The Integration of Renewable Energy with Agriculture
Transitioning to solar-powered farm machinery is a crucial step towards a more sustainable agricultural future. Tractors, harvesters, and other essential equipment can be equipped with solar panels, leading to decreased fuel consumption and reduced emissions. This not only benefits the environment but also translates into significant cost savings for farmers in the long run, as fuel prices continue to fluctuate.
Solar-powered machinery can also improve operational efficiency. The consistent energy supply from solar panels ensures reliable performance of farm machinery, minimizing downtime and maximizing productivity. This leads to increased output while reducing the environmental impact of traditional fossil fuel-powered equipment.
Economic Benefits of Solar Integration
Implementing solar power solutions for irrigation and farm machinery offers substantial economic advantages. Reduced reliance on external energy sources can lead to significant savings on fuel costs, potentially offsetting the initial investment in solar equipment over time. Furthermore, the potential for government incentives and tax credits can further enhance the economic viability of solar integration for agricultural operations.
The increased efficiency and reliability of solar-powered systems can also translate into improved crop yields and reduced water waste, leading to higher profitability for farmers. These factors combined create a compelling case for adopting solar power as a central component of modern agricultural practices.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Solar power significantly reduces the environmental impact of agriculture. By replacing fossil fuels with clean solar energy, farmers contribute to a cleaner environment by lowering greenhouse gas emissions and minimizing air pollution. This shift towards renewable energy aligns with global efforts to combat climate change and protect the planet's natural resources.
The sustainable nature of solar power extends beyond energy production. Reduced water usage, optimized resource management, and minimized reliance on external inputs contribute to a more sustainable agricultural ecosystem. These practices foster a harmonious relationship between agricultural production and environmental preservation.
Technological Advancements and Innovation
Continuous technological advancements are driving the evolution of solar power solutions for irrigation and farm machinery. Improved solar panel efficiency, battery storage technology, and smart grid integration are making solar power more accessible and cost-effective for agricultural applications. This innovation ensures that solar power becomes increasingly integrated into the agricultural sector.
The development of sophisticated control systems and data analytics further enhance the efficiency and precision of solar-powered irrigation and machinery. This allows for optimized energy usage, precise water management, and improved overall farm productivity.
Addressing Challenges and Considerations
While solar power offers numerous benefits, some challenges need careful consideration. Factors such as fluctuating sunlight intensity, geographical location, and initial investment costs can influence the feasibility of solar integration. However, various financial incentives and government support programs can mitigate these challenges and make solar power more accessible to farmers.
Careful planning and detailed assessments of specific farm requirements are essential for optimizing the effectiveness of solar power solutions. This includes considering factors such as energy demand, available space, and local weather patterns to ensure the most efficient and cost-effective implementation.
AI-powered personalized learning paths are revolutionizing education by tailoring educational experiences to individual student needs and learning styles. This approach recognizes that students learn at different paces and possess diverse strengths and weaknesses, and it aims to optimize the learning journey for each individual. By leveraging data analytics and machine learning algorithms, these platforms can identify knowledge gaps, pinpoint areas where students excel, and adapt the curriculum dynamically to meet those specific needs. This dynamic adaptation ensures that students receive the right support at the right time, fostering a more effective and engaging learning experience.
Beyond Power: Utilizing Renewable Energy for Enhanced Efficiency

Harnessing Solar Energy
Solar energy, derived from the sun's radiant power, is a remarkably abundant and sustainable resource. Harnessing its potential is crucial for reducing reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating climate change. Photovoltaic (PV) panels convert sunlight directly into electricity, while solar thermal systems use sunlight to heat water or produce steam for various applications. This clean energy source has the potential to revolutionize our energy infrastructure and provide power to communities in remote areas.
The technology behind solar energy is constantly evolving, with advancements in panel efficiency and cost-effectiveness making it increasingly competitive with traditional energy sources. Furthermore, the integration of solar energy into existing power grids is becoming more sophisticated, enabling efficient energy storage and management.
Wind Power's Steady Growth
Wind power, another significant renewable energy source, is driven by the kinetic energy of moving air. Wind turbines, strategically positioned in areas with consistent wind patterns, capture this energy and convert it into electricity. This technology has proven its ability to generate substantial amounts of clean energy, reducing our dependence on volatile fossil fuel prices. The advancements in turbine design and wind farm management have led to greater efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
The construction and maintenance of wind farms can present challenges, including potential environmental impacts and concerns about visual aesthetics. However, careful planning and mitigation strategies can minimize these impacts and ensure that these projects are undertaken responsibly.
Hydropower: A Timeless Power Source
Hydropower harnesses the energy of flowing water, utilizing the force of rivers and streams to generate electricity. This ancient method of energy production has been refined over centuries, and remains a significant contributor to renewable energy sources globally. Hydropower plants can offer reliable and consistent power generation, making them valuable components of diversified energy portfolios. Dams, strategically located to capture the natural flow of water, play a critical role in this process.
The environmental impact of hydropower projects is a complex issue, with concerns about dam construction affecting natural ecosystems and river flows. However, modern designs and environmental assessments aim to minimize these impacts and ensure sustainable water management practices.
Geothermal Energy: Harnessing Earth's Heat
Geothermal energy taps into the Earth's internal heat, utilizing steam or hot water from deep beneath the surface to generate electricity. This renewable energy source is abundant in certain geographic regions, and the technology needed to harness it is constantly improving. Geothermal power plants can provide a reliable and continuous source of energy, offering a significant advantage over other intermittent renewable sources like solar and wind.
