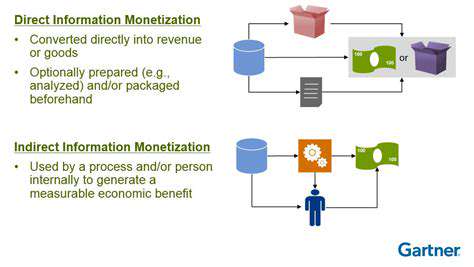
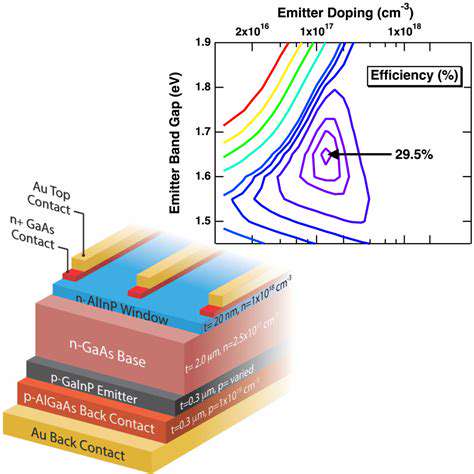
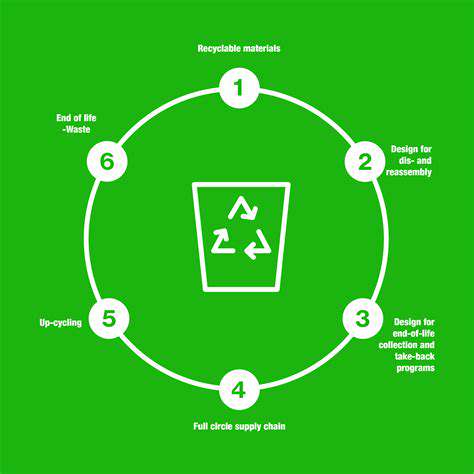
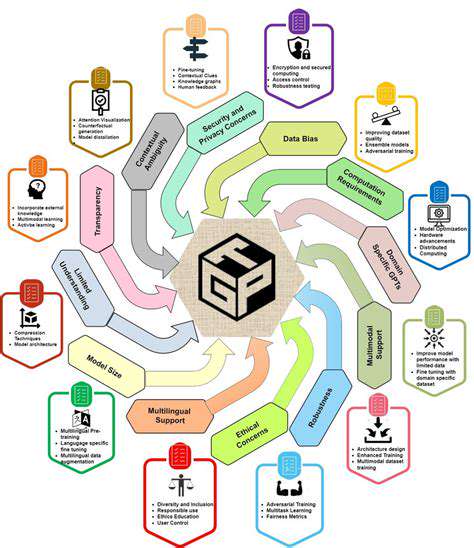
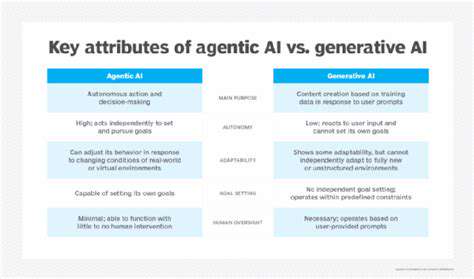
Innovation Driven by Decentralization of Energy Generation: New Business Models
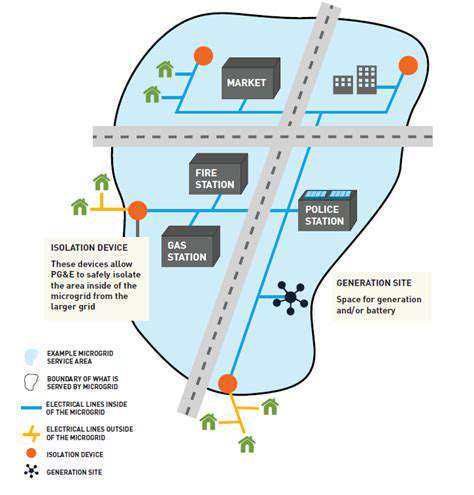
Community Microgrids: A Decentralized Approach
Community microgrids represent a significant shift in the way we generate and distribute electricity. Instead of relying solely on a centralized grid, these systems utilize distributed generation sources, often renewable, within a specific geographic area. This decentralized approach offers a multitude of benefits, particularly in areas with unreliable or inadequate access to the traditional grid.
This distributed model allows for greater resilience and stability during grid outages, providing a more reliable power source for communities. It also fosters local control and ownership over energy resources, potentially leading to significant cost savings and increased community engagement.
