Energy Storage as a Service (ESaaS) Models
Contents
ESaaS transforms enterprise software delivery into a cloud-based service model.
ESaaS offers a scalable, on-demand alternative to traditional software ownership.
ESaaS emphasizes cloud solutions over on-premises software for businesses.
ESaaS provides flexible, subscription-based enterprise software solutions.
ESaaS shifts software management from companies to service providers.
Introduction to ESaaS

Understanding the Essence of ESaaS
ESaaS, or Enterprise Software as a Service, represents a paradigm shift in how businesses approach software solutions. Instead of purchasing and maintaining complex on-premises software, companies can now leverage cloud-based applications provided by vendors. This shift offers significant advantages in terms of cost-effectiveness and scalability, allowing businesses to focus on their core competencies without the burden of IT infrastructure management.
A key benefit of ESaaS lies in its flexibility and adaptability. Software updates and upgrades are often handled automatically by the vendor, freeing up internal IT teams for more strategic initiatives. This agility allows businesses to respond quickly to evolving market demands and technological advancements.
Key Features and Benefits of ESaaS
Several key features differentiate ESaaS from traditional software. These include scalability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness. ESaaS solutions are designed to easily adapt to changing business needs, allowing for seamless expansion or contraction of resources without significant upfront investments.
Enhanced accessibility is another crucial aspect of ESaaS. Employees can access essential applications from anywhere with an internet connection, fostering collaboration and improving productivity across geographical boundaries. This remote access capability is invaluable for distributed teams and international operations.
The cost-effectiveness of ESaaS is often a primary driver for adoption. Subscription-based pricing models eliminate the need for large upfront capital expenditures, making it more accessible to businesses of all sizes. The reduced maintenance costs and streamlined IT management further contribute to the overall cost savings associated with this approach.
Implementation Considerations for ESaaS
Implementing an ESaaS solution requires careful planning and consideration. Businesses must identify their specific needs and choose a provider that aligns with their organizational goals. Thorough due diligence of the vendor's reputation and security protocols is essential.
A comprehensive assessment of existing processes and workflows is crucial before transitioning to an ESaaS model. This ensures seamless integration and avoids potential disruptions to daily operations. Careful planning for data migration and security protocols is also vital for a smooth and secure deployment.
Security and Compliance in ESaaS
Security is paramount when using any cloud-based service, and ESaaS is no exception. Choosing a provider with robust security measures and adherence to industry best practices is critical for safeguarding sensitive business data. Businesses should thoroughly evaluate the security protocols and certifications offered by potential vendors to mitigate risks.
Compliance with relevant regulations and standards is another crucial aspect to consider. Businesses must ensure that the chosen ESaaS solution complies with all applicable legal requirements, such as data privacy regulations and industry-specific standards. This requires careful review of the vendor's compliance documentation and ongoing monitoring.

Challenges and Considerations for ESaaS Adoption
Understanding the Complexity of Implementation
Implementing an ESaaS solution is not a simple plug-and-play operation. A thorough understanding of existing infrastructure, energy consumption patterns, and the specific needs of the facility or grid is crucial. This often requires detailed assessments and potentially significant upfront investment in data collection and analysis. Careful planning and consideration of potential integration challenges with existing systems are essential to ensure a smooth transition and avoid unforeseen complications.
Furthermore, the varying technical specifications and compatibility issues between different ESaaS providers can lead to significant hurdles. A comprehensive evaluation of vendor capabilities, service level agreements, and support mechanisms is necessary to ensure a reliable and scalable solution.
Financial Considerations and ROI
The financial implications of ESaaS adoption are multifaceted and require careful budgeting. Initial setup costs, ongoing subscription fees, and potential maintenance expenses need to be meticulously evaluated to determine the true cost of ownership. It's essential to assess the potential return on investment (ROI) by comparing the expected savings in energy costs with the total investment.
Regulatory and Policy Landscape
Navigating the complex regulatory landscape surrounding energy storage and the potential implications of new policies is critical for successful ESaaS implementation. Understanding local regulations, permitting processes, and grid integration requirements is essential to avoid potential delays and compliance issues. This often involves consulting with legal experts and regulatory bodies to ensure a compliant deployment.
Grid Integration and Interoperability
Integrating ESaaS solutions with existing grid infrastructure can present significant technical challenges. Ensuring seamless communication and interoperability between the storage system and the broader energy network is vital for optimal performance. This involves careful consideration of grid codes, standards, and potential impacts on grid stability.
Data Security and Privacy Concerns
With the increasing reliance on digital systems for Energy Management, data security and privacy are paramount concerns in ESaaS adoption. Establishing robust security protocols to protect sensitive energy data from unauthorized access or breaches is crucial. This includes implementing data encryption, access controls, and regular security audits to safeguard the integrity and confidentiality of the stored information.
Scalability and Future Growth
The ability to scale the ESaaS solution to meet future energy demands is crucial for long-term sustainability. The chosen provider should demonstrate a clear strategy for expanding capacity and adapting to evolving energy needs. A flexible and adaptable solution is essential to accommodate potential growth and ensure the system remains relevant and effective over time.
The Future of ESaaS in the Energy Landscape

Emerging Technologies Shaping the ESaaS Landscape
As the energy sector advances, innovative technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning are revolutionizing ESaaS solutions, enabling more efficient energy management and predictive analytics. These technologies allow service providers to optimize energy consumption patterns, reduce waste, and improve overall system reliability. Furthermore, the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices facilitates real-time monitoring and control of energy assets, leading to smarter grids and more responsive energy distribution networks.
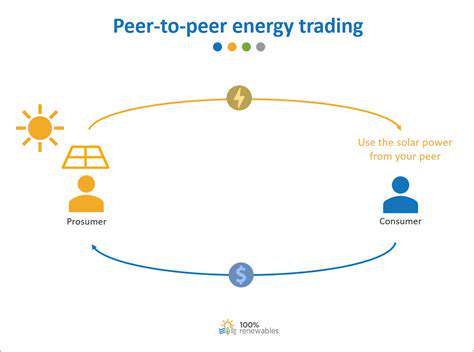
Another pivotal development is the adoption of blockchain technology, which promises enhanced transparency and security in energy transactions. Blockchain can streamline peer-to-peer energy trading, facilitate transparent billing processes, and ensure data integrity across distributed energy resources. As these technologies mature, they will play a crucial role in shaping a more resilient, efficient, and customer-centric ESaaS ecosystem, paving the way for a sustainable energy future.
Challenges and Opportunities in the Evolution of ESaaS
The future of ESaaS is not without its challenges. One significant hurdle is the need for standardization across various platforms and devices, which is essential for seamless integration and interoperability. Without common standards, the deployment of ESaaS solutions could become fragmented, hindering widespread adoption and scalability. Additionally, concerns regarding cybersecurity and data privacy remain paramount as more energy systems become interconnected and dependent on digital infrastructures.
Despite these challenges, the opportunities for growth and innovation are immense. The increasing demand for renewable energy sources and the transition toward decentralized energy systems create a fertile ground for ESaaS solutions to thrive. By addressing existing barriers and leveraging Emerging Technologies, the energy industry can achieve a more sustainable, efficient, and resilient future. Stakeholders who invest in innovative ESaaS models today will likely be at the forefront of the energy revolution in the coming decades.