Operational Risk Management for Renewable Energy Assets
Implementing Mitigation Strategies and Controls
Identifying Potential Risks
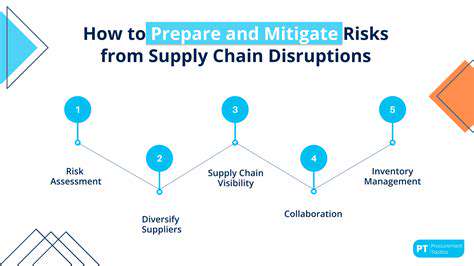
A crucial first step in implementing mitigation strategies and controls is the thorough identification of potential operational risks. This involves a comprehensive assessment of all areas within the organization, considering internal processes, external factors, and technological dependencies. Understanding the specific vulnerabilities and potential impacts of these risks is paramount to developing effective countermeasures. This process should involve collaboration across different departments and levels of the organization to ensure a holistic view of potential risks.
Developing Mitigation Strategies
Once potential risks are identified, the next step is to develop tailored mitigation strategies. These strategies must be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). Strategies should aim to reduce the likelihood of a risk event occurring and/or limit the potential impact should an event occur. This may involve implementing new policies, procedures, or technologies, and should consider the resources and expertise required for successful implementation.
Implementing Control Measures
Effective mitigation strategies require the implementation of specific control measures. These controls should be designed to address the identified risks and should be tested and monitored regularly to ensure they are functioning as intended. Examples of control measures include enhanced security protocols, improved internal controls, and robust disaster recovery plans. The effectiveness of controls must be continuously evaluated to ensure they remain relevant and adapt to changing circumstances.
Monitoring and Evaluating Controls
Implementing controls is only the first step. Continuous monitoring and evaluation are critical to ensuring controls remain effective. Regular audits, reviews, and reporting mechanisms are essential to detect any weaknesses or gaps in controls. This process allows for timely adjustments to the control framework as needed, ensuring it remains aligned with the organization's objectives and the evolving risk landscape. Regular reporting on control effectiveness is vital for transparency and accountability.
Communication and Training
Effective mitigation strategies and controls require buy-in and understanding from all stakeholders. Clear communication of the implemented controls, their purpose, and the rationale behind them is essential. Comprehensive training programs should be developed to equip employees with the knowledge and skills necessary to effectively use and maintain the implemented controls. This fosters a culture of risk awareness and responsibility, ultimately contributing to a more resilient operational environment.
Review and Adaptation
The operational risk landscape is dynamic and constantly evolving. Regular reviews of the implemented mitigation strategies and controls are necessary to ensure their continued relevance and effectiveness. This involves assessing the effectiveness of the controls in light of new risks, changes in regulations, and technological advancements. Flexibility and adaptability are crucial in ensuring that the risk management framework remains robust and capable of responding to the changing needs of the organization. This includes considering the potential impact of new technologies and regulatory changes.