Wind Energy Advancements in Offshore Applications

Technological Advancements in Turbine Design
Offshore wind turbines are constantly evolving, with advancements in blade design, materials, and control systems driving increased efficiency and reduced costs. These improvements are crucial for maximizing energy capture in challenging marine environments and minimizing maintenance needs. New materials like carbon fiber composites are being used to create stronger and lighter blades, enabling larger rotor diameters and higher energy output.
Furthermore, sophisticated control systems are being implemented to optimize turbine performance in real-time. These systems allow for dynamic adjustments to blade pitch and generator output, maximizing energy capture and minimizing stress on the turbine components. This adaptability is critical for harnessing the variable nature of wind resources offshore.
Expanding the Offshore Footprint
The growing demand for clean energy is pushing the boundaries of offshore wind development, with projects increasingly venturing into deeper waters and further from the coast. This expansion necessitates the development of innovative mooring systems, floating platforms, and transmission infrastructure to support these remote installations.
The development of floating offshore wind turbines is a significant step in this expansion, allowing deployment in locations previously inaccessible to traditional bottom-fixed foundations. This opens up vast untapped wind resources and reduces the environmental impact associated with coastal development.
Economic and Job Creation Potential
The offshore wind sector is poised to become a significant driver of economic growth, creating numerous jobs in manufacturing, installation, maintenance, and related industries. The construction and operation of these large-scale projects require a skilled workforce, leading to the creation of jobs from the ground up.
Furthermore, the economic benefits extend beyond direct employment opportunities. The development of supporting industries, such as port facilities and specialized logistics, will also contribute to economic growth and regional development. This economic stimulation will have a positive impact on local communities and the wider economy.
Environmental Considerations and Sustainability
While offshore wind energy is a crucial component of a sustainable energy future, careful consideration must be given to its environmental impacts. This includes assessing the potential effects on marine ecosystems, migratory bird populations, and marine mammals. Careful planning and mitigation strategies are essential to minimize any negative environmental consequences.
Sustainable practices throughout the lifecycle of offshore wind farms, from material sourcing to decommissioning, are crucial for ensuring a minimal ecological footprint. Addressing potential environmental concerns proactively is essential for ensuring long-term environmental sustainability.
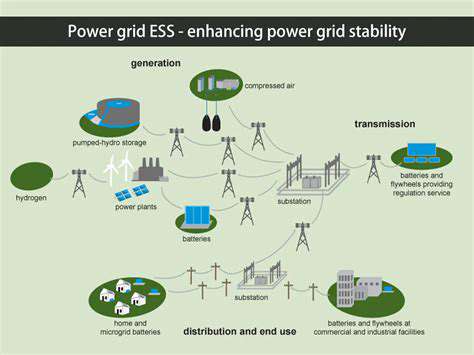
Grid Integration and Energy Storage
Integrating large-scale offshore wind energy into existing power grids presents significant technical challenges. These challenges require the development of advanced grid infrastructure and smart grid technologies to manage the intermittent nature of wind power. Effective solutions are necessary to ensure the reliable and efficient transmission of energy from offshore wind farms to consumers.
The integration of energy storage technologies with offshore wind farms will be critical for mitigating the intermittency issues and ensuring a consistent supply of renewable energy. This will enable the reliable and consistent provision of clean energy, supporting the transition to a more sustainable energy system.
Policy and Regulatory Frameworks
Establishing clear and supportive policy frameworks is essential to accelerate the development of offshore wind energy. These frameworks should address issues such as permitting processes, land use regulations, and grid connection requirements. Creating a stable and predictable regulatory environment is crucial for attracting investment and fostering innovation.
Government incentives and subsidies can also play a significant role in encouraging investment and accelerating the deployment of offshore wind projects. These incentives can stimulate the growth of the industry and contribute to a more sustainable energy future.