Investment Flows into Renewable Energy Infrastructure Worldwide

The Growing Demand for Clean Energy Sources
The global energy landscape is undergoing a significant transformation, with a pronounced shift towards renewable energy sources. This burgeoning interest is driven by a multitude of factors, including a growing awareness of climate change and the need for sustainable energy solutions. The increasing cost of fossil fuels is further motivating the transition, as renewable energy options become increasingly competitive financially.
Environmental concerns are paramount in this transition. The detrimental effects of fossil fuels on the planet, including air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions, are pushing governments and industries to explore cleaner alternatives.
Technological Advancements in Renewable Energy
Significant advancements in renewable energy technologies are contributing to the surge. Solar panel efficiency has improved dramatically, making solar power more cost-effective and accessible. Wind turbine technology has also evolved, leading to greater energy capture and reduced maintenance costs.
Battery storage technology is another critical advancement. Improved battery storage solutions are crucial for storing excess renewable energy generated during peak production periods, making it available for use when needed, thereby further enhancing the reliability of renewable energy grids.
Government Policies and Incentives
Government policies play a pivotal role in fostering the adoption of renewable energy. Many countries are implementing supportive policies, including tax incentives, subsidies, and feed-in tariffs, to encourage investment in renewable energy projects. These policies aim to lower the cost of renewable energy, making it more competitive with traditional energy sources.
Furthermore, regulations are being put in place to limit the use of fossil fuels. These policies are helping to create a more favorable environment for renewable energy to flourish.
Economic Benefits of Renewable Energy
The transition to renewable energy presents significant economic benefits. Investments in renewable energy infrastructure create job opportunities in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance. These industries bring about economic growth and contribute to the development of local economies.
Furthermore, reduced reliance on imported fossil fuels can lead to energy security and independence for countries, creating a more stable and sustainable energy supply.
Environmental Impact of Renewable Energy
Renewable energy sources have a considerably lower environmental impact compared to fossil fuels. Solar and wind power produce little to no greenhouse gas emissions during operation, significantly reducing the carbon footprint of the energy sector. This reduction in emissions helps mitigate climate change and protects the environment.
Public Awareness and Acceptance
Growing public awareness of climate change and the environmental benefits of renewable energy is crucial for the transition. Increased awareness has led to greater acceptance of renewable energy and support for policies that promote its growth.
Public education campaigns and initiatives highlighting the positive impacts of renewable energy are further encouraging public support.
Challenges and Future Considerations
While the surge in renewable energy investment is promising, several challenges remain. Intermittency is a key challenge for solar and wind energy, as their output fluctuates with weather conditions. Efficient energy storage solutions are crucial to address this issue. Further research and innovation in battery technology and other storage solutions are essential to overcome this obstacle.
The integration of renewable energy into existing power grids also presents challenges. Smart grids and advanced grid management systems are needed to ensure a smooth transition and efficient energy distribution.
Key Drivers of Investment in Renewable Energy Infrastructure

Technological Advancements
Significant advancements in renewable energy technologies, particularly in solar and wind power, have drastically reduced production costs and improved efficiency. This has made renewable energy sources more competitive with traditional fossil fuels, attracting significant investment capital. The falling cost of solar panels, for example, is a major driver for investment in residential and commercial solar installations.
Government Policies and Incentives
Government policies and incentives play a crucial role in driving investment in renewable energy. These policies often include tax credits, subsidies, and mandates for renewable energy procurement. These measures create a supportive environment for renewable energy businesses and investors, encouraging greater adoption and investment. For example, renewable portfolio standards (RPS) mandate a certain percentage of electricity generation from renewable sources, incentivizing utilities to invest in these technologies.
Growing Environmental Concerns
Increasing public awareness and concern about climate change and environmental degradation are driving a growing demand for sustainable energy sources. Consumers, businesses, and investors are increasingly prioritizing environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors in their decision-making, leading to heightened interest in renewable energy investments. This rising awareness and demand are fundamentally changing the investment landscape and pushing more capital toward renewables.
Investor Confidence and Market Maturity
A growing number of institutional investors and private equity firms are recognizing the long-term potential of renewable energy investments. This growing confidence is fueled by the market maturity of renewable energy technologies and the increasing stability of the sector. The established supply chains and robust regulatory frameworks within the renewable energy sector inspire greater investor confidence. This creates a virtuous cycle of further investment and market expansion.
