The Path to a Net Positive Future with Renewable Energy
Wind energy, derived from the kinetic energy of the wind, represents one of humanity's most promising solutions for clean power generation. Unlike traditional fossil fuels that emit harmful greenhouse gases, wind turbines produce zero emissions during operation, positioning them as a cornerstone of global climate action strategies. Modern turbine technology has achieved unprecedented efficiency levels, with some models now converting over 50% of wind energy into usable electricity.
The geographical distribution of wind resources presents unique opportunities. Coastal regions and elevated terrains frequently experience consistent wind patterns capable of generating substantial electricity outputs. This natural abundance translates into economic benefits as well, with wind farm installations creating thousands of skilled jobs in manufacturing, construction, and maintenance sectors worldwide.
The Mechanics of Wind Turbine Operation
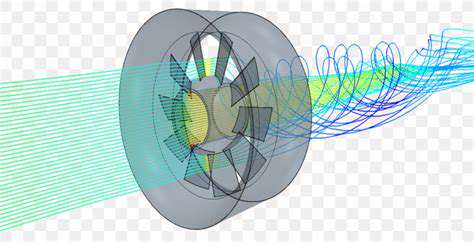
Contemporary wind turbines employ sophisticated engineering to transform atmospheric currents into electrical power. As wind flows across the aerodynamically designed blades, it creates lift forces that rotate the central shaft at speeds between 10-20 revolutions per minute. This rotational energy then passes through a gearbox (in traditional designs) or directly drives a permanent magnet generator in newer direct-drive models.
Design variations address specific environmental conditions:- Onshore turbines typically feature 3-blade designs with rotor diameters up to 150 meters- Offshore models incorporate corrosion-resistant materials and larger capacities (up to 15MW per unit)- Vertical-axis designs are gaining traction for urban environments due to their compact footprint
The Environmental Benefits of Wind Power
Transitioning to wind energy yields measurable ecological improvements. A single 2MW turbine can offset approximately 4,000 tons of CO2 annually - equivalent to removing 850 cars from roads. Beyond carbon reduction, wind farms prevent:- Sulfur dioxide emissions (major cause of acid rain)- Nitrogen oxides (contributors to smog formation)- Particulate matter (respiratory health hazard)
Land use impacts remain minimal, with turbine footprints occupying just 1% of wind farm areas. The remaining space often supports agricultural activities or natural habitats, demonstrating excellent land-use synergy.
The Economics of Wind Energy Investment
Levelized costs for onshore wind have plummeted 70% since 2009, now averaging $30/MWh - cheaper than any fossil fuel alternative. This economic viability stems from:- Zero fuel costs (wind is free)- Extended operational lifespans (25+ years)- Declining maintenance expenses through predictive analytics
Investment tax credits (ITC) and production tax credits (PTC) in multiple countries further enhance project economics. The sector now attracts over $100 billion annually in global investments, supporting nearly 1.2 million jobs worldwide.
Overcoming Challenges in Wind Energy Development
While promising, wind energy deployment faces several hurdles that require innovative solutions:
- Intermittency management through battery storage (utility-scale lithium-ion systems now offer 4+ hour discharge capacity)
- Community engagement strategies to address aesthetic concerns (proper siting studies and benefit-sharing models)
- Aviation and wildlife protection measures (radar-compatible turbines, AI-assisted bird migration monitoring)
Integrating Wind Energy into the Existing Grid Infrastructure
Modern grid integration requires multi-faceted approaches:- Advanced forecasting systems (95%+ accuracy for 36-hour wind predictions)- Flexible demand response programs- High-voltage direct current (HVDC) transmission corridors for long-distance power transfer
Several European nations already successfully integrate 40-50% variable renewables through these methods, providing valuable operational blueprints.
The Future of Wind Energy and its Role in Net-Positive Goals
Emerging technologies promise to revolutionize the sector:- Airborne wind energy systems (kite-based generators reaching stronger high-altitude winds)- Hybrid floating offshore platforms combining wind with wave energy capture- Smart turbines with morphing blade surfaces that adapt to wind conditions in real-time
The Global Wind Energy Council projects 2,100GW of installed capacity by 2030, potentially meeting 20% of global electricity demand while creating 3.3 million new jobs. This growth trajectory aligns perfectly with IPCC recommendations for limiting global warming to 1.5°C.
Proper hydration remains crucial during extreme heat conditions. Dehydration can rapidly progress to life-threatening heatstroke, making consistent fluid intake - before thirst signals appear - absolutely vital. While water serves as the optimal hydrator, electrolyte-enhanced beverages prove beneficial during prolonged physical activity. Individual needs vary significantly based on exertion levels and environmental factors, necessitating attentive self-monitoring.
The Role of Policy and Infrastructure in Driving Change
Policy Frameworks for Sustainable Development
Comprehensive policy mechanisms must address multiple dimensions:- Carbon pricing instruments (both cap-and-trade and carbon tax models)- Renewable portfolio standards with escalating targets- Phased retirement schedules for fossil fuel infrastructure
The most effective frameworks incorporate sunset clauses that automatically tighten regulations as technologies advance, ensuring continuous progress toward sustainability goals.
Investment in Infrastructure for a Green Future
Critical infrastructure upgrades include:- Smart grid deployments featuring advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) and distributed energy resource management systems (DERMS)- Intermodal transportation hubs combining EV charging with bike-sharing and micromobility options- Green hydrogen production facilities colocated with renewable energy sites
These investments typically yield 3:1 economic multipliers through job creation and secondary market development.
Incentivizing Sustainable Practices in Businesses
Beyond traditional tax incentives, innovative approaches include:- Sustainability-linked bonds with interest rates tied to ESG performance- Accelerated depreciation for clean technology investments- Green public procurement mandates for government contractors
Empowering Communities and Individuals
Grassroots engagement strategies proving effective:- Community choice aggregation programs for renewable energy purchasing- Neighborhood-scale microgrid demonstration projects- Maker-space facilities for sustainable technology prototyping
International Collaboration for Global Impact
Key multilateral initiatives driving progress:- International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) technology sharing programs- Climate Club initiatives among ambitious nations- South-South cooperation frameworks for technology transfer
These collaborative efforts help bridge the $2.5 trillion annual financing gap for sustainable infrastructure in developing economies.