The Future of Grid Modernization for Renewable Energy Integration
Grid technologies have revolutionized the way we manage and utilize resources, from computing power to energy distribution. These systems offer a flexible and scalable approach to resource allocation, enabling organizations to optimize performance and efficiency. Understanding the intricacies of advanced grid technologies is crucial for navigating the evolving landscape of distributed systems. This exploration delves into the key components and benefits of these powerful tools.
The fundamental concept behind advanced grids is the ability to connect and coordinate diverse resources in a dynamic environment. This interconnectedness allows for the seamless sharing of resources and the optimized utilization of available capacity.
Grid Computing: A Deeper Dive
Grid computing, a cornerstone of advanced grid technologies, involves connecting geographically dispersed computers to form a virtual supercomputer. This allows for the tackling of complex problems that would be computationally impossible for a single machine. Grid computing enables massive parallel processing, which is essential for scientific research, data analysis, and other demanding applications.
The architecture of grid computing is designed to handle heterogeneous resources, meaning that computers with different capabilities and characteristics can be integrated into the network. This flexibility is critical for maximizing resource utilization and achieving optimal performance.
Energy Grids: Smart Solutions
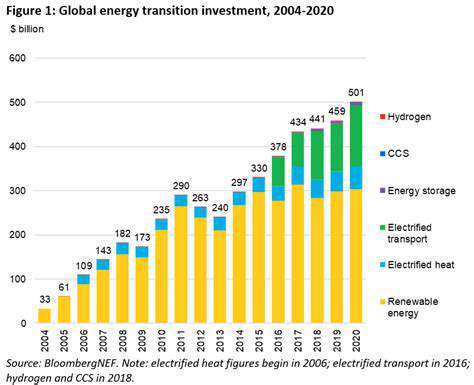
Smart grids, a vital aspect of advanced grid technologies, leverage digital technologies to enhance the efficiency and reliability of energy distribution. These intelligent systems monitor energy flow, predict demand, and optimize resource allocation in real-time. This leads to significant savings in energy consumption and reduced risks of outages.
Smart grid technologies incorporate advanced sensors, communication networks, and control systems to create a dynamic and responsive energy delivery system. This sophisticated approach enables proactive management of energy resources, leading to a more sustainable and resilient energy infrastructure.
Data Grids: Managing the Flood of Information
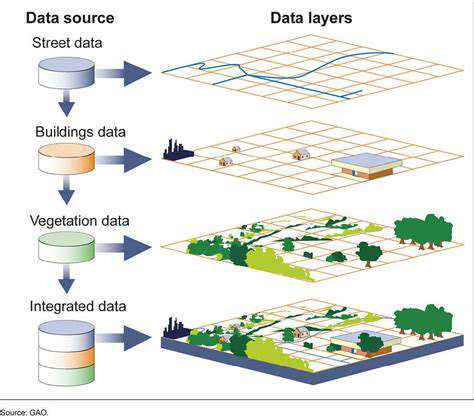
Data grids are specialized grid technologies designed for managing and processing massive datasets. These systems provide a framework for distributed storage, processing, and retrieval of data, enabling researchers and analysts to tackle complex data analysis tasks. This is particularly crucial in fields like genomics, astronomy, and climate science.
Cloud Grids: A Hybrid Approach
Cloud grids combine the advantages of cloud computing and grid computing, offering a flexible and scalable platform for resource management. This hybrid approach leverages the scalability of cloud computing while retaining the control and security features of grid computing. Cloud grids are particularly well-suited for organizations seeking to optimize their IT infrastructure and enhance application performance.
Security and Management in Advanced Grids
Security is a paramount concern in advanced grid technologies. Secure communication channels, robust authentication protocols, and access controls are essential to protect sensitive data and resources. Effective management strategies are crucial for maintaining the integrity and reliability of these complex systems. Robust security measures are vital for ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of grid resources.
Future Trends and Applications
The future of advanced grid technologies is bright, with ongoing research and development focusing on enhanced scalability, improved security, and greater interoperability. These advancements will open up new avenues for innovation in various fields, from scientific research to industrial applications. The potential for innovation through these technologies is enormous.
Ongoing research is investigating new ways to improve energy efficiency, optimize resource allocation, and enhance the overall performance of grid systems. This continuous evolution promises to drive significant advancements in fields ranging from healthcare to environmental monitoring.