Offshore Wind and the Blue Economy
Offshore wind farms, far from being just energy producers, are increasingly recognized as crucial components of a thriving blue economy. The construction and operation of these massive structures create substantial employment opportunities, from engineering and installation to maintenance and monitoring. These jobs extend beyond the immediate project site, fostering a ripple effect throughout local communities, supporting related industries like shipbuilding, and creating a demand for specialized equipment and services. This economic boost, coupled with the reduction in carbon emissions, positions offshore wind as a key driver of sustainable development within the blue economy framework.
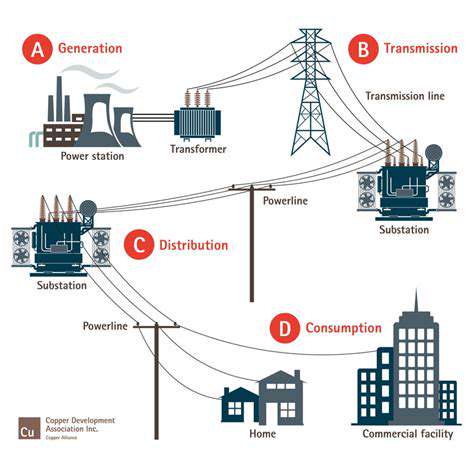
Beyond direct employment, the infrastructure built for offshore wind farms can serve multiple purposes. For instance, the extensive cabling and communication networks required for these projects can be adapted for other marine applications, such as underwater communication or data transmission. This adaptability allows for a more comprehensive and integrated approach to utilizing the marine environment, further bolstering the blue economy's potential.
Harnessing Marine Resources for Energy Production
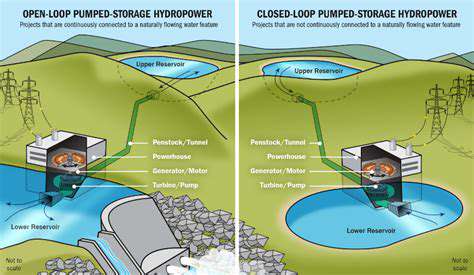
The blue economy isn't just about wind; it encompasses a diverse array of marine resources and their potential for energy generation. Exploring and developing innovative technologies for harnessing wave energy, tidal currents, and ocean thermal energy conversion (OTEC) systems are vital steps in expanding the scope of sustainable energy sources. These technologies, while still in various stages of development and refinement, hold immense promise for reducing reliance on fossil fuels and diversifying the energy mix.
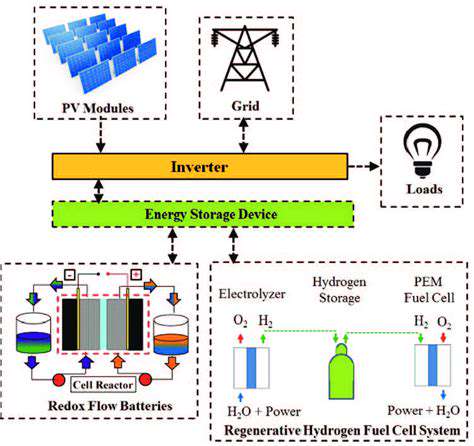
Innovative research and development are crucial to maximizing the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of these alternative marine energy sources. Technological advancements in materials science, energy storage, and data analysis are essential to overcoming the challenges associated with harnessing these resources. The integration of these technologies with existing infrastructure and the development of robust supply chains are essential to ensuring their successful implementation.
Sustainable Practices and Environmental Considerations
The development of the blue economy, including offshore wind projects, necessitates a strong emphasis on sustainable practices and environmental considerations. Minimizing the environmental impact of these large-scale operations is paramount, requiring careful site selection, mitigation strategies for marine ecosystems, and adherence to strict environmental regulations. The use of sustainable materials in construction, the implementation of noise reduction technologies, and the development of effective monitoring systems are all critical elements of achieving a harmonious coexistence between energy production and the marine environment.
Careful consideration must be given to the potential impacts on marine life, including migratory patterns, habitat disruption, and noise pollution. Addressing these concerns through proactive research, robust environmental impact assessments, and ongoing monitoring programs is essential to ensuring that the blue economy's growth doesn't come at the expense of the delicate ecosystems it relies upon. Furthermore, the adoption of circular economy principles throughout the lifecycle of these projects is key to maximizing resource utilization and minimizing waste.
Careful consideration of potential conflicts between energy development and other marine activities, like fishing and tourism, is equally critical. Finding ways to balance these competing interests through careful planning and stakeholder engagement is essential to ensure the long-term sustainability and inclusivity of the blue economy.