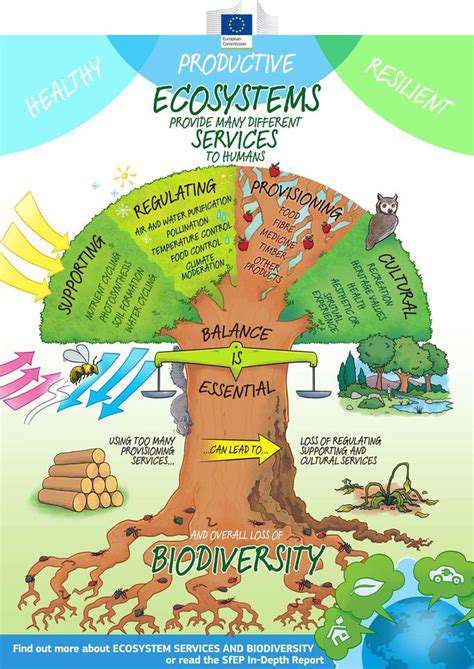
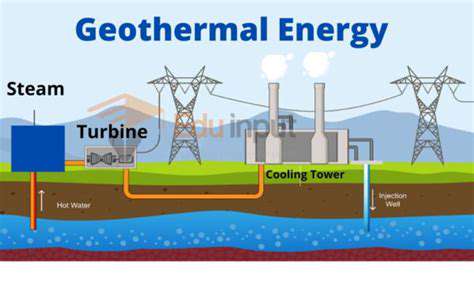
The Convergence of Biotechnology and Renewable Energy
Energy Security Advantages
Nations relying less on foreign oil enjoy a significant strategic advantage. The renewable energy transition means no longer being at the mercy of unpredictable global fuel markets or geopolitical tensions. By generating power domestically from sun, wind, and other local resources, countries gain true energy sovereignty, insulating themselves from price shocks and supply disruptions that have long plagued fossil fuel-dependent economies.
Social Benefits
Clean energy is proving to be a great equalizer. Communities that previously lacked reliable power now access electricity that improves health, education, and economic prospects. Renewable projects often prioritize local hiring, creating jobs where they're needed most. Perhaps most importantly, shifting away from polluting energy sources means cleaner air and water for everyone, particularly benefiting vulnerable populations who've historically borne the brunt of environmental harm.
Policy Drivers
Forward-thinking governments are accelerating the energy transition through smart policies. Tax incentives make renewable projects more attractive to investors, while clear regulations provide the stability businesses need to commit long-term. When policymakers set ambitious renewable targets and back them with concrete measures, they create the conditions for rapid, sustainable growth in clean energy adoption across all sectors of the economy.
Biofuels: A Promising Alternative to Fossil Fuels
The Potential of Plant-Based Fuels
Biofuels derived from crops and algae offer a renewable path away from petroleum dependence. Unlike finite oil reserves, these biological sources can be replenished, potentially reducing environmental damage from fossil fuel extraction and use. The challenge lies in perfecting production methods to ensure true sustainability - minimizing land use impacts while maximizing energy output. When done right, biofuels could play a crucial role in our climate change response.
Beyond environmental benefits, biofuels bring economic advantages to rural areas. New processing facilities create local jobs, while reduced reliance on global oil markets provides economic stability. As biofuel technology advances, it could spark innovation across multiple industries, leading to more diversified and resilient energy systems.
Innovations in Biofuel Technology
Cutting-edge science is revolutionizing biofuel production. Genetic modifications allow crops to produce more fuel per acre while requiring fewer resources. Specialized microbes and improved fermentation techniques are making the process cleaner and more efficient. These technological improvements are crucial for making biofuels cost-competitive with conventional fuels, removing one of the biggest barriers to widespread adoption.
The refining process itself is seeing significant upgrades. New methods produce higher-quality biofuels that work better in existing engines and infrastructure. These advancements address one of the key challenges in biofuel adoption - compatibility with current technology, smoothing the transition away from petroleum-based products.
Environmental Considerations
While promising, biofuels aren't without environmental concerns. Converting natural land for fuel crops can threaten ecosystems if not managed carefully. Sustainable practices must ensure biofuel production doesn't create new environmental problems while solving old ones. This means selecting appropriate feedstocks and implementing responsible farming techniques.
