Green Bonds and Sustainable Finance: Fueling Renewable Energy Growth
Understanding Green Bonds
Green bonds are a specific type of bond that is issued to finance projects and initiatives that contribute to environmental sustainability. These bonds are designed to channel capital towards projects that reduce greenhouse gas emissions, improve energy efficiency, protect biodiversity, and promote sustainable resource management. Investors are attracted to green bonds because they offer a way to support environmentally responsible projects while potentially earning a return on their investment. This alignment of financial goals with environmental objectives is a key feature of the green bond market.
The Role of Renewable Energy in Green Bond Funding
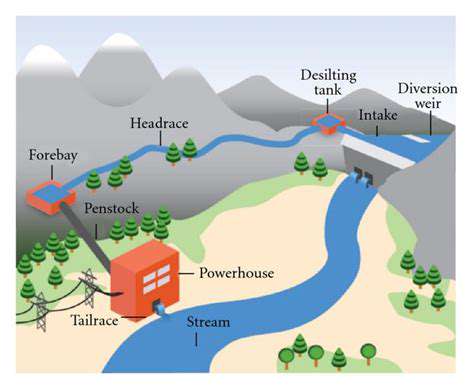
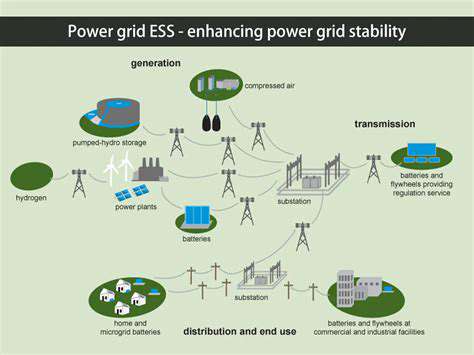
Renewable energy projects are a major target for green bond funding. These projects, which include solar, wind, hydro, geothermal, and biomass energy, offer a crucial pathway to a cleaner energy future. Green bonds provide the necessary capital for the development, construction, and operation of these projects, stimulating investment in infrastructure that reduces reliance on fossil fuels and mitigates climate change. The potential for long-term returns and positive environmental impact makes renewable energy a compelling investment area for green bond issuers and investors alike.
Attracting Investment in Renewable Energy
Green bonds offer a structured and transparent mechanism for attracting investment in renewable energy. By clearly defining the environmental impact of the projects, green bonds create a market-based mechanism for identifying and rewarding projects with the greatest potential for environmental impact. The standardized structure and reporting requirements of green bonds enhance investor confidence, encouraging greater participation in funding renewable energy projects. This structured approach makes it easier for investors to evaluate and select projects that align with their environmental and financial objectives.
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Factors
Beyond the financial return, green bonds are increasingly tied to environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors. This means that projects financed by green bonds are often assessed not only for their financial viability but also for their positive social impact and adherence to strong governance standards. This integrated approach recognizes that environmental sustainability cannot be achieved in isolation but requires consideration of broader social and governance factors. This holistic approach encourages a more sustainable and responsible approach to investment.
Challenges and Opportunities in Green Bond Markets
While green bonds offer significant opportunities for funding renewable energy projects, challenges remain. Standardization of reporting and verification procedures is crucial to ensure the credibility and transparency of green bond projects. Improved data collection and analysis on the environmental impact of renewable energy projects are essential for effective project evaluation and risk assessment. Nonetheless, the growing demand for green bonds provides a clear opportunity for the market to evolve and address these challenges, ensuring that green bond funding effectively drives the transition to a sustainable energy future. This evolution will allow for more sophisticated and comprehensive investment strategies that consider the full impact of projects.
The ocean, a vast and mysterious realm, holds within its depths a multitude of dangers that often go unnoticed. From the seemingly harmless coral reef to the shadowy depths of the abyss, marine life and environmental factors pose significant threats to those who venture too close. Understanding these hidden hazards is crucial for ensuring safety and responsible exploration of this captivating environment. The sheer volume of water, coupled with the unique pressures and temperatures, can create perilous conditions for even the most experienced divers and marine biologists.

The Future of Green Bonds and Renewable Energy

Green Bond Market Trends
The green bond market is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing investor interest in sustainable finance and a rising global awareness of environmental challenges. This expansion is not just limited to developed economies; emerging markets are also showing a keen interest in green bonds, recognizing their potential for attracting foreign investment and supporting domestic green projects. This growing demand demonstrates a shift in investor priorities, with a clear preference for investments that align with environmental sustainability goals.
Several key trends are shaping the evolution of the green bond market. These include the increasing sophistication of green bond frameworks, which are becoming more robust and transparent in their methodologies for evaluating and classifying green projects. This enhanced transparency is crucial for building investor confidence and ensuring that funds are deployed effectively to achieve genuine environmental benefits. Furthermore, investors are increasingly demanding greater disclosure and verification of green bond projects, seeking to minimize the risk of greenwashing and ensure that the projects are truly environmentally sound. This heightened scrutiny reflects the importance of accountability and the need to ensure that green bonds are not just a marketing tool but a genuine driver of sustainable development.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite the promising growth, the green bond market faces several challenges. One significant hurdle is the need for standardized and globally recognized methodologies for evaluating and classifying green projects. A lack of consistency across different regions and jurisdictions can create confusion and hinder the efficient allocation of capital to environmentally beneficial projects. Moreover, ensuring the environmental integrity of projects financed by green bonds requires robust monitoring and reporting mechanisms to track progress and identify potential deviations from intended outcomes.
However, these challenges also present exciting opportunities. The development of more sophisticated and standardized green bond frameworks can foster greater investor confidence and attract more capital to critical environmental initiatives. Additionally, the emphasis on transparency and accountability can lead to better project design and implementation, ultimately maximizing the positive environmental impact of green bonds. Innovation in green bond structures and financial instruments can unlock further investment opportunities and accelerate the transition to a low-carbon economy.
Regulatory Landscape and Policy Support
The regulatory landscape surrounding green bonds is evolving rapidly, with governments and international organizations increasingly recognizing the importance of sustainable finance. These evolving regulations are aiming to provide a stable and supportive environment for green bond issuance and investment. Many countries are implementing policies to promote green bond markets, providing incentives for companies and governments to issue these bonds, and creating frameworks for project evaluation and verification. These measures are essential for fostering a thriving green bond market that will effectively mobilize capital for environmentally sustainable projects.
Strong policy support and regulatory frameworks are vital for guiding the growth of green bond markets. Such frameworks will not only help in the efficient allocation of capital but also contribute to the creation of a more transparent and sustainable financial system. The development of robust and internationally harmonized standards is crucial in fostering investor confidence and ensuring the long-term viability of the green bond market.