Building Resilient Communities with Renewable Energy in Vulnerable Regions
The Pervasive Impact of Climate Change on Vulnerable Regions

The Escalating Threat of Extreme Weather Events
Climate change is undeniably altering weather patterns globally, leading to a dramatic increase in the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events. These events, ranging from devastating hurricanes and floods to prolonged droughts and wildfires, are causing widespread damage and displacement, impacting communities and economies in profound ways. The sheer scale of these disasters is becoming increasingly concerning, highlighting the urgent need for proactive measures to mitigate the effects of climate change and bolster resilience to these escalating threats.
The Disruption of Global Food Systems
Climate change poses a significant threat to global food security. Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns are disrupting agricultural cycles and impacting crop yields. This disruption has the potential to lead to widespread food shortages and price increases, exacerbating existing inequalities and potentially triggering social unrest. The impact on livestock production is also substantial, as changing weather conditions affect feed availability and animal health.
Furthermore, rising sea levels and saltwater intrusion threaten coastal agricultural lands, further diminishing food production capacity in vulnerable regions.
The Impact on Human Health and Well-being
The implications of climate change extend far beyond environmental damage. The health and well-being of human populations are directly affected by rising temperatures, increased air pollution, and the spread of vector-borne diseases. Heat waves, for example, can lead to heatstroke and exacerbate existing health conditions, while the spread of diseases like malaria and dengue fever is amplified by changing climate patterns. Access to clean water and sanitation is also threatened, leading to the potential for waterborne illnesses to become more common.
The Economic Costs of Inaction
Ignoring the effects of climate change will come at a substantial economic cost. From the damage caused by extreme weather events to the disruption of global supply chains, the costs associated with inaction are considerable and far-reaching. Infrastructure damage, lost productivity, and the need for disaster relief efforts all contribute to a significant economic burden. These costs are not evenly distributed, with developing nations often bearing the brunt of the consequences despite contributing the least to the problem. The economic costs of inaction far outweigh the investment required to transition to a more sustainable future.
The Urgency for Global Cooperation and Action
Addressing climate change demands a global response, requiring international cooperation and a commitment to meaningful action from all nations. The scientific evidence is clear, and the consequences of inaction are dire. This necessitates collective efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, invest in renewable energy sources, and adapt to the unavoidable impacts of climate change. Developing and implementing effective policies and strategies at both national and international levels is critical to mitigating the risks and building a more sustainable future for all.
Renewable Energy as a Cornerstone of Resilience
Harnessing the Power of Solar
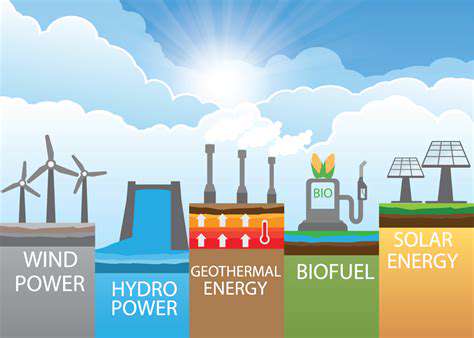
Solar energy, a clean and abundant resource, plays a critical role in building community resilience. Harnessing the power of the sun through photovoltaic (PV) panels offers a sustainable energy solution, reducing dependence on fossil fuels and mitigating the impact of volatile energy markets. The integration of solar power into residential and commercial structures not only decreases reliance on centralized grids but also creates local energy independence. This distributed generation model fosters a more resilient infrastructure, capable of withstanding grid outages and ensuring consistent energy access, particularly in remote or vulnerable areas. Furthermore, the decreasing costs of solar technology make it increasingly accessible and economically viable for communities to invest in their own renewable energy future.
Beyond individual installations, community-scale solar projects offer significant benefits. These projects can provide a collective source of renewable energy, powering essential services like streetlights, water pumps, and communication networks. By establishing community solar farms, residents can participate in the project and reap the rewards of a sustainable energy system while supporting the broader community's resilience. The ability to generate and store solar energy significantly enhances the community's capacity to withstand disruptions and maintain critical services during times of crisis.
Wind Power and its Synergistic Role
Complementing solar energy, wind power provides another crucial component of a resilient energy infrastructure. Wind turbines, especially in areas with consistent wind patterns, can generate substantial amounts of clean energy, reducing reliance on traditional power sources. The integration of wind energy into community grids enhances the overall energy portfolio, diversifying energy sources and improving the system's reliability. This diversification is vital in the face of potential disruptions, ensuring a more resilient and stable energy supply for communities.
