Energy Storage for Blackout Prevention
The Growing Need for Backup Power
The Escalating Frequency of Outages
The increasing frequency of power outages, whether due to extreme weather events, infrastructure failures, or grid instability, is a significant concern for both residential and commercial consumers. These disruptions can cause substantial financial losses, impacting businesses through lost productivity and customers, and causing significant inconvenience and stress for individuals. The need for reliable backup power solutions is becoming more apparent as the reliability of the main power grid comes under greater strain.
Proactive measures for preventing power outages are increasingly important as the frequency and duration of blackouts continue to rise, posing a threat to the delicate balance of modern life.
The Impact on Critical Infrastructure
Power outages can have a devastating impact on critical infrastructure, including hospitals, data centers, and emergency services. Maintaining operational efficiency and safety in these facilities during outages is paramount. The disruption caused by a prolonged power outage can have far-reaching consequences, impacting the health and well-being of countless individuals and jeopardizing the smooth functioning of essential services.
The Importance of Business Continuity
Businesses are increasingly recognizing the critical need for backup power solutions to maintain continuity of operations. Prolonged outages can result in significant losses, including lost revenue, damage to reputation, and disruption to supply chains. Implementing backup power solutions can help mitigate these risks and safeguard the financial well-being of businesses.
A robust backup power system ensures that a business can continue to operate uninterrupted, minimizing the negative impact of a power outage and maintaining productivity levels.
Technological Advancements in Energy Storage
Recent advancements in energy storage technologies, such as lithium-ion batteries and pumped hydro storage, have made backup power solutions more efficient and cost-effective. These innovations are crucial in meeting the growing demand for reliable and sustainable backup power options.
The development of more efficient and affordable energy storage technologies is paving the way for more robust and accessible backup power solutions.
Cost-Effectiveness of Backup Power Systems
While initial investment in backup power systems may seem substantial, the long-term cost-effectiveness of such systems is undeniable. The cost savings from preventing lost productivity, data loss, and potential damage to equipment often outweigh the upfront investment. A careful assessment of the financial implications of a power outage is essential in determining the viability and cost-effectiveness of implementing a backup power solution.
Environmental Considerations
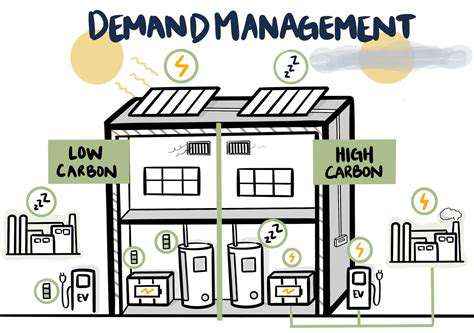
As concerns about environmental sustainability grow, the selection of backup power solutions should also consider their environmental impact. Renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, can be integrated into backup systems to minimize the reliance on fossil fuels and reduce the carbon footprint.
Consumer Awareness and Preparedness
Consumer awareness regarding the importance of backup power solutions is crucial in ensuring preparedness for potential outages. Educating consumers about the various options available, including generator installations and battery backups, empowers them to make informed decisions about protecting their homes and businesses. Individuals and households can take proactive steps to mitigate the risks and challenges posed by power outages.
Exploring Diverse Energy Storage Technologies
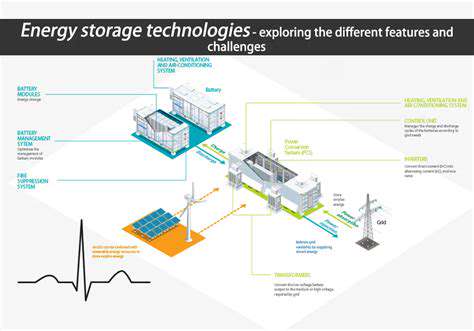
Harnessing the Potential of Batteries
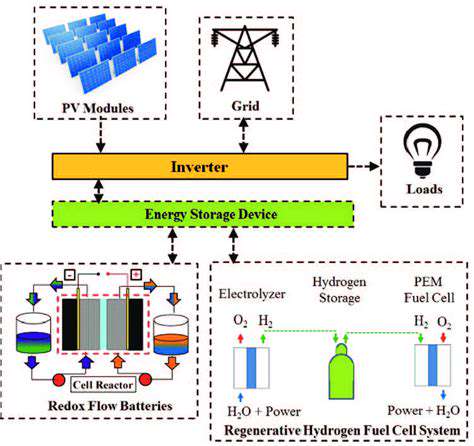
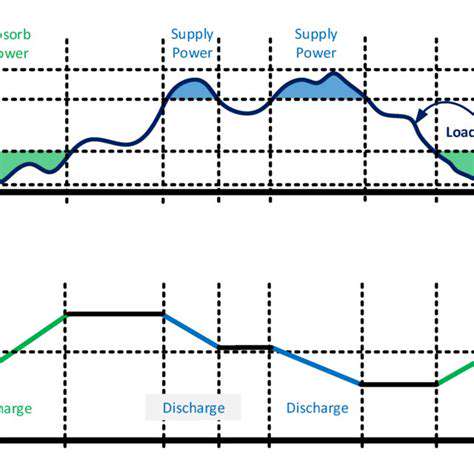
Battery technology is rapidly evolving, offering a crucial solution for storing energy generated from renewable sources like solar and wind. Advancements in battery chemistry, particularly lithium-ion batteries, have significantly improved their energy density and lifespan, making them a viable option for large-scale energy storage. Furthermore, ongoing research into solid-state batteries promises to further enhance safety and performance, potentially paving the way for even more efficient and reliable energy storage systems. This progress is critical for integrating intermittent renewable energy sources into the grid, ensuring a stable and sustainable energy supply.
Different types of batteries, each with unique characteristics, cater to various energy storage needs. Lithium-ion batteries, while dominant in the market, face limitations regarding cost and environmental impact. Alternative battery chemistries, such as sodium-ion and flow batteries, are being actively explored to address these concerns. These alternatives offer promising potential for cost reduction and improved sustainability, though further research and development are necessary to fully realize their advantages. The ongoing quest for optimal battery technology is essential for the global transition to a cleaner energy future.
Exploring Alternative Energy Storage Methods
Beyond batteries, a diverse range of energy storage technologies are under investigation. Compressed air energy storage (CAES) utilizes the compression and expansion of air to store energy, offering a large-scale solution for storing excess renewable energy. This method has the potential to address the intermittency of renewable energy sources effectively, providing a reliable energy supply. However, large-scale CAES implementation requires significant infrastructure investment and careful consideration of environmental impacts.
Another promising approach is pumped hydro storage, which leverages the elevation difference between two water bodies to store potential energy. This established technology offers high efficiency and long-duration energy storage, making it a valuable component of a renewable energy system. While geographically constrained, pumped hydro remains a crucial option for balancing energy supply and demand, particularly in regions with suitable topographical features.
Further advancements in thermal energy storage, such as molten salt storage, are also gaining traction. These technologies offer high energy density and long storage durations, suitable for various applications, including concentrated solar power. Harnessing these diverse storage methods is critical for enabling the widespread adoption of renewable energy sources and achieving a sustainable energy future. The ongoing research and development in these areas are vital to unlock the full potential of clean energy and create a more resilient and sustainable energy system.