompass improvements in solar panel efficiency, particularly in terms of cost-effectiveness and performance in diverse climates. Furthermore, advancements in battery technology are critical, enabling increased energy storage capacity, faster charging times, and enhanced longevity, which are all essential for managing the intermittent nature of solar and wind power. The integration of smart grid technologies and advanced power electronics allows for better control and management of energy flow within the hybrid system, optimizing its overall performance.
Innovations in wind turbine design, including vertical axis wind turbines, are also contributing to the development of more efficient and cost-effective hybrid systems. These advancements aim to capture wind energy across a wider range of wind speeds and conditions. Improved energy harvesting techniques, such as advancements in wave and tidal energy technologies, present promising avenues for incorporating additional renewable energy sources into hybrid systems, diversifying the energy portfolio and enhancing resilience against weather fluctuations. The development of advanced materials with improved thermal properties is also critical for enhancing the performance and durability of components in hybrid systems.
System Design Considerations for Optimal Performance
A key design consideration for hybrid renewable energy systems is the optimal sizing and configuration of the different renewable energy sources. Careful analysis of local weather patterns, energy demands, and cost factors is essential for determining the most appropriate mix of solar, wind, or other renewable sources. This involves considering factors like solar irradiance levels, average wind speeds, and typical energy consumption patterns to ensure the system meets the anticipated energy needs.
Integrating energy storage solutions, like batteries, is also critical for maintaining a stable and reliable power supply. The capacity of the energy storage system must be carefully matched to the variability of the renewable energy sources, preventing power outages during periods of low generation. Equally important is the selection of appropriate inverters and converters to ensure seamless energy transfer between the various components of the hybrid system. Proper system design also incorporates safety protocols and protection mechanisms to mitigate potential risks associated with the operation of the hybrid system.
Finally, the design should incorporate monitoring and control systems to optimize the performance of the hybrid system over time. This includes real-time data collection and analysis of energy production and consumption, allowing for adjustments to the system configuration and operation to maximize efficiency. Furthermore, a robust and user-friendly monitoring system is essential for maintenance and troubleshooting, reducing downtime and ensuring system longevity.
Economic and Environmental Impacts

Economic Impacts of Resource Depletion
Resource depletion, whether it's from fossil fuels, minerals, or water, has significant economic consequences. Businesses reliant on these resources face escalating costs as supplies dwindle and extraction becomes more challenging and expensive. This translates to higher production costs, potentially impacting profitability and competitiveness in the global market. Furthermore, the need to find alternative resources and develop sustainable practices adds further financial burdens for businesses. The economic repercussions ripple throughout supply chains, affecting industries directly and indirectly connected to the depleted resources.
The economic burden of resource depletion extends beyond individual businesses. Government spending on infrastructure, research, and development to mitigate the impacts of resource scarcity can place a strain on public finances. This can divert funds from other essential sectors like education and healthcare. The long-term economic instability caused by resource scarcity can also lead to social unrest and political instability, ultimately impacting economic development in the affected regions.
Environmental Impacts of Pollution
Pollution, a significant byproduct of resource extraction and consumption, causes substantial environmental damage. Air and water pollution from industrial processes and transportation contribute to climate change and negatively impact human health. This degradation of ecosystems has far-reaching consequences, including reduced biodiversity, disruptions to natural cycles, and increased vulnerability to natural disasters. The loss of biodiversity is not only environmentally devastating but also impacts the various industries that rely on natural resources and ecosystems.
Furthermore, pollution degrades land quality, impacting agricultural productivity and food security. The contamination of water sources poses a direct threat to human health and can lead to widespread illness, impacting the overall well-being of communities. Sustainable solutions need to be implemented to address these issues and prevent further environmental damage, ensuring the long-term health of our planet.
Climate Change and its Economic Effects
Climate change, driven largely by greenhouse gas emissions from human activities, presents a significant economic threat. Extreme weather events, such as floods, droughts, and storms, cause widespread damage to infrastructure and property, resulting in substantial economic losses. These events disrupt supply chains, impacting businesses and livelihoods across various sectors. The consequences of climate change are not limited to immediate costs; there are also long-term effects on economic stability and sustainable development.
The cost of adapting to climate change, including measures like infrastructure upgrades and disaster preparedness, will also impose a considerable financial burden on governments and communities. Furthermore, the shift towards renewable energy sources and sustainable practices will require significant investment, impacting economic growth and potentially creating job displacement in certain sectors. However, the long-term benefits of mitigating climate change, such as a more stable climate and a healthier environment, will ultimately outweigh the short-term costs.
Sustainable Resource Management
The adoption of sustainable resource management practices is crucial for mitigating the negative economic and environmental impacts of depletion and pollution. Sustainable practices involve minimizing resource use, promoting resource efficiency, and implementing waste reduction strategies. Implementing these strategies can lead to significant cost savings for businesses in the long run, and reduce the financial burden from environmental disasters. This approach fosters economic stability and environmental protection.
Sustainable resource management also encourages innovation and the development of new technologies that promote environmental protection and economic growth. This leads to the creation of new industries and job opportunities. Promoting responsible consumption and production patterns is equally important for long-term sustainability.
The Interconnectedness of Economic and Environmental Impacts
The economic and environmental impacts are deeply interconnected. Environmental degradation often leads to economic losses, while unsustainable economic practices often lead to environmental damage. These issues are complex and require holistic solutions that consider both the economic and environmental dimensions. The long-term sustainability of our economies is inextricably linked to the health of our environment. Addressing these issues requires a shift in societal values and priorities, prioritizing environmental protection and resource conservation. This requires cooperation between governments, businesses, and individuals to create a more sustainable future.
The interconnected nature of these impacts necessitates a fundamental shift in economic thinking. Moving away from a purely profit-driven model towards one that integrates environmental considerations is crucial for long-term economic prosperity. This requires a comprehensive approach that considers the long-term consequences of our actions on both the environment and the economy.