Energy Security and Independence
Concerns about energy security and dependence on volatile global energy markets are prompting many countries to increase investment in domestic renewable energy resources. Diversifying energy sources and reducing reliance on imported fossil fuels are crucial strategic goals for many nations. This focus on energy security translates directly into investment opportunities in renewables, as countries seek to bolster their energy independence. Government policies often reflect this strategic imperative, further fueling investment in renewable energy.
Economic Benefits and Job Creation
The renewable energy sector offers numerous economic benefits, including job creation and economic stimulus. The development and deployment of renewable energy technologies create new industries and employment opportunities across various sectors. The construction, operation, and maintenance of renewable energy facilities stimulate economic growth in local communities, creating a positive ripple effect. Furthermore, the manufacturing and supply chains associated with renewable energy generate substantial economic activity.
Decarbonization Initiatives and Corporate Social Responsibility
Many corporations are now integrating decarbonization initiatives into their business strategies, viewing renewable energy as a crucial component of their corporate social responsibility (CSR) efforts. These companies are increasingly incorporating sustainability goals into their investment decisions, driving investment in clean energy projects. This trend toward sustainability is leading to increased demand for renewable energy solutions and further investment from corporate entities.
Consumers are increasingly aware of the impact their purchasing decisions have on the environment, social justice, and animal welfare. This growing awareness is driving a significant shift in consumer behavior, pushing companies to adopt more sustainable and ethical practices. Consumers are demanding transparency and accountability from brands, wanting to know the origin of their products and the working conditions of those who produced them. This heightened scrutiny is forcing companies to reassess their supply chains and production methods, ultimately leading to a more responsible and conscious approach to business.
Investment Channels and Structures
Direct Investments
Direct investments in renewable energy infrastructure encompass a wide range of activities, from establishing new solar farms and wind turbine installations to upgrading existing facilities and acquiring operational plants. This approach often involves significant upfront capital expenditure, but it provides direct control over project development, operations, and long-term returns. Investors typically assess factors like project location, resource availability, regulatory environment, and the potential for cost reductions and technological advancements when considering direct investment opportunities. These investments can be highly impactful, contributing directly to the growth of the renewable energy sector and its capacity to meet growing energy demands.
Furthermore, direct investments can involve equity stakes in renewable energy companies, providing investors with a share in the company's profits and growth potential. This approach allows investors to participate in the full lifecycle of a project, from initial development to operation and maintenance. However, direct investments often require a higher level of due diligence and ongoing management involvement to ensure the success of the venture.
Investment Funds and Structures
Investment funds play a crucial role in aggregating capital and facilitating investment in renewable energy infrastructure. These funds often employ specialized expertise and resources to identify, evaluate, and manage portfolios of renewable energy projects. They can leverage their collective capital to undertake larger, more complex projects that might be beyond the scope of individual investors. This structure allows for diversification across different technologies, geographies, and project stages, mitigating risk and maximizing returns.
Various structures, such as private equity funds, infrastructure funds, and dedicated renewable energy funds, cater to different investor objectives and risk tolerances. These funds employ a range of strategies, including project financing, debt financing, and equity investments, to support the development and deployment of renewable energy projects. The structure of these funds often involves professional management teams responsible for project selection, financial management, and operational oversight, ensuring efficient allocation of capital and maximizing returns for investors.
The use of investment funds can also foster collaboration among various stakeholders, including developers, financiers, and policymakers. This collaborative environment can streamline project development processes and accelerate the transition to a more sustainable energy future. However, transparency and accountability within these investment structures are critical to maintaining investor confidence and ensuring responsible deployment of capital.
Furthermore, these funds often have specialized knowledge about the intricacies of the renewable energy sector, which allows them to navigate the regulatory landscape and identify promising investment opportunities that might be missed by individual investors.
