Investment in Floating Offshore Wind: Future Growth
Successful implementation requires careful assessment of site-specific conditions including wave heights, wind patterns, and seabed geology. Advanced mooring systems must account for the dynamic forces acting on floating structures, which differ significantly from fixed installations. Engineers use sophisticated computer modeling to predict how platforms will behave under various weather scenarios.
Corrosion resistance presents another critical challenge. The marine environment demands specialized materials and coatings to prevent degradation from saltwater exposure. Regular maintenance protocols must account for the increased difficulty of accessing equipment that's constantly in motion on the ocean's surface.
The development of purpose-built installation vessels represents a key enabling technology for scaling up floating wind projects. Traditional jack-up vessels used for fixed turbines can't service floating installations, creating both a challenge and opportunity for maritime industries.
Market Expansion and Investment Potential

Industry Trends and Growth Drivers
The global floating wind sector is experiencing remarkable growth, with projections suggesting capacity could increase fortyfold by 2030. This rapid expansion is fueled by several factors including technological advancements, policy support, and the urgent need for clean energy solutions. Countries with limited shallow coastal waters view floating technology as their primary pathway to developing offshore wind resources.
Cost reduction remains a central focus throughout the industry. While floating wind currently carries a cost premium compared to fixed-bottom projects, experts anticipate significant cost declines as the technology matures. The learning curve effect, combined with economies of scale and technological improvements, could bring costs down by 40-50% this decade.
Strategic Investment Approaches
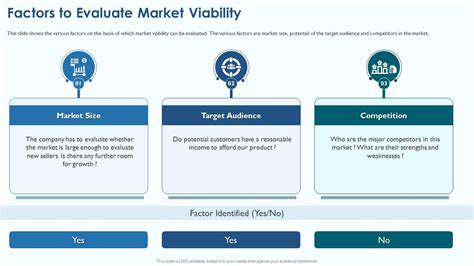
Investors exploring this sector should consider several promising avenues. Direct investment in floating wind project developers offers exposure to the technology's growth trajectory. Alternatively, component manufacturers specializing in floating-specific equipment like dynamic cables or advanced mooring systems represent another attractive option. Supporting industries such as port infrastructure development and specialized marine services also present compelling opportunities.
Geographic diversification can mitigate risk, as different regions progress at varying speeds with floating wind adoption. Early-stage investments in technology innovators working on next-generation platforms or installation methods may yield substantial returns for patient capital.
Policy Framework and Regulatory Considerations
Government support mechanisms significantly influence project economics. Many countries have implemented targeted auction systems specifically for floating wind projects. Understanding the nuances of different national regulatory environments is crucial for assessing project viability. Policies addressing grid connection responsibilities, permitting timelines, and maritime spatial planning can dramatically impact development timelines and costs.
International collaboration is accelerating technology transfer and best practice sharing. The North Sea countries have established a particularly robust cooperation framework, while emerging markets in Asia and North America are developing their own approaches tailored to local conditions.
Environmental Benefits and Sustainability Impact
Beyond electricity generation, floating wind farms offer several environmental advantages. Their placement further offshore reduces potential conflicts with coastal ecosystems and bird migration routes. The technology enables countries to dramatically increase renewable energy production without competing for scarce terrestrial land resources. Life cycle analyses indicate floating wind has one of the lowest carbon footprints among electricity generation technologies.
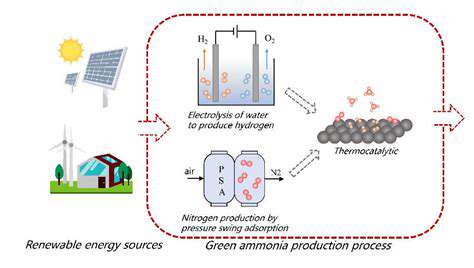
Emerging applications like offshore hydrogen production could further enhance the environmental benefits. Some projects now integrate electrolyzers directly onto floating platforms, creating green hydrogen without the need for electricity transmission to shore. This innovation could address energy storage challenges while opening new markets for floating wind technology.