Renewable Energy for Urban Sustainability

The Urgency of the Transition
The urban energy transition is no longer a futuristic concept; it's a pressing global necessity. Cities, as engines of economic activity and centers of population, are disproportionately responsible for energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. Delaying the transition will only exacerbate the effects of climate change, impacting everything from public health to infrastructure resilience. This urgent need demands immediate action across all sectors.
Driving Forces Behind the Shift
Several key factors are driving the urban energy transition. Rising energy costs, coupled with the growing awareness of environmental degradation, are compelling cities to explore sustainable alternatives. Technological advancements in renewable energy sources, energy storage, and smart grids are making these alternatives increasingly viable and cost-effective. Furthermore, policy incentives and public pressure are pushing cities to embrace cleaner energy solutions.
Technological Innovations and Solutions
Innovative technologies are pivotal in facilitating the urban energy transition. Smart grids, for instance, enable more efficient energy distribution and consumption management. Renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, are becoming increasingly affordable and reliable, making them viable alternatives to fossil fuels. Energy storage solutions are also crucial in ensuring a stable and reliable energy supply, particularly for fluctuating renewable energy sources. Furthermore, advancements in energy efficiency technologies are helping to reduce energy consumption across various urban sectors.
Policy Frameworks and Incentives
Strong policy frameworks are essential to guide and accelerate the urban energy transition. Governments need to implement policies that incentivize the adoption of renewable energy technologies and encourage energy efficiency measures. Financial incentives, such as tax credits and subsidies, can play a significant role in driving private investment in sustainable energy solutions. Furthermore, regulations and standards can help to ensure the quality and performance of renewable energy projects and energy-efficient buildings. Robust policy frameworks create a supportive environment for innovation and investment.
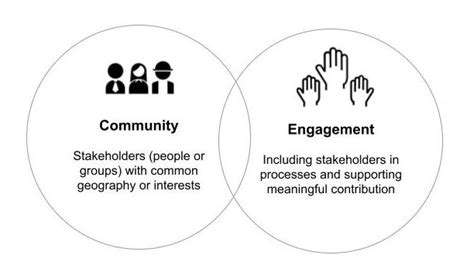
Community Engagement and Public Awareness
The urban energy transition is not just a technical or policy issue; it's a societal one. Engaging communities and raising public awareness is crucial for successful implementation. Educating residents about the benefits of sustainable energy choices and empowering them to participate in energy-saving initiatives is essential for long-term success. Community-based projects and initiatives can foster a sense of ownership and responsibility, motivating citizens to contribute to the transition. Open dialogue and collaboration between stakeholders, including government, businesses, and communities, are vital for achieving meaningful progress.
Solar Power: Illuminating the Urban Landscape
Harnessing Sunlight for Urban Homes
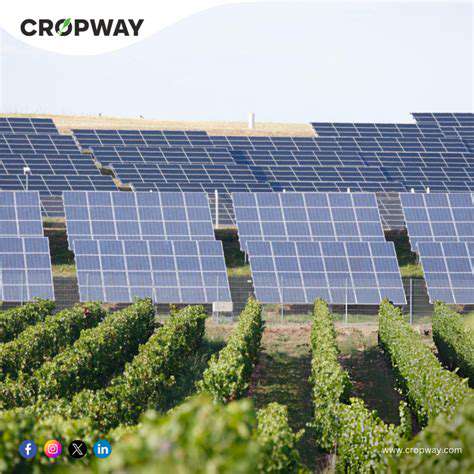
Solar power is rapidly becoming a viable and increasingly attractive option for homeowners in urban environments. The benefits extend beyond simply reducing energy bills; it represents a significant step towards environmental sustainability. Installation of solar panels on rooftops, even in densely populated areas, can significantly offset reliance on fossil fuels, reducing carbon emissions and contributing to cleaner air quality in urban centers. This translates to tangible improvements in public health and a more vibrant, sustainable urban landscape.
Furthermore, many municipalities are implementing incentives and programs to encourage solar adoption in urban areas. These incentives can make the upfront investment more manageable, making solar power a realistic choice for a wider range of homeowners. The integration of solar panels into urban architecture can even enhance aesthetics, creating aesthetically pleasing and environmentally responsible structures. This blend of practicality and design is crucial for the successful integration of renewable energy into the urban fabric.
Solar Power's Role in Urban Infrastructure
Beyond residential applications, solar power plays a critical role in powering urban infrastructure, from streetlights to public buildings. Implementing solar-powered streetlights can significantly reduce energy consumption and maintenance costs associated with traditional grid-powered systems. This transition towards renewable energy sources in urban infrastructure not only reduces the city's carbon footprint but also fosters a more sustainable and resilient urban environment.
The deployment of solar panels on public buildings, such as schools and community centers, can further reduce the city's overall energy demand. This not only lowers operational costs but also serves as a tangible demonstration of commitment to sustainability, inspiring residents and businesses to follow suit. The integration of solar technology into urban infrastructure projects is pivotal in creating a model for future sustainable cities, showcasing the potential for large-scale renewable energy implementation within urban environments.
This demonstrates a forward-thinking approach to urban development, showcasing how renewable energy sources can be strategically integrated into existing and new infrastructure projects. Furthermore, the creation of community solar gardens or shared solar installations can offer a cost-effective and accessible option for residents who may not have the space for individual rooftop installations, fostering a sense of community and shared sustainability.
The use of solar power in urban infrastructure, through strategic planning and implementation, can significantly contribute to the overall success of sustainability initiatives and showcase the positive impact of renewable energy in urban settings.
Utilizing solar energy in transportation infrastructure, such as charging stations for electric vehicles, is a crucial step towards a more sustainable urban transportation system. This interconnected approach to urban development reinforces the concept of a circular economy, highlighting the multifaceted benefits of a comprehensive shift towards renewable energy sources.
