Addressing the Water Energy Food Nexus with Renewable Energy
Integrating Renewable Energy into the Food-Energy-Water Nexus
Understanding the Interconnectedness
The food-energy-water nexus highlights the intricate relationship between these three crucial resources. Sustainable development requires a holistic approach, recognizing that decisions impacting one sector inevitably affect the others. Integrating renewable energy sources is paramount to decoupling our reliance on fossil fuels and fostering a more resilient and environmentally conscious system. This interconnectedness extends to water usage in agriculture, energy production, and consumption patterns, necessitating a comprehensive approach to resource management.
The nexus framework underscores the need to consider the synergistic and often conflicting demands placed on these resources. For instance, bioenergy production can compete with food production for land and water resources, highlighting the critical need for careful planning and prioritization to ensure equitable access and environmental sustainability.
Renewable Energy's Role in Agriculture
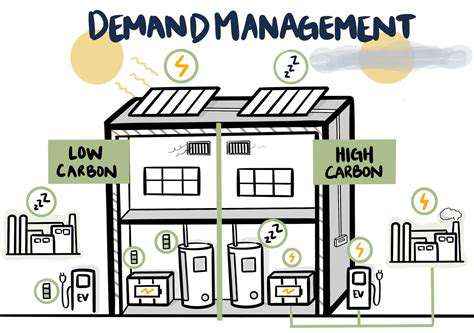
Renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, can significantly reduce the environmental footprint of agriculture. Modernizing irrigation systems with renewable energy-powered pumps can dramatically improve water use efficiency, reducing water waste and promoting conservation. This, in turn, benefits both agricultural productivity and water availability for other uses, creating a virtuous cycle within the nexus.
Furthermore, renewable energy can power farm machinery and processing facilities, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering greenhouse gas emissions. This transition fosters a more sustainable and resilient agricultural sector, contributing to the overall well-being of the food-energy-water nexus.
Water Management Strategies with Renewable Energy
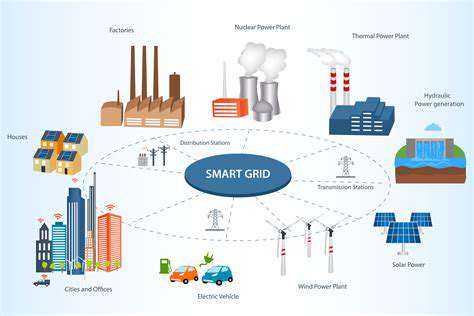
Integrating renewable energy into water management strategies is crucial for optimizing water use efficiency. Renewable energy can power desalination plants, enabling access to freshwater in water-scarce regions. This addresses the critical challenge of providing clean water for both human consumption and agricultural needs, while minimizing the environmental impact of traditional water extraction methods.
Additionally, renewable energy can be used to power advanced wastewater treatment facilities, reducing pollution and improving water quality. This integrated approach to water management ensures a clean and sustainable water supply for future generations, reinforcing the interconnectedness of the food-energy-water nexus.
Challenges and Opportunities in Implementation
Despite the numerous benefits, integrating renewable energy into the food-energy-water nexus presents certain challenges. These include the high initial investment costs associated with renewable energy infrastructure and the need for supportive policies and incentives to encourage adoption. Overcoming these obstacles requires a collaborative effort between governments, businesses, and communities, fostering innovation and investment in renewable energy technologies.
However, the opportunities are immense. Investing in renewable energy infrastructure can create new jobs, stimulate economic growth, and enhance energy security. This approach ensures that future food production, water management, and energy needs are met in a sustainable and equitable manner, solidifying the interconnectedness of the food-energy-water nexus.
Policy and Governance for a Sustainable Future
Effective policies and robust governance structures are essential for successfully integrating renewable energy into the food-energy-water nexus. These policies should incentivize the adoption of renewable energy technologies, promote research and development in the sector, and ensure equitable access to resources. This involves establishing clear regulations for water use in agriculture, energy production, and consumption, while simultaneously fostering international cooperation to address transboundary water issues.
Promoting public awareness about the interconnectedness of these resources and the benefits of sustainable practices is also crucial. Education and outreach programs can empower individuals and communities to adopt more sustainable consumption patterns and support policies promoting renewable energy solutions within the food-energy-water nexus. This is vital for ensuring a sustainable future for all.