Renewable Energy Integration
A key strength of community microgrids lies in their ability to seamlessly integrate renewable energy sources. Solar panels, wind turbines, and even small-scale hydroelectric plants can contribute to the microgrid's power output, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering carbon emissions. This integration is crucial for achieving sustainability goals and creating a more environmentally conscious energy system.
Enhanced Reliability and Resilience
In areas with frequent or prolonged grid outages, microgrids provide a vital lifeline, ensuring continued power supply for essential services like hospitals, schools, and communication networks. This enhanced resilience is particularly important in disaster-prone regions, where a robust, decentralized energy system can help communities recover and rebuild more quickly. The local generation aspect of microgrids means less dependence on the larger grid.
Economic Benefits and Community Engagement
Community microgrids can stimulate local economies by creating jobs in installation, maintenance, and operation. These projects also foster greater community engagement, empowering residents to participate in the decision-making processes surrounding energy production and consumption. This can lead to a stronger sense of community ownership and responsibility regarding energy resources.
Technological Advancements and Cost-Effectiveness
Advancements in energy storage technologies, like batteries and pumped hydro, are making community microgrids more cost-effective and reliable. These advancements allow microgrids to store excess energy generated during peak production periods, ensuring a consistent supply throughout the day and evening. This also improves the overall cost-effectiveness of the system.
Addressing Grid Infrastructure Challenges
In remote or underserved areas, traditional grid infrastructure may be absent or unreliable. Community microgrids offer a viable solution to these challenges by providing a decentralized and localized power source. This is particularly beneficial in areas with limited access to the national grid, as it brings electricity to where it is needed most. This can lead to significant improvements in quality of life for residents.
The Role of Technology in Enabling Decentralization
The Foundation of Decentralization
Technology plays a pivotal role in enabling decentralization by providing the infrastructure and tools necessary to distribute power and control away from centralized entities. This foundational aspect encompasses the development of robust and secure platforms that allow for the independent operation of various components within a system. Decentralized systems, by their very nature, necessitate a shift from a top-down hierarchy to a more distributed and interconnected model, and technology is the key enabler in achieving this transition. This fundamental shift is crucial for fostering innovation and empowering individuals by removing reliance on a single point of failure or a centralized authority.
Crucially, this technology must also ensure data integrity and security, which are paramount in maintaining trust and confidence within the decentralized system. Robust cryptographic methods and consensus mechanisms are essential to prevent manipulation and ensure the authenticity of data and transactions. Without this foundational layer of technological security, decentralization efforts are vulnerable and ultimately unsustainable.
Blockchain Technology: A Cornerstone of Decentralization
Blockchain technology stands out as a primary driver of decentralization. Its immutable and transparent ledger system allows for secure and verifiable transactions without intermediaries. This characteristic is crucial for eliminating the need for centralized authorities in various applications, from finance and supply chain management to voting systems and identity management. The decentralized nature of blockchain fosters trust and accountability by allowing all participants to view and verify transactions, ensuring transparency throughout the system.
The cryptographic security inherent in blockchain technology is a key component in enabling secure and trustless transactions. This security is essential for building decentralized applications (dApps) that can operate without relying on central servers or authorities. The ability to create and execute smart contracts on a blockchain further enhances the potential of decentralized systems.
Decentralized Applications (dApps) and their Impact
Decentralized applications (dApps) are software applications that leverage blockchain technology to operate in a decentralized manner. They represent a significant advancement in the application of decentralized principles, allowing for a more democratic and transparent approach to various services, from social media platforms to financial instruments. The potential for dApps to disrupt existing centralized models and empower users is substantial.
The Role of Cryptocurrencies in Decentralization
Cryptocurrencies play a critical role in facilitating decentralized transactions and operations. Their decentralized nature, based on blockchain technology, allows for peer-to-peer transactions without the need for intermediaries. Cryptocurrencies enable a new paradigm of financial transactions, empowering individuals and fostering financial inclusion in previously underserved communities. The ability to send and receive cryptocurrencies directly between parties without relying on traditional financial institutions is a key component of the decentralization process.
Emerging Technologies and the Future of Decentralization
Beyond blockchain, several emerging technologies are poised to further advance the decentralization movement. These include decentralized storage solutions, like IPFS, which provide a more distributed and resilient approach to data storage, and decentralized social media platforms, which aim to provide greater user control and privacy. These advancements signify a shift towards a more distributed and autonomous digital landscape, fostering innovation and empowering users in unprecedented ways. The integration of these emerging technologies with existing decentralized structures will determine the future of decentralization.
The continued advancement and integration of these technologies will undoubtedly shape the future of decentralization, paving the way for a more inclusive and innovative digital ecosystem.