Beyond Solar and Wind: Exploring Other Renewable Options
Harnessing Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy, derived from the Earth's internal heat, offers a compelling alternative to solar and wind power, particularly in areas with suitable geological conditions. This sustainable energy source taps into steam and hot water reservoirs deep beneath the Earth's surface. These resources can be used to generate electricity directly, or for heating and cooling purposes, making it a versatile option for urban environments. While the initial infrastructure investment can be substantial, the long-term operational costs are often lower than those associated with traditional fossil fuel-based systems, contributing to a more sustainable and cost-effective energy solution over time.
The efficiency of geothermal energy extraction varies considerably based on factors like reservoir temperature and depth. Careful geological surveys and assessments are crucial in identifying suitable geothermal sites, ensuring optimal energy production and minimizing environmental impact. Furthermore, geothermal power plants require specialized technologies for drilling and managing the extracted fluids, which can introduce specific operational challenges that must be addressed effectively.
Exploring Tidal and Wave Energy
Tidal energy, harnessed from the rhythmic rise and fall of ocean tides, presents a potential source of clean energy in coastal urban areas. This renewable energy source relies on the consistent movement of water to drive turbines, generating electricity. The predictable nature of tidal cycles makes it a reliable energy source, particularly in regions with significant tidal ranges. However, the geographical limitations of suitable tidal zones mean that this source may not be viable in all urban settings.
Wave energy, another marine-based renewable option, captures the kinetic energy of ocean waves. While wave energy conversion technology is still under development, advancements in wave energy capture devices could make it a significant contributor to urban energy portfolios. The variability of wave energy production compared to the consistency of tidal energy creates unique engineering challenges. The intermittent nature of wave energy requires innovative energy storage solutions to ensure a reliable power supply for urban grids.
Bioenergy and Biomass Resources
Bioenergy and biomass resources offer an intriguing approach to renewable energy generation, drawing upon organic matter. This can include agricultural residues, forestry waste, and even municipal solid waste. Converting these biomass resources into biofuels or biogas can generate heat, electricity, and transportation fuels. Careful consideration of the environmental impacts of biomass collection and processing is essential. This includes assessing the potential for deforestation, land use changes, and emissions from the conversion process to ensure a truly sustainable approach.
The development and implementation of bioenergy technologies in urban areas can create new economic opportunities, supporting local industries and creating green jobs. Furthermore, the use of locally sourced biomass can reduce reliance on long-distance transportation of fuels. However, issues related to the availability and sustainability of biomass resources, and the potential for greenhouse gas emissions during processing, must be carefully assessed to optimize the environmental and economic benefits of bioenergy solutions in urban environments.
The Economic and Social Benefits of Renewable Energy Adoption

Economic Growth and Development
A strong economy, fueled by innovation and entrepreneurship, is essential for a thriving society. Economic growth, driven by factors like increased productivity and investment, creates jobs and opportunities for individuals and communities. This growth leads to higher incomes, enabling people to afford better housing, education, and healthcare, which in turn further boosts the economy and creates a positive feedback loop.
Furthermore, economic development fosters a more diversified and resilient economy, reducing reliance on a single industry or sector. This diversification makes the economy less vulnerable to external shocks and promotes sustainable long-term growth.
Improved Living Standards
Economic prosperity directly translates to improved living standards for citizens. Higher incomes allow individuals to access better quality goods and services, leading to enhanced well-being. This includes access to nutritious food, safe housing, quality education, and healthcare, all vital components of a fulfilling life.
Improved living standards are also linked to better health outcomes and increased life expectancy. Access to quality healthcare and nutritious food significantly contributes to overall well-being, making individuals healthier and more productive members of society.
Increased Employment Opportunities
Economic growth and development are intrinsically linked to job creation. Businesses expanding in a healthy economy need more workers, leading to increased employment opportunities for individuals. This is crucial for reducing unemployment rates and poverty, creating a more equitable society.
Furthermore, a robust job market provides individuals with a sense of purpose and security. Stable employment allows individuals to contribute meaningfully to society and build a better future for themselves and their families.
Enhanced Social Cohesion
Economic well-being often fosters social cohesion and reduces social disparities. Increased income and access to resources can lead to a more unified community, where individuals feel a stronger sense of belonging and shared purpose.
By reducing income inequality and providing opportunities for everyone, a thriving economy can contribute to a more harmonious and inclusive society. This in turn creates a more supportive and collaborative environment for all members of the community.
Investment in Infrastructure
Economic prosperity often enables significant investments in crucial infrastructure, such as transportation networks, communication systems, and public utilities. These investments not only improve the quality of life for citizens but also create a conducive environment for businesses to thrive. Improved infrastructure can facilitate trade, boost productivity, and attract further investment.
Positive Impacts on Public Services
A strong economy allows governments to invest more in public services, including education, healthcare, and public safety. Increased tax revenues from economic activity enable governments to provide better quality services and support the well-being of their citizens. This leads to a more equitable and prosperous society.
These public services are fundamental for a functioning society and contribute significantly to the overall quality of life for its citizens. Improved public services, in turn, enhance productivity and contribute to greater economic growth.
Sustainable Development and Environmental Protection
A growing economy doesn't necessarily have to come at the expense of the environment. Sustainable development practices can be integrated into economic growth models, ensuring long-term prosperity while minimizing negative environmental impacts. This involves adopting eco-friendly technologies, promoting sustainable agriculture, and implementing policies that protect natural resources.
Sustainable development ensures that the needs of the present are met without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. This approach balances economic growth with environmental protection, creating a more resilient and sustainable future.