Advanced Modular Reactors (AMRs) and Their Role in Decarbonization
Safety and Risk Mitigation: A Focus on Enhanced Protection
Enhanced Safety Features in Advanced Modular Reactors
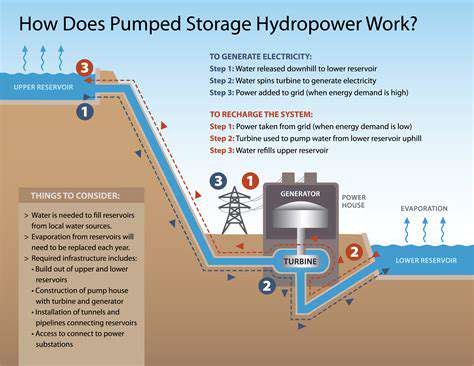
Advanced Modular Reactors (AMRs) prioritize safety through inherent design features that mitigate potential risks. These reactors leverage passive safety systems, reducing reliance on active components and external power sources. This inherent safety is crucial, especially in areas with limited infrastructure or potential natural disasters. The design philosophy emphasizes a layered approach, combining multiple independent safety mechanisms to ensure containment and prevent accidents, even under extreme conditions. This proactive approach to safety is a key differentiator of AMRs compared to traditional reactor designs.
Specific safety features include advanced containment structures, designed to withstand extreme pressures and temperatures, preventing the release of radioactive materials. Furthermore, the modular design itself contributes to safety by allowing for smaller, more manageable units. This reduces the potential consequences of a localized incident and simplifies emergency response protocols, leading to faster and more effective containment.
Risk Mitigation Strategies for Operational Environments
Operational environments for AMRs require specific risk mitigation strategies to address potential hazards. These strategies involve comprehensive training programs for personnel, ensuring that they are equipped to handle emergencies effectively and efficiently. Robust emergency response plans, including evacuation protocols and procedures for containing radioactive releases, are crucial to minimize the impact of unforeseen events. This proactive approach emphasizes the importance of human factors in safety, ensuring that personnel are equipped with the knowledge and skills to manage potential risks.
Regular and rigorous inspections, coupled with advanced monitoring systems, are vital for identifying and addressing potential issues proactively. These inspections and monitoring systems provide real-time data, facilitating early detection of deviations from normal operating parameters. Advanced diagnostic tools and predictive maintenance strategies are further employed to anticipate potential failures and minimize downtime, further contributing to the overall safety and reliability of the system.
Accident Prevention Through Redundancy and Diversity
Accident prevention in AMRs is paramount and is achieved through the implementation of robust redundancy and diversity. Multiple independent safety systems are integrated into the design, ensuring that if one system fails, others can take over automatically. This inherent redundancy minimizes the likelihood of a cascading failure scenario. The diversity of these systems further enhances safety by employing different physical principles and operating mechanisms. This approach ensures that the potential for a single point of failure is significantly reduced. This layered approach to safety is crucial for the long-term reliability and safety of the reactor.
Emergency Preparedness and Response Protocols
Comprehensive emergency preparedness and response protocols are integral to the operation of AMRs. These protocols, encompassing all aspects from potential accidents to natural disasters, are crucial for minimizing the impact on personnel and the environment. Regular drills and simulations are essential to ensure that personnel are prepared to respond effectively in real-time. This includes detailed evacuation plans, procedures for containing radioactive releases, and coordination with external emergency response teams. The protocols are designed to be adaptable, addressing different potential scenarios and ensuring the safety of nearby communities.