The carbon footprint of biofuels depends heavily on production methods. Poor practices can actually increase emissions, while optimized systems offer significant reductions. Comprehensive environmental assessments are essential to guarantee biofuels deliver on their green promise, from field to fuel tank.
Enzyme-Based Processes for Biofuel Production
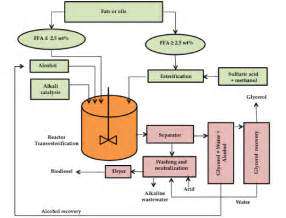
Breaking Down Biomass with Enzymes
Enzyme-driven processes are revolutionizing biofuel production. Specialized proteins act as biological scissors, chopping complex plant materials into simple sugars ready for conversion to fuel. The efficiency of this process depends on multiple factors: choosing the right enzymes, maintaining ideal reaction conditions, and properly preparing the raw materials. Modern techniques allow scientists to target specific plant components, boosting yields while reducing waste and costs.
Greener Biodiesel Production
Enzymes offer a cleaner way to make biodiesel from plant oils. Instead of harsh chemicals, natural enzymes facilitate the chemical reactions that transform oils into fuel. This biological approach uses less energy and generates fewer harmful byproducts than conventional methods, making the entire process more environmentally friendly from start to finish.
Fermentation Boosted by Enzymes
Turning plant sugars into alcohol-based fuels like ethanol benefits tremendously from enzymatic assistance. Specialized proteins accelerate and improve these biological conversions, making fermentation processes faster and more productive. By carefully selecting enzymes and optimizing conditions, producers can achieve better yields with lower energy inputs - a win for both economics and the environment.
Compared to traditional fuel production, enzyme-enhanced fermentation offers a significantly cleaner alternative. This method reduces reliance on fossil fuels at every stage, from growing the feedstocks to processing them into usable energy.
Stabilizing Enzymes for Efficiency
Immobilizing enzymes on solid supports represents a major advance in biofuel technology. This technique allows repeated use of the same enzymes, dramatically cutting costs that would otherwise go toward constantly replacing these biological catalysts. Different attachment methods suit different applications, but all share the benefit of making the process more economical and scalable.
The stability provided by immobilization translates directly to more consistent, reliable production. This reliability is key for making biofuels competitive with conventional energy sources in terms of both price and performance.
Our planet is drowning in a sea of plastic waste, a visible testament to humanity's careless habits. Walk along any beach, and you'll find plastic bottles bobbing in the waves; hike through remote forests, and you'll spot plastic bags tangled in branches. This isn't just an environmental issue - it's a crisis that's literally choking our ecosystems. Marine animals mistake plastic for food, while toxic microplastics are finding their way into our food chain with consequences we're only beginning to understand.
The Future of Biotechnology in Renewable Energy

Tailored Medical Treatments
Biotechnology enables healthcare customized to individual genetic profiles, promising more effective treatments with fewer side effects. By decoding each patient's unique biology, doctors can prescribe therapies precisely matched to their needs, particularly valuable for complex conditions like cancer where standard treatments often fall short.
Precision Gene Editing
CRISPR and similar technologies allow unprecedented precision in modifying genetic code. These tools offer hope for curing inherited diseases once considered untreatable, from blood disorders to neurological conditions. While still developing, gene editing's potential to correct genetic errors represents one of medicine's most exciting frontiers.
Next-Generation Farming
Agricultural biotechnology creates crops that thrive despite climate challenges. These advances mean more reliable harvests using fewer chemical inputs, crucial for feeding growing populations without exhausting our planet's resources. The resulting food systems are both more productive and more sustainable.
Nature's Cleanup Crew
Engineered microorganisms can break down pollutants more effectively than conventional methods. This biological approach to environmental cleanup offers sustainable solutions for oil spills, industrial waste, and other contamination, often at lower cost and with less collateral damage than traditional remediation techniques.
Green Manufacturing
Biotechnology transforms industrial processes, enabling production of fuels, plastics, and chemicals from renewable sources. This shift toward biology-based manufacturing reduces reliance on fossil fuels while creating new materials with enhanced properties for various applications.
Navigating Ethical Waters
As biotech capabilities expand, so do important ethical questions. Society must carefully consider how to harness these powerful technologies responsibly, establishing clear guidelines to ensure benefits outweigh risks. Ongoing public dialogue and thoughtful regulation will be crucial as these technologies continue to evolve.