Accelerating Renewable Energy Transition in Developing Countries
Identifying Key Barriers to Renewable Energy Integration
Technological Challenges
One significant barrier to wider renewable energy integration lies in the ongoing technological advancements needed to improve the efficiency and reliability of renewable energy sources. For instance, advancements in battery storage technology are crucial for mitigating the intermittency of solar and wind power. Current battery technologies often struggle with cost-effectiveness and lifespan, hindering their widespread adoption in grid-scale energy storage solutions. Overcoming these technological limitations is essential for ensuring a stable and reliable energy supply as renewable energy sources become more prominent.
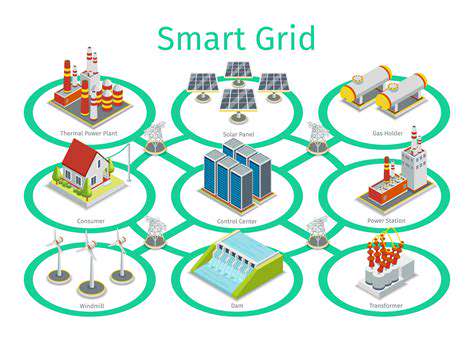
Furthermore, the development of smart grids is essential for managing the fluctuating nature of renewable energy generation. Smart grids, with their advanced monitoring and control systems, can optimize the flow of electricity, balancing supply and demand in real-time. The implementation of these technologies requires significant investment in infrastructure and expertise, which can be a considerable hurdle for many regions.
Policy and Regulatory Hurdles
Existing energy policies and regulations often create obstacles to the smooth integration of renewable energy sources. In many jurisdictions, outdated regulations favor fossil fuel-based power plants, creating an uneven playing field that makes it difficult for renewable energy projects to compete economically. These policies need to be revised to support and incentivize the transition to renewable energy, offering clear pathways for developers and investors.
Furthermore, a lack of clear policy frameworks and regulatory certainty can deter investment in renewable energy projects. Uncertainty regarding permitting processes, environmental regulations, and grid access can significantly increase project costs and timelines. Establishing transparent and predictable regulations is crucial for attracting investment and accelerating the transition to a renewable energy future.
Economic and Financial Constraints
The transition to renewable energy requires substantial upfront investment in infrastructure, technology, and skilled labor. The high initial costs associated with renewable energy projects, particularly in the early stages of deployment, can be a significant deterrent for both private and public investors. Developing innovative financing mechanisms, such as tax incentives, subsidies, and public-private partnerships, can help to mitigate these financial challenges and encourage investment in renewable energy.
Furthermore, the economic viability of renewable energy projects often depends on the price of fossil fuels and the availability of government support. Fluctuations in fuel prices can impact the competitiveness of renewable energy sources, making it difficult to achieve long-term economic sustainability. Stable and predictable policies and market conditions are essential for ensuring the long-term financial viability of renewable energy projects.
Social and Community Acceptance
The integration of renewable energy projects can sometimes face resistance from local communities due to concerns about visual impacts, land use, and potential environmental consequences. Effective communication and engagement with local communities are crucial for building support and addressing concerns. Transparent project planning, public consultations, and community involvement initiatives can help to foster acceptance and ensure that renewable energy projects are integrated harmoniously into local landscapes.
Moreover, public awareness and education campaigns are vital for promoting understanding and acceptance of renewable energy technologies. Educating the public about the benefits of renewable energy, dispelling myths, and highlighting positive case studies can help to overcome skepticism and foster a more supportive environment for the transition to a cleaner energy future.
Leveraging Innovative Financing Mechanisms for Renewable Energy Projects
Innovative Financing Structures for Solar Projects
Renewable energy projects, particularly solar installations, often face challenges securing sufficient funding. Traditional financing methods can be cumbersome and slow, hindering the rapid deployment needed to meet climate goals. Innovative financing structures, such as project finance, where the project's cash flows are used to repay debt, are emerging as crucial tools to overcome these hurdles. These structures can attract a wider range of investors, including institutional and private equity funds, leading to more readily available capital and potentially lower borrowing costs.
