Global Supergrids and Intercontinental Renewable Energy Transmission
Enhancing Energy Security and Reliability
Intercontinental grids dramatically strengthen energy security. Diversifying supply sources across regions creates unprecedented system stability. When one area faces disruptions, others can instantly compensate, reducing vulnerability to local outages or geopolitical tensions. This interconnectedness promises more dependable energy access worldwide.
Moving beyond centralized plants in specific regions significantly bolsters system-wide reliability. A global network dynamically adapts to shifting demand across time zones and weather patterns, ensuring steady power flow and preventing large-scale blackouts.
Unlocking Renewable Energy's Potential
Supergrids maximize renewable energy utilization. By connecting resource-rich areas with high-demand zones, we fully harness clean power potential. This shift from fossil fuels substantially cuts greenhouse emissions, combating climate change effectively.
Economic and Societal Benefits
Supergrid implementation drives economic growth, spurring tech innovation and energy sector employment. Efficient renewable distribution could lower global energy costs while boosting economies in resource-abundant regions. The system also expands energy access to underserved communities worldwide.
Beyond economics, supergrids foster international collaboration. Cross-border partnerships accelerate development of advanced technologies, hastening our transition to sustainable energy globally.
Overcoming Transmission Limitations
Improving Transmission Infrastructure
Modernizing transmission networks is fundamental for efficient long-distance renewable energy transfer. Upgrades include higher-capacity conductors, smart grid tech for real-time control, and strategic new corridors. Robust infrastructure investment ensures reliable delivery, offsetting renewable intermittency issues.
Developing Advanced Transmission Technologies
HVDC system breakthroughs are vital for overcoming distance limitations. These systems excel in minimizing power loss across vast spans, making them ideal for renewable transmission. Emerging tech like superconducting cables could revolutionize capacity and efficiency further.
Optimizing Grid Management Systems
Sophisticated grid management is crucial for renewable integration. Systems requiring real-time analytics, predictive modeling, and automated control ensure optimal power flow and minimal losses. Such capabilities also accommodate renewable variability, enhancing supply stability.
Addressing Geographic Challenges
Terrain obstacles demand innovative solutions. Mountainous regions may need specialized tech, while urban areas could utilize underground lines. Tailored approaches considering environmental and social factors are essential for successful implementation.
Enhancing Energy Storage Solutions
Storage integration helps balance renewable intermittency. Large-scale batteries and pumped hydro can store surplus energy during peak production for later use, stabilizing grid supply.
Facilitating Cross-Border Cooperation
International collaboration is paramount for intercontinental projects. Harmonizing standards, joint infrastructure development, and clear energy trade agreements overcome political and regulatory barriers, unlocking global renewable potential.
Promoting Public Awareness and Acceptance
Community support is vital for project success. Transparent engagement and education about benefits - job creation, economic growth, environmental protection - build essential public backing.
The Role of Renewable Energy Sources
Harnessing Solar Power for Global Grids
Solar energy's decentralized nature makes it ideal for supergrids. Strategically located farms capture sunlight across time zones, providing continuous clean energy. When paired with storage solutions, this model reliably integrates solar into global networks.
Wind Power's Contribution to Intercontinental Energy Flow
Wind farms in high-wind regions generate substantial electricity. Cross-continent transmission balances supply and demand across different time zones and weather patterns.
Hydropower's Crucial Role in Energy Storage
Hydropower dams serve as natural batteries. They regulate electricity flow and smooth renewable intermittency, providing grid stability through controlled water release.
Geothermal Energy's Steady Flow for Baseload Power
Geothermal offers reliable baseline generation. Its constant output complements intermittent renewables, maintaining grid stability during low solar/wind periods.
Biomass Energy's Potential for Sustainable Energy Mix
Sustainably managed biomass diversifies the energy portfolio. It provides alternatives in regions with limited solar/wind resources, reducing fossil fuel reliance when properly implemented.
Energy Storage Technologies: The Critical Link in Renewable Integration
Advanced storage is indispensable for renewable grids. Batteries and pumped hydro store excess energy during peak production for later use, ensuring consistent supply.
Policy and Infrastructure: Enabling Global Energy Cooperation
Successful supergrids require international coordination. Standardized protocols, cross-border agreements, and infrastructure investment are essential for seamless global renewable integration.
Infrastructure Development and Investment
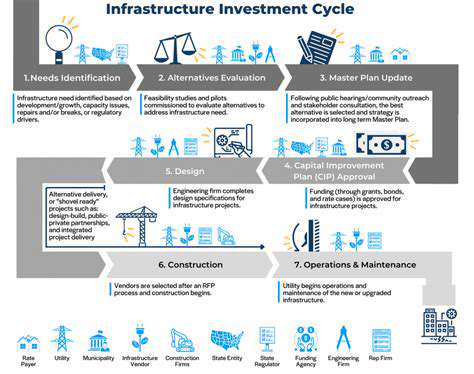
Infrastructure Development and Investment Strategies
Infrastructure underpins economic and social progress. Strategic investments yield long-term dividends through enhanced productivity, job creation, and improved living standards. Careful planning ensures maximum benefit and sustainability.
Prioritizing Critical Infrastructure
Identifying key projects is essential. Assessing current systems and potential impacts guides effective prioritization, with focus on transportation, communications, and energy networks for economic stability.
Public-Private Partnerships
PPPs effectively combine sector strengths. These collaborations bring efficiency, innovation, and risk-sharing to infrastructure projects, often yielding more sustainable outcomes.
Financing Infrastructure Projects
Creative funding solutions are crucial. Exploring bonds, loans, grants, and alternative sources ensures adequate capital for vital projects.
Project Management and Implementation
Meticulous execution drives success. Clear planning, stakeholder engagement, and budget adherence maximize investment returns, with monitoring ensuring goal alignment.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
Green infrastructure is non-negotiable. Projects must minimize ecological impact through sustainable materials and energy-efficient designs, ensuring long-term environmental stewardship.
Community Engagement and Impact Assessment
Projects profoundly affect localities. Comprehensive engagement and impact studies address community concerns, ensuring broad benefits and conflict mitigation.
Potential Benefits and Challenges
Enhanced Productivity and Efficiency
Streamlined operations and advanced tech boost output significantly. Automating routine tasks frees staff for strategic work, improving turnaround times and overall performance. Collaboration tools further enhance coordination, directly benefiting profitability.
Improved Decision-Making
Data analytics enable smarter choices. Insights inform strategy adjustments and resource allocation, leading to better outcomes.
Increased Innovation and Creativity
Supportive environments spark ingenuity. Empowered employees generate breakthrough solutions, driving competitive advantage through novel products and processes.
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
Efficient systems improve experiences. Quick, personalized service boosts loyalty and generates positive referrals.
Reduced Operational Costs
Process optimization saves substantially. Automation and supply chain improvements lower expenses, freeing funds for growth initiatives.
Potential for Job Displacement
Technological shifts require adaptation. Retraining programs help workers transition to evolving job markets.
Maintaining Competitive Advantage
Continuous adaptation is essential. Companies embracing innovation and skill development stay ahead in dynamic markets, while laggards risk obsolescence.