Wind Energy Advancements: Driving the Renewable Energy Transition
Offshore Wind Farms: Harnessing Powerful Coastal Winds

Offshore Wind Farms: A Renewable Energy Revolution
Offshore wind farms are rapidly emerging as a crucial component of the global transition to renewable energy sources. These expansive installations, situated in the vast expanse of oceans, harness the powerful winds to generate clean, sustainable electricity. This technology offers a significant opportunity to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and mitigate the effects of climate change. The potential for large-scale energy production from offshore wind is substantial, promising a cleaner and more sustainable energy future.
The development of offshore wind farms is driven by the need for greater energy independence and a commitment to environmental responsibility. These projects represent a significant investment in both infrastructure and human capital, fostering economic growth and job creation. The long-term benefits of offshore wind energy extend far beyond the economic sphere, contributing to a healthier planet and a more sustainable global economy.
Technological Advancements in Offshore Wind
Significant advancements in turbine technology have made offshore wind farms more efficient and cost-effective. Modern turbines are larger and more powerful, capable of capturing more wind energy and generating higher electricity outputs. This leads to reduced costs per unit of energy produced.
Furthermore, innovative materials and construction techniques are enhancing the durability and longevity of offshore wind farm components. These improvements reduce maintenance needs and increase the overall reliability of these crucial energy sources.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Offshore wind farms, while offering a significant renewable energy source, do have some environmental impacts that need careful consideration. These installations can impact marine ecosystems, potentially affecting migratory patterns and habitats of various species. Careful environmental impact assessments and mitigation strategies are essential to minimize any adverse consequences.
Despite these potential challenges, the overall environmental impact of offshore wind farms is considerably lower compared to traditional fossil fuel power plants. These farms contribute to a cleaner environment and a more sustainable energy future.
Economic Benefits and Job Creation
The construction and operation of offshore wind farms create numerous job opportunities in various sectors, from engineering and construction to maintenance and operation. This stimulates economic growth in coastal communities and contributes to the overall prosperity of the region.
The long-term economic benefits are substantial, with ongoing revenue generation from the sale of clean energy. This creates a stable and reliable energy source that can power homes and businesses for decades to come.
Challenges and Considerations in Deployment
Deploying offshore wind farms presents some significant challenges. The harsh marine environment requires robust and reliable infrastructure, potentially leading to high initial capital costs. These costs can be a barrier to widespread adoption, especially in the early stages of project development.
Furthermore, permitting and regulatory processes can be complex and time-consuming, adding further hurdles to the deployment of these essential renewable energy projects.
Public Perception and Community Engagement
Public perception of offshore wind farms is a critical factor in successful development. Addressing concerns about visual impact, noise pollution, and potential disruptions to marine life is essential to garner community support. Transparent communication and meaningful engagement with local communities are critical to building trust and cooperation.
Active community involvement in the planning and development process is vital for ensuring that offshore wind farms are integrated successfully into local environments. This can help to mitigate potential negative impacts and foster a sense of shared ownership and responsibility for these important energy projects.
Future of Offshore Wind: Growth and Innovation
The future of offshore wind looks promising, with ongoing technological advancements and increasing demand for clean energy sources. Significant investments in research and development are expected to further enhance the efficiency and affordability of offshore wind farms. This will pave the way for even greater deployment of these vital renewable energy sources globally.
Offshore wind farms are poised to become a major player in the global energy mix, contributing significantly to a cleaner and more sustainable future for generations to come.
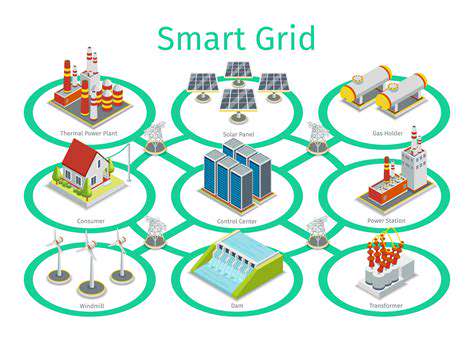
Smart Grid Integration: Optimizing Energy Distribution

Smart Grid Technologies
Smart grid integration involves the implementation of advanced technologies to modernize existing electrical grids. These technologies are designed to enhance grid reliability, efficiency, and sustainability. This includes smart meters, advanced sensors, and communication networks that allow for real-time data collection and analysis. This data-driven approach enables grid operators to make informed decisions, optimize energy flow, and proactively address potential issues.
The integration of these technologies creates a dynamic and responsive grid capable of handling fluctuating energy demands, integrating renewable energy sources, and improving overall energy management. Smart grid technology also plays a crucial role in enhancing grid resilience by enabling faster fault detection and restoration, reducing the impact of outages, and improving overall system security.
Economic Benefits of Smart Grid Integration
Implementing smart grid technologies offers substantial economic benefits for both consumers and utilities. Reduced energy waste and improved grid efficiency lead to lower energy costs for consumers. By optimizing energy distribution and consumption patterns, smart grids can help utilities reduce transmission and distribution losses, leading to significant cost savings.
Furthermore, the integration of renewable energy sources is facilitated by smart grids. This integration reduces reliance on fossil fuels, thereby lowering operating costs and minimizing environmental impact. Smart grids also enable the development of new revenue streams for utilities, such as demand response programs and energy efficiency services.
Environmental Impacts of Smart Grid Integration
Smart grid integration plays a critical role in mitigating the environmental impact of energy production and distribution. By optimizing energy use and integrating renewable energy sources, smart grids contribute to a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions. This transition towards cleaner energy sources is essential for achieving environmental sustainability goals and mitigating climate change.
Furthermore, smart grid technologies enable a more efficient use of energy resources. This translates to reduced energy consumption and decreased environmental impact associated with the generation and transmission of electricity. By improving energy efficiency, smart grids help conserve natural resources and reduce the strain on ecosystems.
Challenges and Considerations for Smart Grid Integration
Despite the numerous benefits, smart grid integration presents several challenges. One significant challenge is the high initial investment required for infrastructure upgrades and the implementation of new technologies. Careful planning and financing strategies are crucial for successful deployment. Moreover, data security and privacy concerns are paramount in a system that relies heavily on interconnected digital devices and the transmission of sensitive information.
Interoperability issues between different smart grid components and systems can also present a significant obstacle. Standardization and interoperability are critical to ensure seamless integration and prevent conflicts in the operation of the system. Thorough analysis of existing infrastructure and the needs of future users is paramount for successful integration.