The Environmental Benefits of Renewable Energy in Agriculture

Improved Air Quality
Significant strides in reducing air pollution have been made in recent years, driven by advancements in technology and stricter environmental regulations. These improvements translate directly into better public health outcomes, as cleaner air reduces respiratory illnesses and other health problems. Improved air quality also fosters a more vibrant and sustainable environment, allowing people to enjoy outdoor activities without the detrimental effects of pollution.
Many cities have implemented comprehensive strategies focusing on cleaner transportation, industrial emission controls, and increased green spaces. These measures have yielded noticeable improvements in air quality indices, resulting in lower levels of harmful pollutants like particulate matter and nitrogen oxides. The positive impacts are evident in reduced hospital admissions for respiratory conditions and improved overall well-being for residents.
Enhanced Water Quality
The ongoing efforts to improve water quality are demonstrating positive results, with cleaner rivers, lakes, and coastal areas. This progress is vital for aquatic ecosystems and the human populations that rely on these resources. Stricter regulations on industrial discharge and agricultural runoff are helping to mitigate contamination, leading to healthier aquatic life and safer water for drinking and recreational use.
Furthermore, the development and implementation of advanced water treatment technologies are playing a crucial role in purifying water sources. These advancements are crucial to ensuring the safety and accessibility of clean water for communities globally. This progress is not only essential for human health but also for the survival of countless aquatic species, maintaining the delicate balance of our ecosystems.
Sustainable Practices
The focus on sustainable practices is crucial for long-term air and water quality improvement. Sustainable agriculture, for example, aims to reduce the use of harmful pesticides and fertilizers that can contaminate water sources. This approach emphasizes the importance of preserving natural resources and minimizing environmental impact. This is essential for future generations and the health of our planet.
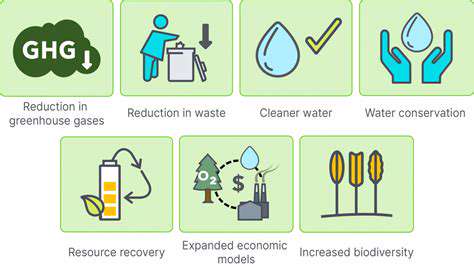
Renewable energy sources are also contributing significantly to cleaner air and water. Transitioning from fossil fuels to solar, wind, and other renewable energy sources significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions, a major contributor to air pollution. This shift towards sustainability is essential for protecting the planet and ensuring a healthy future.
Economic Benefits
Investments in improved air and water quality initiatives often yield significant economic benefits. Reduced healthcare costs associated with respiratory illnesses and other pollution-related diseases represent a major positive impact. Moreover, improved water quality can lead to increased tourism and recreational activities, boosting local economies. These factors highlight the importance of prioritizing environmental protection for both public and economic well-being.
Improved air and water quality also fosters a more attractive and livable environment for businesses and residents, encouraging investment and economic growth. This creates a positive feedback loop where economic prosperity and environmental sustainability go hand in hand. This long-term approach is essential for building resilient and sustainable communities.

Promoting a Circular Economy in Agriculture
Enhancing Resource Efficiency
Adopting circular economy principles in agriculture necessitates a significant shift towards resource efficiency. This involves minimizing waste generation at every stage of the production process, from input sourcing to product disposal. By maximizing the utilization of resources, such as water and nutrients, and minimizing the reliance on finite resources like fossil fuels, we can drastically reduce the environmental impact of agricultural practices.
This approach extends to the use of organic matter and compost, which can replace synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, thus reducing pollution and enhancing soil health. The efficient use of water resources through precision irrigation techniques and water-saving technologies is also crucial.
Promoting Biological Diversity
A circular economy in agriculture prioritizes biodiversity. Diverse ecosystems are more resilient to pests and diseases, requiring fewer interventions with synthetic pesticides and herbicides. This approach fosters a healthier environment for both humans and the surrounding ecosystem. Encouraging crop rotations, integrating livestock into farming systems, and creating habitats for pollinators and other beneficial organisms are vital strategies.
Reducing Food Waste
A significant portion of agricultural production is lost due to post-harvest waste, processing inefficiencies, and consumer behavior. Implementing strategies to reduce food waste throughout the supply chain is crucial for a circular economy in agriculture. This includes developing better storage and transportation methods, optimizing packaging, and educating consumers about reducing food waste at home.
Improving Soil Health
Healthy soil is fundamental to sustainable agriculture. Circular economy principles emphasize the importance of soil health and its role in carbon sequestration. Techniques like cover cropping, no-till farming, and crop rotation enhance soil structure, improve water retention, and increase nutrient availability, reducing the need for external inputs.
Developing Closed-Loop Systems
Circular economy models in agriculture aim to create closed-loop systems where waste from one stage of the process becomes a resource for another. This involves utilizing crop residues for animal feed, composting organic waste, and utilizing biogas generated from manure to produce energy. These closed-loop systems minimize waste generation and maximize resource utilization.
Utilizing Renewable Energy Sources
Transitioning to renewable energy sources in agriculture is essential for reducing the carbon footprint of the sector. Solar, wind, and biogas power can replace fossil fuels in various agricultural operations, such as irrigation, transportation, and processing. This shift towards sustainable energy sources is crucial for aligning agricultural practices with environmental goals.
Encouraging Sustainable Consumption Patterns
Consumer choices play a critical role in fostering a circular economy in agriculture. Promoting sustainable consumption patterns, such as reducing meat consumption, opting for locally sourced produce, and choosing products with minimal packaging, can significantly decrease the environmental impact of the food system. Educating consumers about the environmental benefits of sustainable choices is critical.