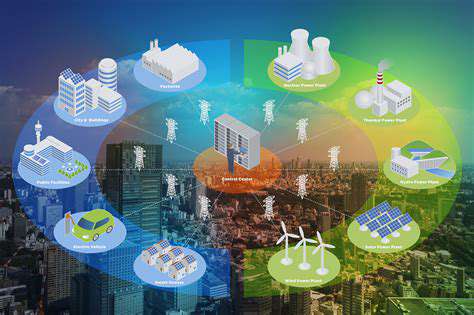
Government Support for Offshore Wind Development

Government Subsidies: A Powerful Tool
Government subsidies play a crucial role in incentivizing various economic activities, from renewable energy development to agricultural production. These financial incentives, often provided in the form of grants, tax breaks, or direct payments, aim to stimulate investment, foster innovation, and encourage the adoption of specific technologies or practices. Subsidies can significantly impact market dynamics and resource allocation, potentially leading to positive societal outcomes.
A key aspect of subsidies is their ability to address market failures. When the market alone doesn't adequately address social needs, such as environmental protection or affordable housing, subsidies can step in to correct these imbalances. For example, subsidies for renewable energy can help reduce reliance on fossil fuels and mitigate climate change, a benefit that often outweighs the direct costs of the subsidy.
Types of Financial Incentives
Subsidies manifest in diverse forms, each tailored to specific objectives. Direct cash grants are a common method, providing a clear financial boost to recipients. Tax credits, on the other hand, reduce the tax burden for qualifying activities, encouraging investment and production. These incentives can significantly lower the overall cost of engaging in a particular industry or activity, stimulating growth. Furthermore, production subsidies directly support the output of a particular good or service, potentially boosting domestic production and employment.
Subsidies are often targeted to specific industries or sectors, depending on the government's policy goals. For instance, a government might provide subsidies for the development of electric vehicles to promote a transition to cleaner transportation. Similarly, agricultural subsidies can support farmers and maintain food security. Understanding the specific type of subsidy and its intended goals is vital for evaluating its effectiveness and impact.
Another type of financial incentive is the provision of low-interest loans. These can encourage investment in capital projects, particularly in industries where large upfront investments are necessary. The reduced cost of borrowing can significantly impact businesses' ability to expand and innovate. These various types of subsidies play a significant role in shaping market behavior and achieving desired social outcomes.
Evaluating the Effectiveness of Subsidies
The effectiveness of subsidies is a complex issue, often debated among economists and policymakers. While subsidies can stimulate desired economic activities, they often come with potential drawbacks, such as the risk of distorting market signals and creating inefficiencies. It's crucial to carefully consider the intended outcomes and potential unintended consequences before implementing a subsidy program.
Careful analysis is needed to assess the cost-benefit ratio of a subsidy. The benefits must be weighed against the cost to the government and the potential for unintended consequences. In evaluating subsidies, factors like the extent of market failure, the magnitude of the subsidy, and the potential for crowding out private investment must be considered.
Furthermore, monitoring and evaluation of subsidy programs are essential to ensure their effectiveness. Regular assessments can help identify areas where the subsidy is working well and areas that need adjustments or improvements. This feedback loop is essential for refining subsidy programs over time to ensure they are achieving their intended goals.