Although geothermal energy has a lower environmental impact compared to fossil fuels, careful consideration of potential impacts on local geology and groundwater resources is crucial for sustainable development.
Biomass Energy: Turning Waste into Power
Biomass energy utilizes organic matter, such as wood, agricultural residues, and municipal waste, to produce energy. This versatile renewable energy source can convert organic waste materials into usable energy, reducing landfill waste and promoting a circular economy. Biomass energy has the potential to replace fossil fuels in various sectors, including heating and transportation.
The sustainability of biomass energy depends on responsible sourcing and management practices. Careful consideration of the environmental impact of harvesting and processing biomass materials is needed to ensure that this energy source is truly sustainable and environmentally friendly.
Challenges and Future Prospects for Renewable Energy in Agriculture
Energy Efficiency in Agricultural Practices
Improving the energy efficiency of agricultural practices is crucial for the widespread adoption of renewable energy. This includes optimizing irrigation systems, using precision farming techniques to minimize fertilizer and pesticide use, and adopting sustainable tillage methods. These strategies not only reduce reliance on fossil fuels but also contribute to enhanced soil health and reduced environmental impact, ultimately lowering the overall operational costs for farmers.
A significant portion of agricultural energy consumption is tied to machinery operations. Transitioning to electric or hybrid tractors and other equipment, while still facing some challenges in terms of battery technology and infrastructure, is a key step towards higher energy efficiency and reduced emissions from farm operations.
The Intermittency of Renewable Energy Sources
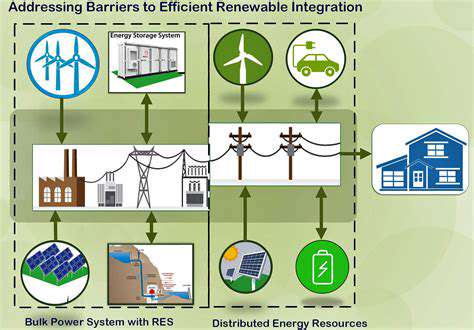
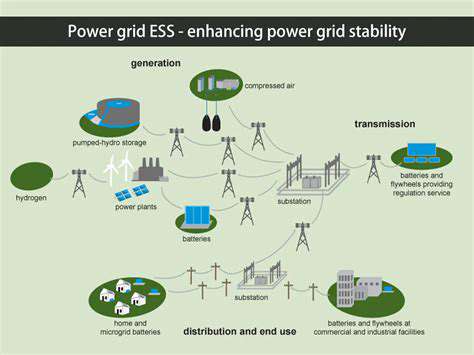
A major hurdle to widespread adoption of renewable energy in agriculture is the intermittent nature of sources like solar and wind power. Storing energy generated during peak production periods for use during periods of low generation is essential for a reliable energy supply. Innovative energy storage solutions, such as large-scale battery banks, pumped hydro storage, or even agricultural biomass storage, are critical to overcome this challenge.
Economic Viability and Financial Incentives
The upfront costs associated with installing renewable energy systems can be a significant barrier for many agricultural businesses. Financial incentives, such as government subsidies, tax credits, and loan programs, are essential to make these investments more attractive and accessible. These incentives can help bridge the gap between the initial investment and the long-term economic benefits of renewable energy adoption.
Furthermore, the long-term cost savings associated with reduced fuel expenses and potentially lower operating costs must be highlighted to support the economic viability of renewable energy solutions for farmers.
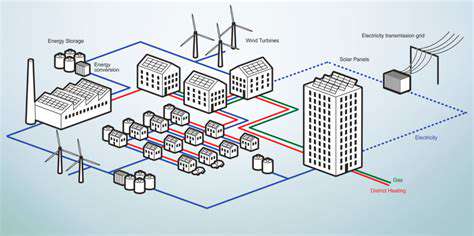
Grid Integration and Infrastructure
Integrating renewable energy sources into existing agricultural electricity grids often requires significant infrastructure upgrades. This includes the development of smart grids, improved transmission lines, and enhanced grid management systems to accommodate the variable nature of renewable energy generation. Addressing these infrastructure needs is crucial for reliable and efficient energy delivery to farm operations.
Technological Advancements and Innovations
Continuous advancements in renewable energy technologies, such as solar panel efficiency and battery storage capacity, are paving the way for more cost-effective and reliable solutions for agriculture. Research and development focused on tailoring these technologies to the specific needs of agricultural operations are crucial for optimizing performance and reducing costs in real-world applications. This could include specialized solar panel designs for agricultural environments or improved battery storage systems that can withstand the rigors of farm settings.
Land Use and Environmental Impact
The potential environmental impact of renewable energy infrastructure needs careful consideration. Careful site selection for solar farms and wind turbines, as well as minimizing the impact on valuable agricultural land, are crucial. It's essential to balance the need for renewable energy with the importance of maintaining productive agricultural lands and preserving biodiversity.
Public Awareness and Education
Farmers need access to comprehensive information and educational resources to understand the benefits and challenges of adopting renewable energy in their operations. Public awareness campaigns that highlight the economic, environmental, and social advantages of renewable energy can help to foster wider acceptance and adoption among the agricultural community. Educational programs should also focus on practical implementation strategies and address the specific technical and financial considerations for farmers.