Furthermore, creative financing models like power purchase agreements (PPAs) can facilitate the development of large-scale solar projects by allowing developers to sell the generated electricity to consumers or utilities without the upfront capital investment required to build and operate the entire system. This approach encourages greater participation from diverse stakeholders, fostering a more robust and sustainable financing ecosystem for renewable energy.
Government Incentives and Subsidies
Government incentives and subsidies play a pivotal role in attracting investment and accelerating the transition to renewable energy. Targeted policies, such as tax credits, grants, and feed-in tariffs, can significantly reduce the cost of renewable energy projects, making them more competitive with traditional energy sources. These incentives often serve as a catalyst, encouraging both public and private sector participation in the renewable energy sector.
Subsidies can take various forms, including direct financial support, preferential tax treatment for renewable energy investments, and streamlined permitting processes. The design and implementation of effective incentive programs require careful consideration of their impact on long-term project viability and overall energy market dynamics.
Crowdfunding and Community Investment
Crowdfunding platforms and community investment initiatives are demonstrating increasing potential in mobilizing capital for renewable energy projects. These platforms allow individuals and small groups to pool their resources to finance smaller-scale projects, fostering a sense of collective ownership and participation in local energy solutions. This bottom-up approach empowers communities to take control of their energy future and reduces reliance on large-scale, centralized funding sources.
By enabling broader participation, crowdfunding can democratize access to renewable energy, potentially leading to more distributed and resilient energy systems. However, careful structuring and regulatory frameworks are necessary to ensure the security and sustainability of these investments.
Impact Investing and ESG Factors
Impact investing, which focuses on investments that generate both financial returns and positive social and environmental impact, is becoming increasingly relevant in the renewable energy sector. Investors are increasingly seeking opportunities to align their portfolios with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria, driving demand for renewable energy projects that demonstrate positive environmental outcomes. This growing trend is further attracting capital to the sector and promoting sustainable practices.
Integration of ESG factors into investment decisions can lead to more rigorous due diligence processes, potentially improving the long-term financial sustainability of renewable energy projects while simultaneously contributing to broader societal goals. This approach fosters a more holistic and responsible approach to financing, encouraging the development of projects that benefit both the environment and investors.
Risk Mitigation Strategies for Renewable Energy Investments
Renewable energy projects, while offering significant long-term benefits, are not without inherent risks. Factors such as fluctuating energy prices, technological advancements, and regulatory changes can impact project profitability. Comprehensive risk mitigation strategies are crucial for ensuring the financial viability of these projects. These strategies should include thorough due diligence, robust project planning, and diversification of investment portfolios.
Effective risk management strategies also involve exploring insurance mechanisms, contingency planning for unforeseen events, and proactive engagement with regulatory bodies. By anticipating potential challenges and implementing appropriate safeguards, investors can increase their confidence in the long-term success of renewable energy projects and encourage wider participation in this critical sector.
Building Capacity and Fostering Local Expertise

Building Capacity
Developing robust capacity within an organization is crucial for long-term success. This involves not only acquiring new skills and knowledge, but also cultivating a culture of continuous learning and improvement. Investing in training programs, mentorship initiatives, and professional development opportunities is essential for empowering employees and fostering a dynamic workforce. This proactive approach ensures that individuals possess the necessary skills to adapt to evolving challenges and capitalize on emerging opportunities. Furthermore, building capacity involves creating a supportive environment where employees feel encouraged to take risks, experiment with new ideas, and contribute their unique perspectives.
A strong foundation of knowledge and expertise is paramount, enabling the organization to tackle complex problems and deliver high-quality results. This translates into improved efficiency, productivity, and overall performance, ultimately driving the organization toward its strategic goals. Building capacity also encompasses the development of systems and processes that facilitate collaboration, communication, and information sharing across different departments. This interconnectedness strengthens the organization's ability to respond effectively to market demands and customer needs.
