Decentralization of Energy Generation for Disaster Preparedness
Decentralized Energy Systems: A Paradigm Shift
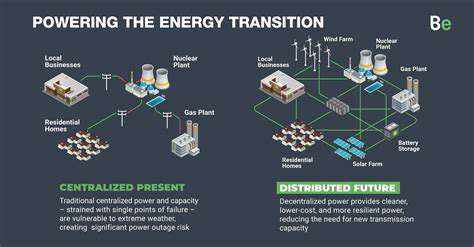
The traditional centralized energy model, reliant on large power plants and extensive transmission networks, is increasingly being challenged by decentralized energy systems. These distributed generation models, powered by renewable sources like solar and wind, offer a more resilient and sustainable approach to energy production. This shift promises a future where energy is generated closer to where it's consumed, reducing reliance on fragile infrastructure and promoting local control.
Centralized systems often suffer from vulnerabilities, such as grid failures, which can disrupt energy supply across vast geographic areas. Decentralized solutions, on the other hand, are better equipped to withstand these disruptions, ensuring greater energy reliability and security. This enhanced resilience is crucial in a world facing increasingly unpredictable weather patterns and heightened geopolitical tensions.
Renewable Energy Integration
Decentralized energy systems are intrinsically linked to the integration of renewable energy sources. By harnessing solar, wind, and other sustainable technologies, these systems can significantly reduce our dependence on fossil fuels and mitigate the detrimental effects of climate change. This transition is not just environmentally beneficial; it also fosters economic opportunities and job creation in renewable energy sectors.
The integration of renewable energy sources into decentralized systems also necessitates innovative energy storage solutions. These solutions are critical to ensuring a consistent and reliable energy supply, especially during periods of low renewable energy generation. The development and deployment of advanced battery technologies and other energy storage methods are essential to the success of this transition.
Community Energy Ownership
Decentralized energy systems foster a sense of community ownership and empowerment. Local communities can actively participate in the design, implementation, and management of their energy infrastructure, fostering a sense of responsibility and collective action. This approach promotes local control over energy resources and empowers communities to shape their energy future.
Economic Benefits and Job Creation
The transition to decentralized energy systems presents significant economic benefits. The creation of local energy generation facilities and related infrastructure can stimulate economic growth in communities, fostering job creation and entrepreneurial ventures. This localized economic development can be particularly beneficial in areas that have historically been underserved or marginalized.
Furthermore, the reduced reliance on centralized energy imports can lead to significant cost savings for communities and nations. This can lead to more stable energy prices, supporting local economies and improving citizens' quality of life. This is a positive feedback loop, creating a cycle of sustainable growth and prosperity.
Technological Advancements
The development of smaller, more efficient energy generation technologies, coupled with advancements in energy storage and grid management, are crucial for the successful implementation of decentralized energy systems. These advancements are paving the way for a more distributed and sustainable energy future. The evolution of smart grids and digital technologies is enabling more efficient energy distribution and management.
Grid Modernization and Resilience
Decentralized energy systems don't replace the existing grid; rather, they work in tandem with it, creating a more resilient and adaptable energy infrastructure. The modernization of the grid is essential to accommodate the integration of decentralized energy sources, ensuring seamless energy flow and grid stability. This modernization also enhances grid resilience to extreme weather events and other disruptions.
Environmental Sustainability
The shift to decentralized energy systems is a crucial step towards achieving environmental sustainability. By reducing reliance on fossil fuels and promoting renewable energy sources, these systems directly contribute to mitigating climate change and improving air quality. This transition is vital for preserving a healthy planet for future generations. The environmental benefits of decentralized energy systems are significant and far-reaching.
The Path Forward: Policy and Investment for a Resilient Future
Policy Frameworks for Decentralization
Effective policies are crucial for fostering a resilient future, particularly in the context of decentralization. These frameworks need to address the specific challenges and opportunities presented by decentralized systems. Such policies should encompass regulations that promote innovation and competition within the decentralized space, while also ensuring consumer protection and market integrity. This includes clear definitions of digital assets, robust legal frameworks for smart contracts, and measures to mitigate potential risks associated with decentralized finance (DeFi).
A critical component of these policies is establishing clear guidelines for data governance and privacy in decentralized systems. This will help to build trust and ensure that individuals' rights are protected in the digital landscape. Ultimately, robust policy frameworks will create a stable and predictable environment for decentralized technologies to flourish.
Investment Strategies for Decentralization
Strategic investment plays a vital role in driving the growth and adoption of decentralized technologies. Investors should focus on projects that demonstrate a strong potential for impact, innovation, and scalability. This involves identifying promising startups in the decentralized space, investing in research and development, and supporting the development of critical infrastructure.
Furthermore, investment strategies should consider the long-term vision for decentralization. Focus should be placed on supporting projects that align with the principles of sustainability and inclusivity, ensuring that the benefits of decentralization are widely shared. This includes supporting initiatives that promote financial inclusion and empower underserved communities.
Decentralized Infrastructure and its Importance
Decentralized infrastructure is fundamental to the long-term success and resilience of decentralized systems. This includes the development of robust and secure blockchain networks, the creation of interoperable platforms, and the improvement of decentralized storage solutions. Strong and scalable infrastructure is critical for supporting the growing number of users and applications built on decentralized platforms.
Incentivizing Participation in Decentralized Ecosystems
Motivating participation in decentralized ecosystems is essential for their sustainable development. This involves establishing incentives that reward contributions to the network, fostering collaboration among participants, and creating opportunities for individuals to benefit from the growth of these ecosystems. This can be achieved through various mechanisms, such as tokenized rewards, governance rights, and community-driven initiatives.
Addressing Security and Regulatory Concerns in Decentralized Systems
Security and regulatory concerns are inherent in the decentralized space. Robust security protocols are crucial for protecting users' assets and data from malicious actors. Continuous monitoring and proactive measures are necessary to mitigate security risks and enhance the overall resilience of these systems. Furthermore, clear and adaptable regulatory frameworks are needed to address the evolving nature of decentralized technologies and ensure responsible innovation.
The Role of Education and Awareness in Decentralization
Education and awareness campaigns are vital for fostering a deeper understanding of decentralized technologies and their potential benefits. Educating the public about the principles of decentralization, the risks and opportunities involved, and the different applications of these technologies is essential for widespread adoption. This includes providing accessible educational resources, engaging with diverse communities, and fostering dialogue to address misconceptions and promote a more informed public discourse about decentralization.