Moreover, the presence of these funds can attract additional investment capital by demonstrating the viability and attractiveness of the renewable energy sector to a broader range of investors.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Financing the Infrastructure Gap
Renewable energy infrastructure projects often require substantial upfront capital investments, creating a significant financing hurdle. Securing long-term funding sources, such as institutional investors, private equity firms, and government grants, is crucial for bridging this gap. The complexity of project development, combined with the fluctuating nature of renewable energy markets, can make it challenging to attract sufficient capital. This often necessitates innovative financing models to ensure projects remain viable and competitive.
Furthermore, the diverse range of financing options available, from traditional debt financing to green bonds and project finance structures, can be overwhelming for developers and investors. Navigating these options effectively, while considering risk profiles and returns, is essential to ensure successful project implementation.
Policy Support and Regulatory Frameworks
Favorable government policies and supportive regulatory frameworks are essential to fostering investment in renewable energy infrastructure. Clear, consistent, and predictable policies regarding permitting, zoning, and interconnection of renewable energy projects are critical to attracting investors and driving project development. Incentives such as tax credits, subsidies, and feed-in tariffs can significantly impact the financial viability of these projects, encouraging greater participation from both public and private sectors.
However, inconsistencies or ambiguities in these policies can create uncertainty and deter investment. Harmonizing policies across jurisdictions and promoting international cooperation are vital to create a stable and attractive investment climate for renewable energy infrastructure.
Technological Advancements and Innovation
Continuous advancements in renewable energy technologies, such as improved battery storage solutions and more efficient solar panels, are crucial for reducing costs and enhancing the performance of these projects. Innovation in design and construction methods can also lead to more sustainable and cost-effective infrastructure solutions. The ongoing research and development in these areas are critical to making renewable energy more competitive with traditional energy sources.
Further development and deployment of smart grids and other smart technologies can optimize energy distribution and reduce transmission losses, ultimately increasing the efficiency of renewable energy infrastructure. This will be vital to achieving greater cost effectiveness and integration into existing energy systems.
Grid Integration and Infrastructure Upgrades
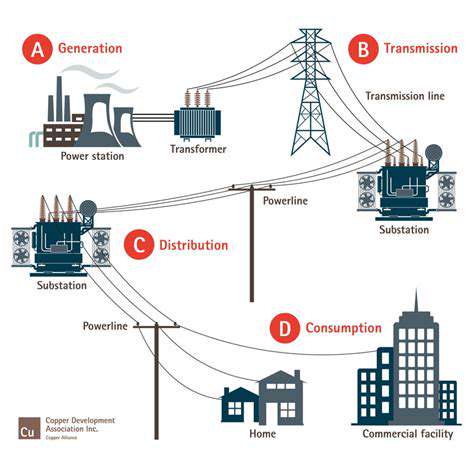
Connecting renewable energy sources to existing electricity grids often requires significant upgrades to transmission and distribution infrastructure. This can be a costly undertaking, particularly in areas with limited grid capacity or outdated infrastructure. Addressing these infrastructure challenges is essential to ensure the reliable and efficient integration of renewable energy into the broader energy system.
Finding innovative solutions, such as microgrids and decentralized energy systems, can help mitigate the challenges of grid integration. These solutions offer the potential to increase resilience and enhance the overall reliability of the power supply, attracting investment and supporting the transition to renewable energy.
Community Engagement and Public Acceptance
Renewable energy infrastructure projects can sometimes face resistance from local communities due to concerns regarding visual impact, noise pollution, and land use. Addressing these concerns proactively through open communication and community engagement is crucial for project success. Involving local stakeholders in the planning and decision-making processes can build trust and foster acceptance of these projects.
Transparent communication about the environmental and social benefits of renewable energy, as well as the potential economic opportunities associated with these projects, can help overcome public resistance and foster greater support for the transition to a sustainable energy future.
Environmental Sustainability and Lifecycle Assessment
Environmental considerations are paramount in the development of renewable energy infrastructure. Careful assessments of the environmental impact of projects, including land use, water consumption, and waste generation, are essential for minimizing negative consequences. Implementing sustainable construction and operation practices throughout the lifecycle of the project is crucial for long-term environmental protection.
Assessing the entire lifecycle of renewable energy projects, from material sourcing to end-of-life disposal, can identify potential environmental risks and opportunities for improvement. Prioritizing sustainability principles throughout the project development process is essential for ensuring that these projects contribute to a more sustainable future and minimize negative environmental impacts.