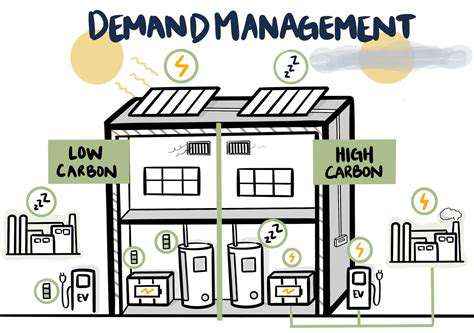
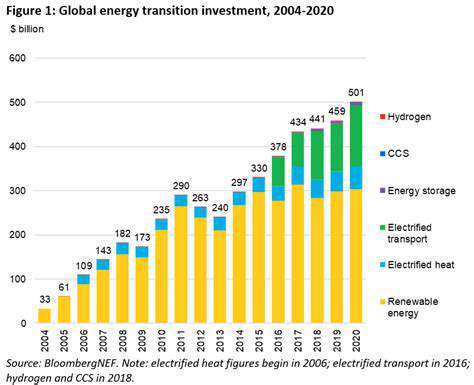
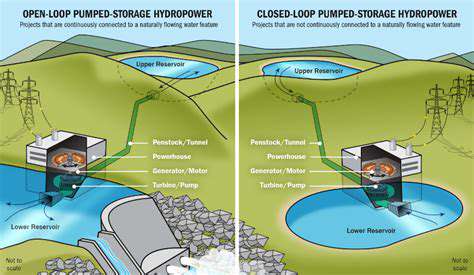
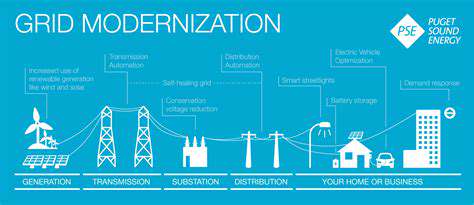
Corporate Renewable Procurement and Carbon Neutrality
Measuring and Reporting on Carbon Footprint Reduction

Defining Carbon Footprint Measurement
A critical first step in measuring and reporting on carbon emissions is defining the scope of the measurement. This involves identifying all relevant sources of greenhouse gas emissions, encompassing direct emissions from owned or operated facilities, indirect emissions from purchased energy, and emissions throughout the supply chain. Understanding these different scopes is crucial for a comprehensive analysis. A robust methodology is essential, ensuring accuracy and comparability across different organizations and reporting periods.
Different industries will have vastly different carbon footprints, and the methods used to measure them must reflect these differences. Furthermore, the chosen measurement methods should be transparent and auditable to ensure stakeholders can trust the reported data. This transparency is vital for building public trust and fostering accountability.
Data Collection and Analysis Techniques
Gathering accurate data requires careful planning and execution. This involves utilizing various tools and techniques, including energy consumption data, fuel usage records, and emission factors specific to different activities. Precise data collection is fundamental for reliable conclusions.
Analyzing the collected data is equally important. Advanced analytics can reveal trends, identify areas for improvement, and quantify the environmental impact of different activities. These insights are essential for developing effective carbon reduction strategies.
Regular audits and reviews of data collection procedures are essential to maintain accuracy and identify any potential issues or errors that may arise.
Reporting Standards and Frameworks
Adhering to established reporting standards and frameworks is vital for consistency and comparability. These frameworks provide a structured approach to measuring, reporting, and verifying carbon emissions. Compliance with these standards enhances the credibility and trustworthiness of the reported data.
Examples of commonly used frameworks include the Greenhouse Gas Protocol, the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD), and the World Resources Institute (WRI) standards. Understanding these frameworks and their implications is key to effective carbon reporting.
Developing Reduction Strategies Based on Data
The data gathered and analyzed provides a clear picture of the organization's carbon footprint. This understanding is crucial for developing targeted reduction strategies. Identifying specific areas where emissions are highest allows for focused interventions. Effective strategies will consider the financial implications, technological advancements, and regulatory requirements.
Implementing these strategies requires careful planning, budgeting, and stakeholder engagement. By addressing the root causes of emissions, organizations can achieve significant reductions in their environmental impact.
These strategies should be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect new information and evolving best practices.
Communication and Stakeholder Engagement
Transparent communication of carbon footprint data to relevant stakeholders is crucial. This includes investors, customers, employees, and the wider community. Open communication fosters trust and encourages collaboration in achieving sustainability goals.
Regular reporting on progress, challenges, and future plans allows stakeholders to understand the commitment to environmental responsibility. This engagement also provides opportunities for feedback and suggestions, leading to more effective and sustainable practices.