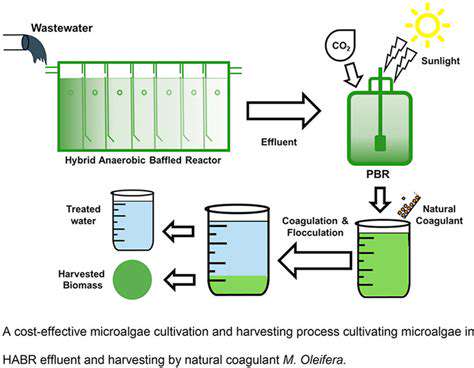
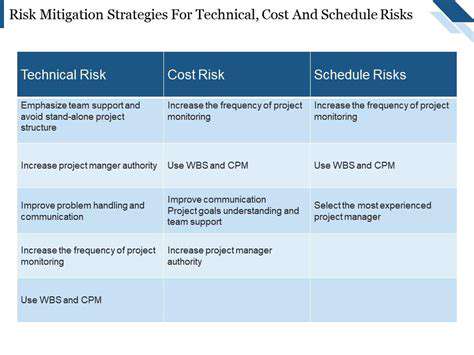
Geothermal Energy: An Underestimated Renewable Energy Source
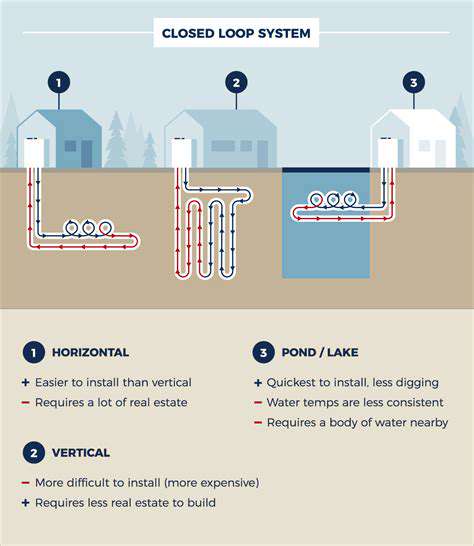
Geological Processes Shaping the Earth
Understanding the Earth's dynamic processes provides crucial insights into our planet's evolution. The gradual movement of tectonic plates and the sudden bursts of volcanic activity continuously reshape mountains, valleys, and ocean basins. These powerful forces demonstrate nature's ability to create and destroy landscapes over geological timescales. Erosion, weathering, and sedimentation work in concert to recycle Earth's materials through an endless cycle of rock transformation.
These geological interactions remain highly dynamic, influencing everything from soil formation to natural disaster patterns. By studying these processes, scientists gain valuable knowledge for predicting earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. The visible evidence in our landscapes offers tangible proof of Earth's incredible transformative power throughout history.
Types of Rocks: Igneous, Sedimentary, and Metamorphic
Earth's crust consists of three primary rock types, each with distinct formation processes. Igneous rocks originate from cooled magma or lava, with textures ranging from the glassy smoothness of obsidian to the coarse grains of granite. Their composition varies dramatically depending on cooling rates and mineral content.
Sedimentary layers accumulate from compressed organic materials and mineral particles, often preserving ancient fossils within their strata. Metamorphic formations undergo complete mineral reorganization under extreme heat and pressure, creating entirely new rock characteristics while maintaining some original features.
Plate Tectonics: The Driving Force Behind Geological Activity
The lithosphere's massive plates move continuously, creating geological activity at their boundaries. These interactions generate Earth's most dramatic surface features, from the Himalayan peaks to deep ocean trenches. The theory explains continental drift over eons, showing how landmasses have separated and collided throughout Earth's history.
This dynamic system produces both constructive and destructive forces that reshape our planet's surface. Understanding these mechanisms proves essential for predicting seismic risks and volcanic activity in vulnerable regions.
Earthquakes and Volcanoes: Natural Hazards and Their Impact
Sudden crustal movements release tremendous energy as earthquakes, while volcanoes discharge molten rock and gases from Earth's interior. Both phenomena can devastate communities and alter landscapes within moments. Comprehensive monitoring systems and hazard preparedness plans remain our best defense against these unpredictable natural events.
Advanced warning technologies and proper land-use zoning help minimize risks to populated areas. These powerful geological events clearly demonstrate our planet's dynamic nature and the need for continued scientific study.
Mineral Resources and Their Importance
Modern civilization relies heavily on mineral extraction for construction, technology, and manufacturing. These finite resources require careful management to balance economic needs with environmental preservation. Sustainable mining practices and responsible resource allocation have become increasingly critical in our resource-dependent world.
Identifying new deposits and improving extraction efficiency helps meet growing demand while reducing ecological impacts. Proper stewardship ensures these essential materials remain available for future technological and infrastructural development.
The Economic Impact and Global Adoption
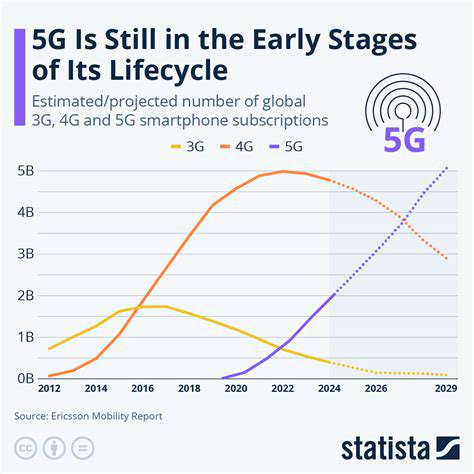
The Global Phenomenon
Technological innovation has transformed global markets, creating new economic paradigms across industries. This revolution challenges traditional business models while generating unprecedented opportunities for adaptable organizations. Workforce requirements continue evolving, emphasizing digital literacy and specialized technical skills.
Global connectivity now enables immediate international commerce and information exchange. This digital integration reshapes consumer expectations and enables businesses to operate without geographical constraints.
Economic Drivers and Challenges
Improved efficiency and reduced operational costs drive widespread technological adoption. As implementation expenses decrease, more organizations can participate in the digital economy. While this increased competition benefits consumers, companies face pressure to continuously innovate or risk obsolescence.
Automation presents workforce challenges requiring comprehensive retraining initiatives. Addressing the digital divide remains crucial for ensuring equitable economic participation across all regions and demographics.
Long-Term Implications and Future Outlook
Technology's pervasive influence will continue reshaping every economic sector, from healthcare delivery to financial systems. Managing this transformation requires balanced policies that encourage innovation while protecting social stability.
Future economic success will depend on adaptability, with organizations prioritizing continuous learning and technological integration. Sustainable growth strategies must address both immediate opportunities and long-term societal impacts.