Fostering Collaboration
Effective collaboration is the cornerstone of successful projects and initiatives. It involves fostering a shared vision and common goals among team members, while recognizing individual strengths and encouraging diverse perspectives. This collaborative spirit, built on trust and mutual respect, creates a synergistic environment where ideas are exchanged freely and innovative solutions are readily conceived.
Open communication channels and transparent decision-making processes are paramount. Active listening and constructive feedback are essential elements in nurturing a collaborative environment. Employees should feel empowered to voice their opinions and concerns, knowing that their input will be valued and considered. When everyone feels included and respected, a more engaged and productive work environment emerges.
Lo
Leveraging opportunities for growth and development is vital for achieving organizational goals. This involves actively seeking out and capitalizing on new ventures, partnerships, and market trends. By staying ahead of the curve and adapting to the changing landscape, organizations can secure a competitive edge and maintain their position in the market. Proactive engagement with external stakeholders is also a key element in this process, fostering relationships and building valuable networks.
A forward-thinking approach, emphasizing innovation and adaptability, is crucial for organizations aiming to thrive in the long term. This includes identifying and addressing emerging challenges effectively and proactively. This approach ensures that the organization remains agile and responsive, allowing it to navigate the complexities of the modern business environment. Thorough research and analysis are necessary to ensure that opportunities are properly evaluated and implemented strategically.
Strengthening Grid Infrastructure and Addressing Energy Access Challenges
Improving Grid Reliability
Robust grid infrastructure is crucial for reliable energy delivery. Investing in advanced monitoring systems, predictive maintenance technologies, and smart grid components can significantly reduce outages and improve the overall performance of the electricity grid. This proactive approach not only ensures consistent power supply but also safeguards critical infrastructure and reduces the economic impact of disruptions, ultimately fostering a more resilient and sustainable energy landscape.
Furthermore, upgrading existing transmission and distribution lines with more efficient and durable materials can enhance grid stability and allow for increased energy capacity. This enhanced capacity is essential for accommodating the growing demand for electricity, especially as renewable energy sources integrate into the grid.
Expanding Access to Rural Communities
Bridging the energy access gap in rural communities requires targeted infrastructure development. This includes the establishment of localized microgrids, which can provide reliable and affordable power sources to remote areas, reducing reliance on expensive and inefficient diesel generators. Such initiatives are vital for boosting local economies, improving quality of life, and fostering sustainable development in under-served regions.
Additionally, innovative financing mechanisms and public-private partnerships can play a key role in driving infrastructure development in underserved areas. This will ensure that the benefits of reliable energy access extend to communities that have historically been excluded from modern energy infrastructure.
Integrating Renewable Energy Sources
Effective grid modernization must embrace the integration of renewable energy sources like solar and wind power. This necessitates the development of sophisticated grid management systems capable of handling intermittent energy generation. These systems will need to optimize energy distribution based on real-time supply and demand, ensuring a balanced and reliable energy mix. This transition is not just environmentally beneficial but also economically advantageous, promoting the growth of a clean energy economy.
Addressing Energy Storage Solutions
Energy storage technologies are critical for stabilizing the grid in response to the fluctuating nature of renewable energy generation. Implementing large-scale energy storage systems, such as pumped hydro or battery storage, can help to mitigate the intermittency of solar and wind power, ensuring a consistent and reliable energy supply. The development and deployment of advanced energy storage solutions are essential for a smooth transition to a sustainable energy future.
Promoting Energy Efficiency Measures
Improving energy efficiency throughout the grid and in end-user applications is fundamental to reducing overall energy consumption. Implementing energy-efficient appliances and lighting, along with promoting sustainable building practices, can significantly decrease the load on the grid. This approach not only lowers energy costs for consumers but also reduces the strain on the infrastructure, promoting long-term grid resilience. Smart meters and energy management systems can play a vital role in educating consumers about energy use and promoting efficient consumption habits.