The synergy between solar and wind energy is particularly beneficial. As solar power production fluctuates with sunlight availability, wind power can step in to fill the gaps. This complementary relationship creates a more stable and reliable energy system, ensuring a constant supply of clean energy to meet the needs of the community. The combination of these two renewable resources creates a robust and resilient energy network, capable of withstanding various challenges and providing uninterrupted power.
Moreover, the development of energy storage technologies, such as batteries and pumped hydro, allows communities to further enhance their resilience by storing excess renewable energy generated during peak production periods. This stored energy can then be used during times of low generation, ensuring a consistent energy supply and reducing the impact of fluctuating weather conditions on energy availability.
The establishment of community-owned wind farms can empower residents to participate in the energy production process, fostering a sense of ownership and responsibility for the community's energy future. Local control over energy resources contributes to community resilience and self-sufficiency.
The integration of wind power, along with other renewable resources, strengthens the community's ability to manage energy resources effectively. This proactive approach to building a resilient energy system is critical for ensuring the long-term sustainability and well-being of the community.


Promoting Collaboration and Funding Mechanisms
Encouraging Inter-Agency Partnerships
Effective community resilience hinges on strong collaboration between various agencies. This involves fostering communication channels, establishing shared goals, and defining clear roles and responsibilities. Successful partnerships require mutual respect, transparency, and a shared understanding of community needs. This collaborative approach ensures that resources are utilized efficiently and that diverse perspectives are incorporated into the development of resilient strategies. By working together, agencies can leverage their individual strengths to create a comprehensive and impactful response to community challenges.
Furthermore, fostering inter-agency partnerships can lead to a more comprehensive understanding of the community's unique dynamics. This knowledge is crucial for developing tailored solutions that address specific vulnerabilities and promote sustainable growth. Agencies can share data, expertise, and best practices, leading to improved outcomes for the entire community.
Developing Community-Based Funding Initiatives
Local communities hold a wealth of knowledge and resources that can be leveraged to build resilience. Developing community-based funding initiatives can empower residents to actively participate in shaping their future. This approach fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility, ensuring that funding decisions are aligned with community priorities and needs. These initiatives can take various forms, including crowdfunding campaigns, community grants, and fundraising events.
Community-based funding initiatives can be especially important for addressing immediate needs and supporting long-term resilience building. They can provide flexible resources that adapt to evolving community challenges and priorities, fostering a more adaptable and responsive approach to resilience development.
Leveraging Private Sector Investments
Private sector involvement is essential for bolstering community resilience efforts. Engaging businesses and corporations can provide crucial financial resources, technical expertise, and manpower to support community projects. This approach can broaden the scope of resilience initiatives and accelerate the pace of progress. Companies that prioritize community well-being can find meaningful ways to contribute to local resilience through financial investments, employee volunteer programs, and partnerships with community organizations.
Exploring Grant Opportunities and Funding Streams
Identifying and accessing relevant grant opportunities and funding streams is crucial for expanding the reach and impact of community resilience initiatives. Thorough research and strategic planning are vital for locating funding mechanisms that align with project goals and objectives. This includes exploring both local and national grant programs, as well as philanthropic organizations and foundations that support community development projects.
Careful consideration of grant application requirements and timelines is paramount. A well-structured proposal that clearly articulates the project's goals, methodology, and anticipated outcomes significantly increases the likelihood of securing grant funding. This proactive approach can unlock substantial resources to support community resilience efforts.
Implementing Sustainable Financing Models
Creating sustainable financing models that ensure the long-term viability of community resilience initiatives is critical. This involves exploring diverse funding sources beyond grants and donations, such as establishing community development funds, implementing impact investing strategies, and exploring innovative financing mechanisms tailored to specific community needs.
These models should prioritize long-term financial stability and ensure the continued support of community resilience projects. A diversified funding approach strengthens the resilience of the community by ensuring that resources are available even during economic fluctuations or unforeseen circumstances.
Building Trust and Transparency in Funding Allocation
Transparency and accountability in the allocation of funding resources are fundamental to building trust within the community. Clear communication channels and easily accessible information about funding decisions are essential. This fosters public confidence and ensures that resources are utilized effectively and equitably. Open and honest communication about project progress and outcomes strengthens the community's commitment to resilience-building efforts.
Evaluating and Adapting Funding Strategies
Regular evaluation of funding strategies is crucial to ensuring their effectiveness and alignment with evolving community needs. Monitoring project outcomes, assessing community feedback, and adapting strategies based on collected data are vital components of a dynamic and responsive approach. This iterative process allows for continuous improvement and ensures that resilience initiatives remain relevant and impactful in the long term. Regular evaluations also provide valuable insights into what is working and what needs adjusting, enabling communities to optimize their resource allocation and improve the effectiveness of their resilience-building initiatives.