Policy Approaches to Enhance Grid Flexibility
The Crucial Need for a Comprehensive Strategy
A robust and well-defined strategy is essential for navigating the complexities of the modern world. Without a clear plan of action, organizations and individuals alike risk becoming lost in a sea of possibilities, failing to achieve their objectives. A comprehensive strategy provides a framework for decision-making, resource allocation, and achieving desired outcomes. This framework offers a roadmap for navigating challenges and capitalizing on opportunities.
Defining the Scope and Objectives
Before embarking on the implementation of any strategy, it's crucial to clearly define the scope and objectives. This involves identifying the specific goals to be achieved and the boundaries within which the strategy will operate. A well-defined scope ensures that efforts are focused and resources are allocated effectively. Without a clear understanding of what is to be accomplished and the limitations involved, the strategy can lose its focus and effectiveness.
Analyzing the Current Situation
A thorough analysis of the current situation is paramount for crafting an effective strategy. This involves evaluating internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as external opportunities and threats. Understanding the prevailing market conditions, competitive landscape, and technological advancements is critical for developing a strategy that is both relevant and responsive to the environment. This analysis provides the foundation upon which a successful strategy is built.
Identifying Key Stakeholders and Their Needs
Successful strategies must consider the needs and expectations of all key stakeholders. Understanding the perspectives of customers, employees, investors, and other relevant parties is essential for developing a strategy that resonates with their interests. This understanding fosters a sense of collaboration and engagement, leading to greater buy-in and support for the strategy. Failing to consider the perspectives of stakeholders can lead to resistance and ultimately hinder the strategy's success.
Developing Actionable Steps and Milestones
A robust strategy must translate broad objectives into specific, actionable steps. This involves outlining the tasks, responsibilities, and deadlines associated with each element of the plan. Setting clear milestones and metrics is critical for monitoring progress and making necessary adjustments along the way. This ensures that the strategy remains relevant and effective in the face of evolving circumstances. Clearly defined steps and milestones act as a guide for implementation and provide a clear picture of the journey ahead.
Resource Allocation and Management
Implementing a strategy requires adequate resources, both human and financial. A crucial aspect of strategy development is the allocation of resources to different initiatives. This includes identifying the necessary personnel, equipment, and financial capital required to execute each step of the plan. Effective resource management ensures that resources are utilized optimally, maximizing the return on investment and driving efficiency. Prioritizing resource allocation based on strategic importance is key to successful implementation. Poor resource allocation can lead to delays and inefficiencies.
Evaluation and Adaptation
A dynamic strategy is one that is constantly evaluated and adapted to changing circumstances. Regular monitoring of progress against planned milestones is essential for identifying any deviations from the intended course. This allows for prompt adjustments to the strategy, ensuring its continued relevance and effectiveness. Adaptability is a critical component of a successful strategy, as unforeseen challenges and emerging opportunities must be addressed in a timely manner. A rigid approach to strategy implementation can lead to stagnation and eventual failure.
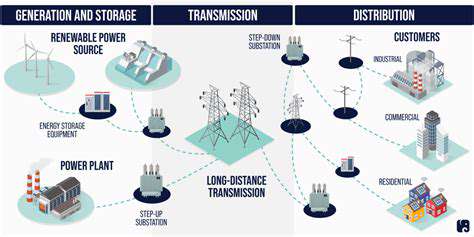
Enhancing Grid Infrastructure and Modernization
Strategic Planning for Grid Modernization
A crucial aspect of enhancing grid infrastructure is the development of a robust strategic plan. This plan should outline clear objectives, timelines, and resource allocation for modernization projects. A well-defined strategy ensures that investments align with long-term goals, maximizing the return on investment and minimizing potential disruptions to service. This strategic planning process should involve stakeholders across the energy sector, including utilities, regulatory bodies, and technology providers, to ensure a collaborative and comprehensive approach. The plan should also consider potential future demands and technological advancements to ensure the grid remains resilient and adaptable.
Investment Strategies for Grid Upgrades
Attracting and allocating sufficient funding for grid modernization is paramount. Innovative investment strategies, such as public-private partnerships (PPPs) and green bonds, can leverage private capital to accelerate the pace of upgrades. These strategies can also help to diversify funding sources, reducing reliance on a single funding mechanism. Furthermore, clear regulatory frameworks that incentivize investment in grid modernization are essential. These incentives should consider the long-term benefits of a reliable and resilient grid, such as improved energy security and reduced risks of outages.
Technological Advancements in Grid Infrastructure
Integrating advanced technologies, such as smart meters, advanced metering infrastructure (AMI), and distributed energy resources (DERs), are crucial for modernizing grid infrastructure. These technologies enable real-time monitoring and control of energy flow, improving grid efficiency and reliability. Smart grids can also facilitate the integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, making the energy system more sustainable. The adoption of these technologies must be carefully planned and executed to ensure interoperability and minimize potential complexities.
Regulatory Frameworks for Grid Modernization
Appropriate regulatory frameworks are essential to guide and facilitate grid modernization initiatives. These frameworks should encourage innovation, while ensuring grid reliability and safety. Clear guidelines for the integration of new technologies, standards for data sharing, and mechanisms for resolving disputes are critical components of such frameworks. Regulatory bodies also need to adapt to the evolving energy landscape to support the integration of renewable energy sources and distributed energy resources. This includes adopting innovative policies to manage fluctuations in energy supply and demand.
Public-Private Partnerships and Funding Models
Public-private partnerships (PPPs) are valuable tools for attracting private investment in grid modernization projects. These collaborations can leverage the expertise and resources of both public and private sectors, accelerating the implementation of upgrades. Exploring diverse funding mechanisms, such as green bonds and dedicated infrastructure funds, can also support modernization efforts. Successful partnerships require clear agreements and transparent processes to ensure accountability and maximize the benefits for all stakeholders.
Community Engagement and Stakeholder Collaboration
Effective grid modernization requires active engagement with communities impacted by the projects. Open communication and transparent discussions with residents, businesses, and other stakeholders are essential for building trust and minimizing potential opposition. Community engagement can help to address concerns, gather feedback, and ensure that modernization efforts align with local needs and priorities. Collaboration among utilities, regulatory bodies, and community representatives is key to successful implementation.
Addressing Cybersecurity Risks in Modern Grids
Modern grids, with their reliance on digital technologies, are increasingly vulnerable to cyberattacks. Robust cybersecurity measures are essential to protect critical infrastructure from malicious actors. Implementing strong encryption, intrusion detection systems, and regular security audits are crucial steps in mitigating these risks. Furthermore, ongoing training and awareness programs for utility personnel are necessary to build a strong security culture within the energy sector, protecting the grid from potential threats and ensuring its continued reliability.