Promoting Policy Frameworks and Incentives for Renewable Energy Adoption
Establishing Clear Policy Frameworks
Effective policy frameworks are crucial for driving the adoption of renewable energy. These frameworks need to be clearly defined, comprehensive, and consistently applied. They must outline specific targets for renewable energy generation, installation, and consumption, and establish clear pathways for achieving these goals. This includes outlining procedures for permitting and licensing renewable energy projects, as well as mechanisms for addressing potential environmental concerns. A robust legal framework is essential to ensure the long-term viability and sustainability of renewable energy initiatives.
Furthermore, policies should incentivize investment in renewable energy technologies through tax breaks, subsidies, and other financial instruments. These incentives can stimulate private sector participation and accelerate the transition to a cleaner energy future. Transparency and public participation in the policy-making process are also vital to fostering public trust and ensuring that policies reflect the needs and priorities of the community.
Creating Financial Incentives for Renewable Energy
Financial incentives play a pivotal role in encouraging investment and adoption of renewable energy. Tax credits, grants, and subsidies can significantly reduce the upfront costs associated with renewable energy projects, making them more competitive with fossil fuel-based alternatives. These incentives can target specific technologies, such as solar panels or wind turbines, or provide broader support for the entire renewable energy sector.
Government subsidies can also support research and development in renewable energy technologies, fostering innovation and driving down costs over time. Furthermore, government-backed loan programs and risk-sharing mechanisms can help to reduce the financial risks associated with renewable energy investments, encouraging greater participation from private investors.
Streamlining Permitting and Regulatory Processes
Bureaucratic hurdles and lengthy permitting processes can significantly hinder the development and deployment of renewable energy projects. Streamlining these processes is essential to accelerate the transition to a sustainable energy future. Simplified permitting procedures, streamlined review timelines, and clear communication channels can significantly reduce the time and cost associated with bringing renewable energy projects online.
Efficient regulatory frameworks should be flexible and adaptable to accommodate technological advancements and evolving market needs. Collaboration between government agencies and industry stakeholders is crucial to identifying and addressing potential bottlenecks in the permitting and regulatory processes. This collaborative approach can lead to more efficient and effective policies that support renewable energy adoption.
Promoting Public Awareness and Education
Promoting public awareness and education about the benefits of renewable energy is critical for fostering widespread acceptance and support. Public understanding of the environmental, economic, and social advantages of renewable energy sources can increase public support for policies and initiatives aimed at accelerating their adoption.
Educational campaigns and outreach programs can highlight the positive impacts of renewable energy on communities, such as job creation, reduced energy costs, and improved air quality. These initiatives should focus on dispelling common misconceptions about renewable energy and presenting credible scientific evidence supporting its potential. Furthermore, engaging communities in renewable energy projects can foster a sense of ownership and responsibility for the transition to a sustainable future.
Addressing Challenges Related to Intermittency
Renewable energy sources like solar and wind power are inherently intermittent, posing challenges to grid stability and energy reliability. Addressing these intermittency issues is crucial for achieving widespread adoption. Smart grid technologies, energy storage solutions, and grid modernization are essential for managing the fluctuating nature of renewable energy generation. Developing robust energy storage solutions, such as batteries and pumped hydro, is vital for ensuring a reliable and consistent energy supply.
Furthermore, innovative solutions for integrating renewable energy into existing grids, such as advanced forecasting tools and demand response programs, are necessary for efficient management of fluctuating renewable energy generation. These measures are crucial for overcoming the challenges associated with intermittency and enabling a smooth transition to a renewable energy-based energy system.
Fostering International Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing
International collaboration plays a vital role in accelerating renewable energy adoption. Sharing best practices, technologies, and policy frameworks across countries can facilitate faster progress and foster innovation. International partnerships can support the development of new renewable energy technologies and provide opportunities for knowledge transfer between countries with advanced renewable energy programs and those still in the early stages of development.
Collaboration can also facilitate the development of common standards and regulations for renewable energy projects, promoting consistency and efficiency in the global transition to a sustainable energy future. Knowledge sharing and international partnerships can accelerate the deployment of renewable energy technologies, driving innovation and reducing costs globally.